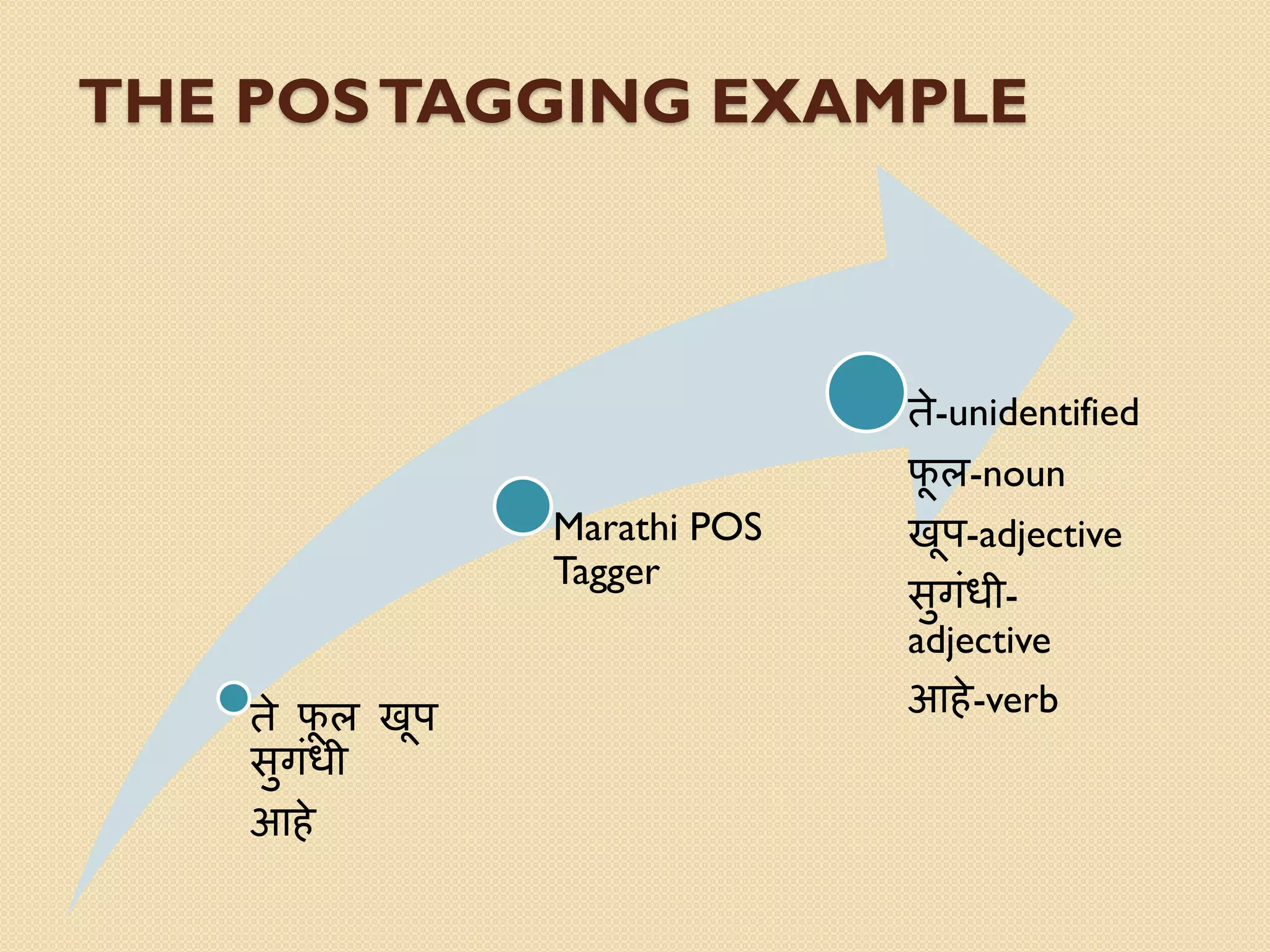
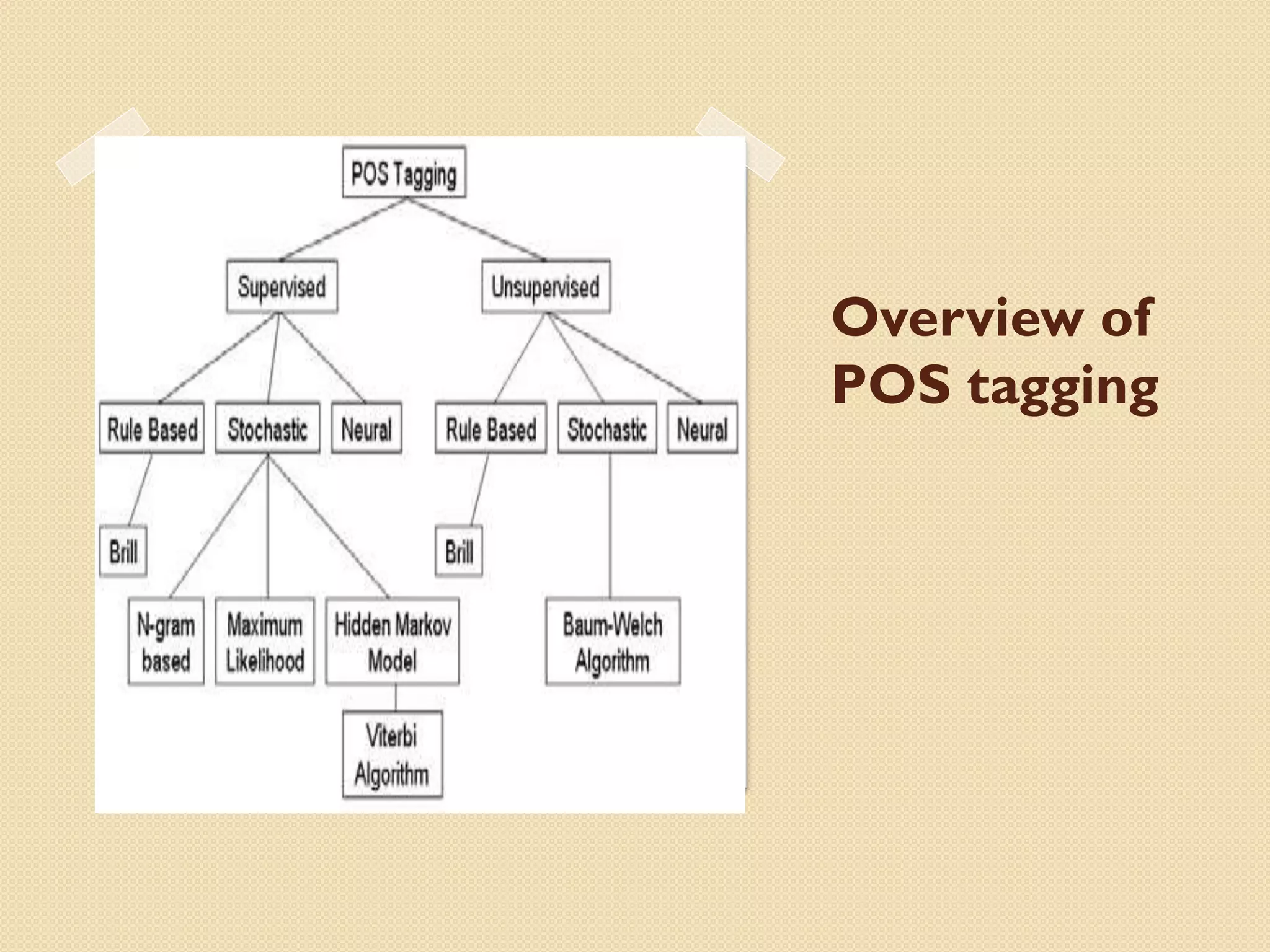
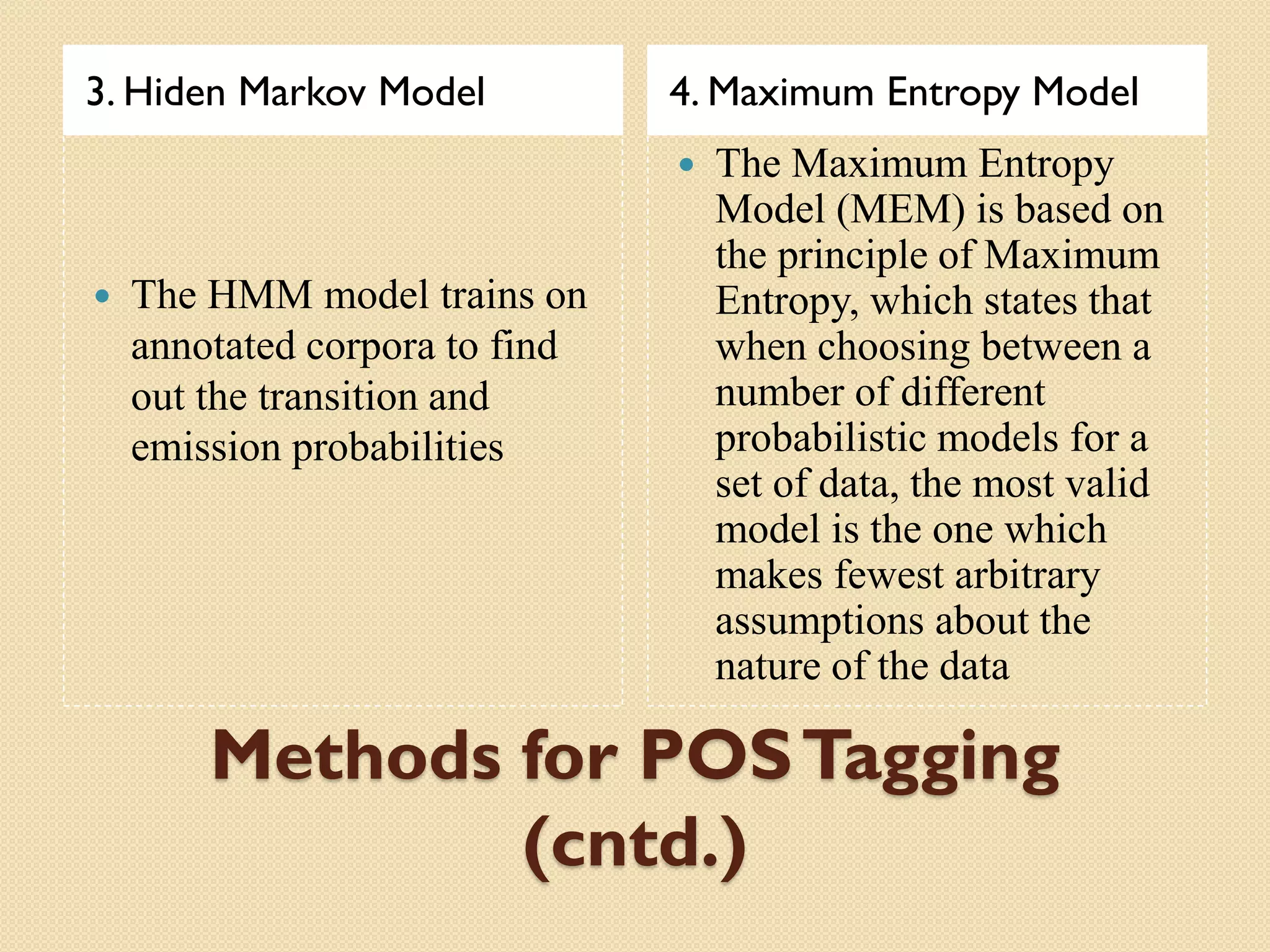
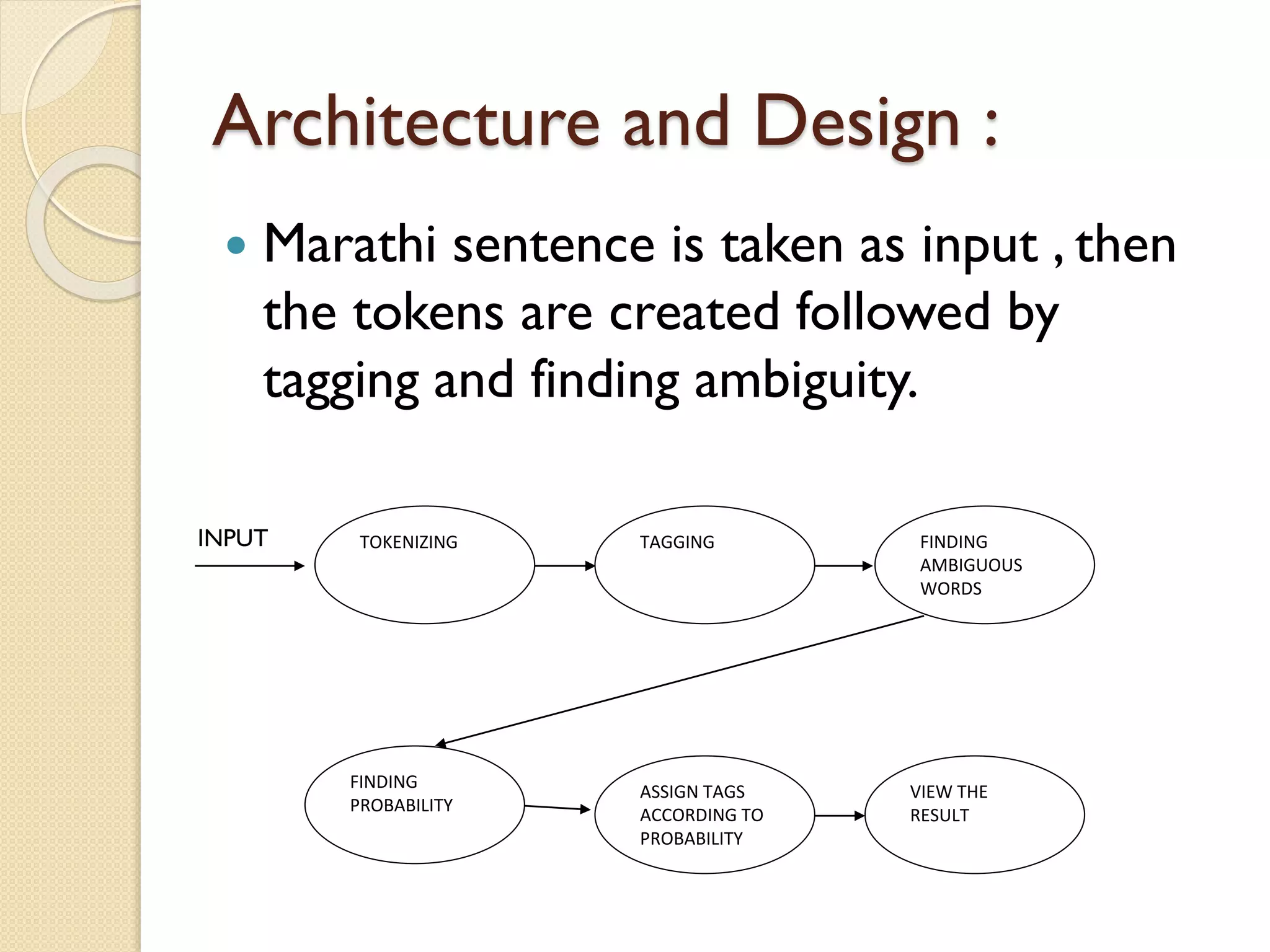
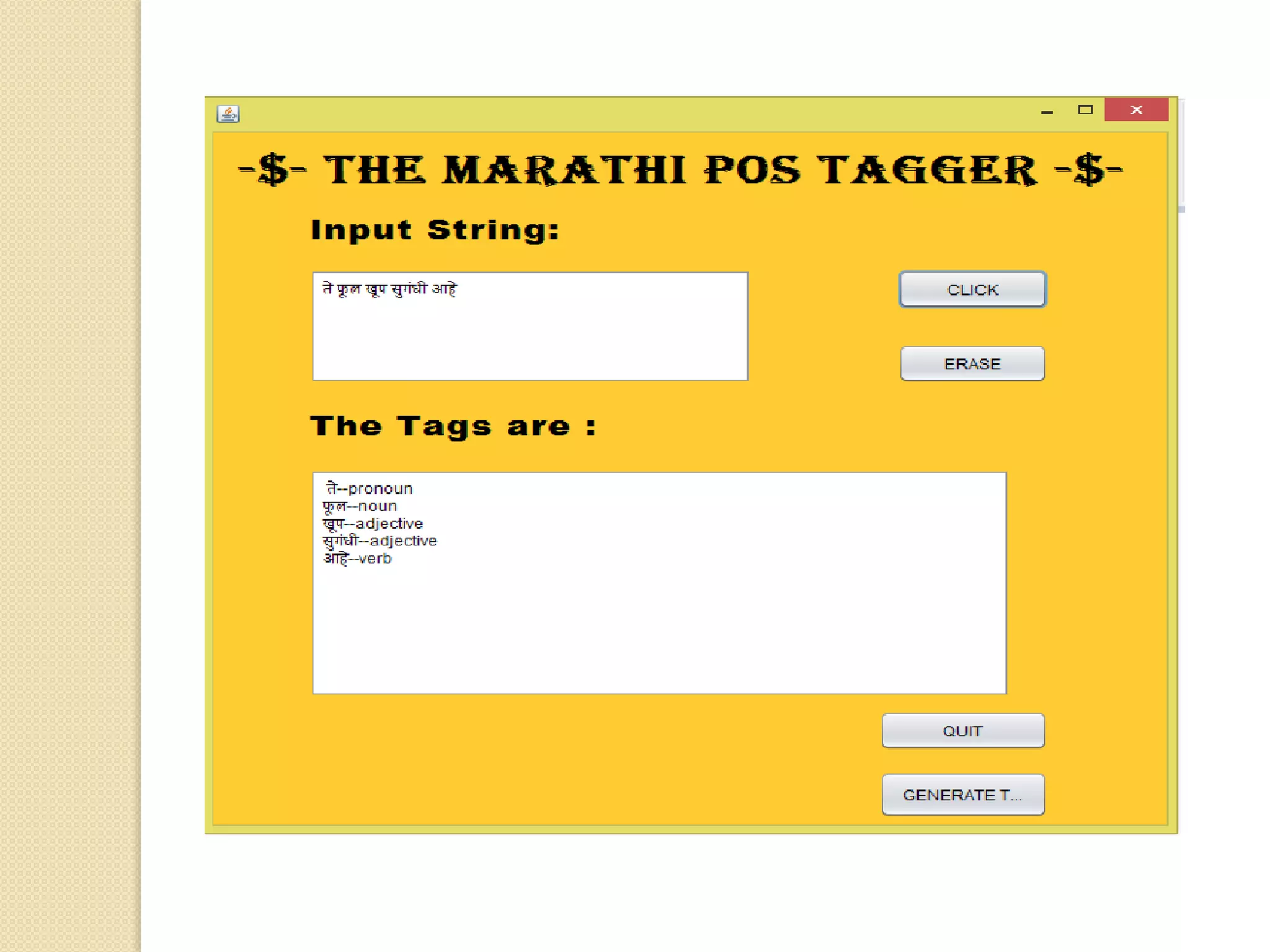
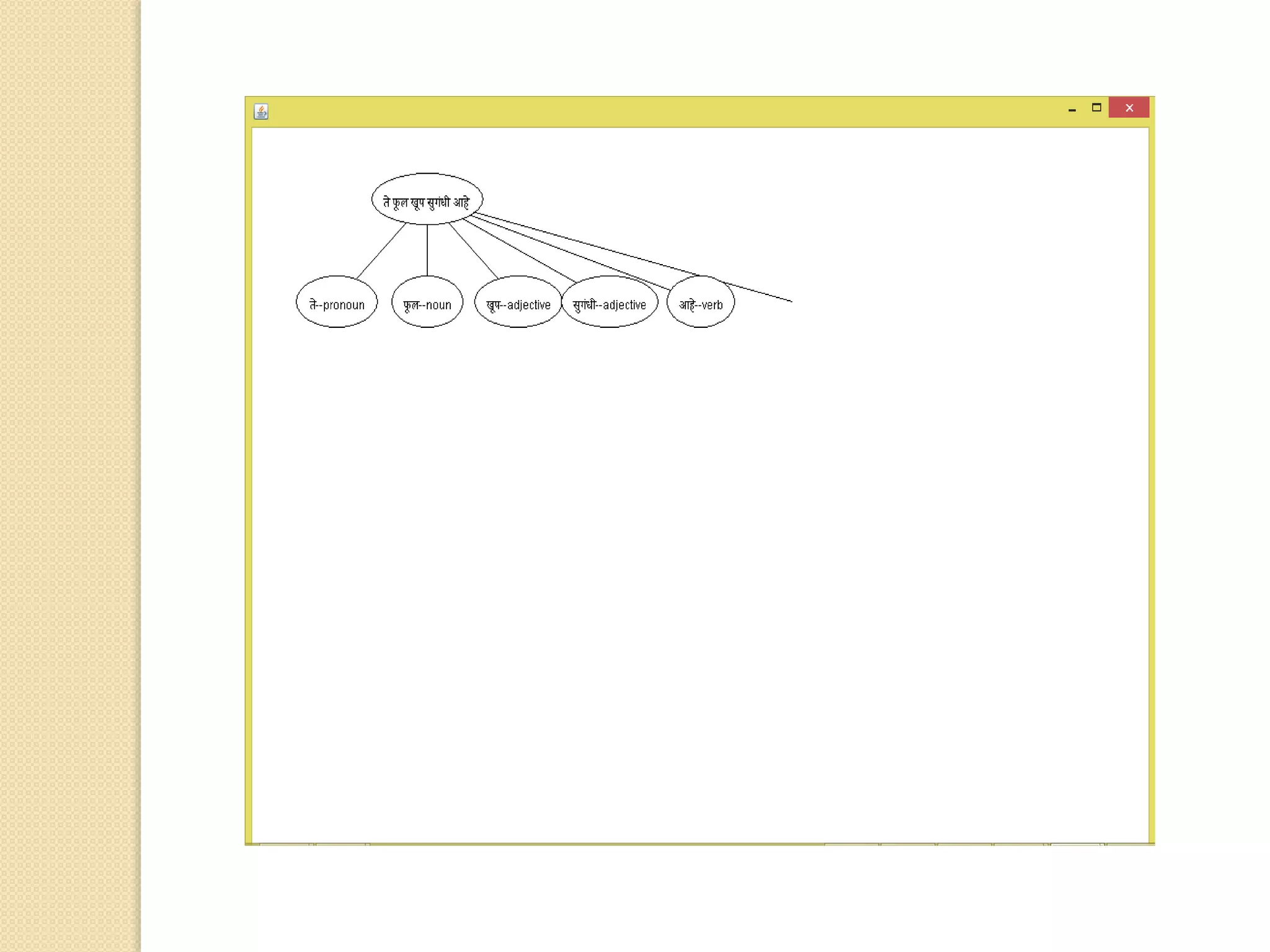
This document discusses part-of-speech (POS) tagging for the Marathi language. It describes POS tagging as assigning lexical class tags like noun, verb, or adjective to each word. The document outlines the need for Marathi POS tagging, common methods like rule-based and statistical approaches, and the architecture of the presented Marathi POS tagger. Experimental results demonstrate assigning tags based on bit patterns. Advantages include aiding other NLP tasks. Limitations involve ambiguity and the system only handling single sentences. Applications are listed as information retrieval and machine translation.