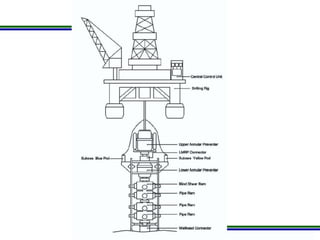
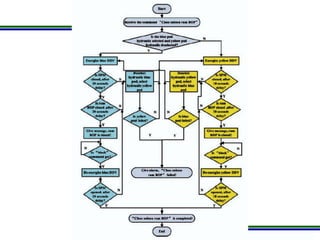
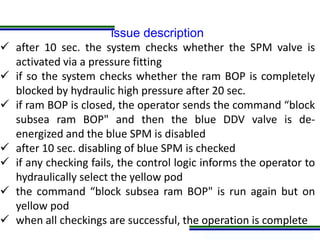
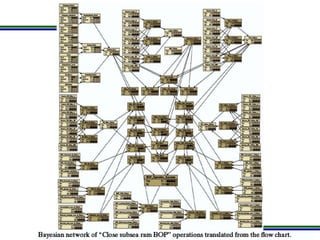
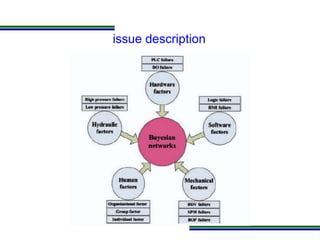
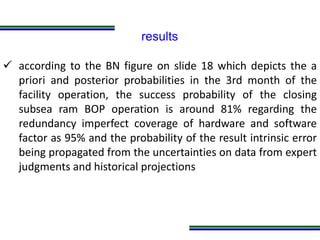
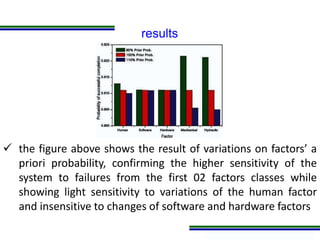
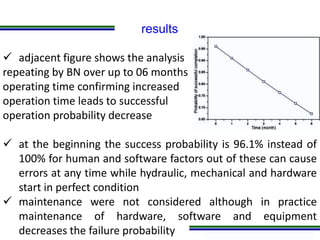
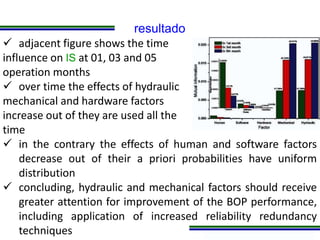
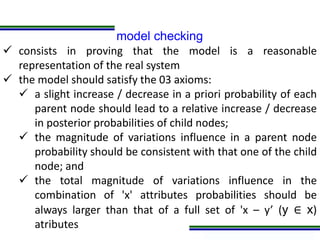
This document presents a methodology for applying Bayesian Networks to quantitatively assess the risk of failures during subsea blowout preventer (BOP) closing operations. The methodology involves modeling the process flowchart as a Bayesian Network to assess the influence of different risk factors on the probability of failure. The analysis identified hydraulic and mechanical factors as the most influential on failure probability. Over time, the effects of these factors increase while human and software factors decrease. The model was partially validated by checking it satisfies three axioms of influence between parent and child nodes.