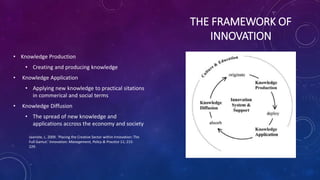
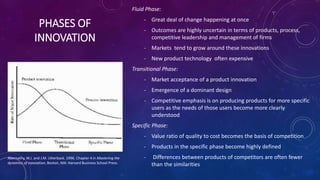
The document discusses innovation in the movie industry. It defines different types of innovation including product, process, radical, incremental, and content creation innovations. Product innovations in movies included adding sound and color, while process innovations involved new camera and editing techniques. A major distribution innovation was the shift from physical to digital formats like streaming. Streaming services are both a process and product innovation that have changed the industry structure by increasing competition and enabling global access. However, streaming also faces issues like piracy and limited content libraries. Overall, innovation has changed how movies are consumed, from theaters to homes, with both benefits and challenges.