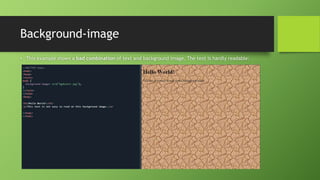
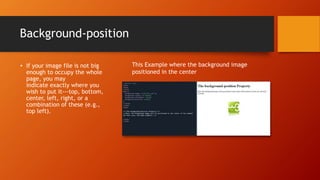
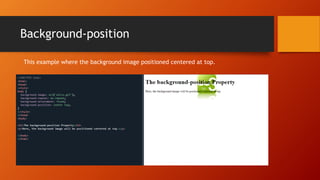
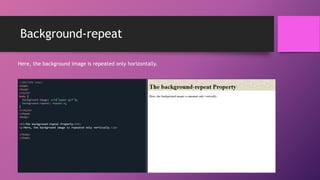
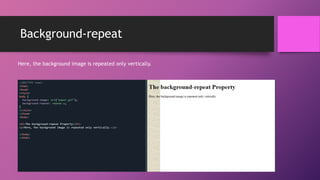
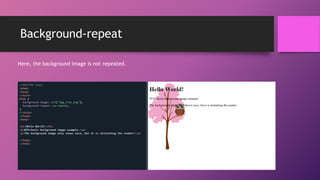
This document discusses CSS background properties including background-image, background-color, background-position, background-repeat, and the background shorthand property. It provides examples and descriptions of how to set images, colors, positioning, repetition, and combining these properties using the shorthand. Key points covered include using URLs or keywords to set images and colors, positioning images in centers or sides, repeating images horizontally, vertically or not at all, and ordering properties in the shorthand.