The document discusses international trade, patents, and the Uruguay Round of trade negotiations (GATT). It also covers India's cosmetic sector, including its history and growth. Some key points:
- The Uruguay Round was the 8th round of multilateral trade negotiations conducted under the GATT framework.
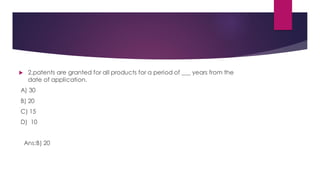
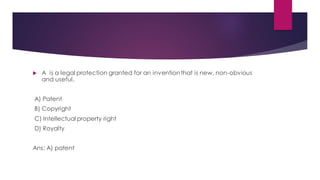
- Patents provide legal protection for inventions and are granted for 20 years from the date of application.
- India's cosmetic industry is one of the fastest growing sectors and was valued at $8.1 billion in 2023, expected to reach $18.4 billion by 2032.
- Leading domestic brands include Lakme, which was founded in 1952 to reduce India's dependence