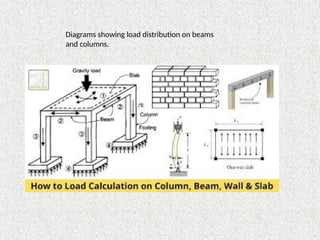
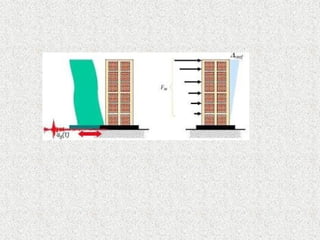
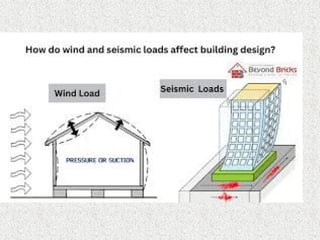
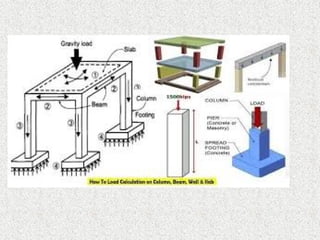
The document provides an overview of structural engineering, emphasizing key principles such as load distribution, types of loads, common structural systems, and analysis methods. It discusses materials used in construction, design considerations like safety and sustainability, and highlights innovations like modular engineering and digital technologies. The aim is to ensure structures can safely support various loads while considering aesthetics and environmental impact.