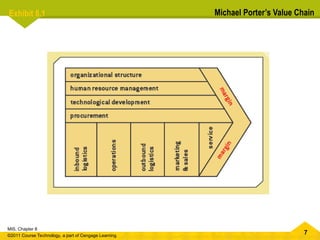
The document provides a comprehensive overview of e-commerce, defining it as the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet while discussing its advantages and disadvantages. It covers various e-commerce models such as business-to-consumer (B2C), business-to-business (B2B), and consumer-to-consumer (C2C), along with supporting technologies and mobile commerce. Additionally, it highlights the importance of Michael Porter's value chain in understanding how e-commerce differs from traditional commerce.