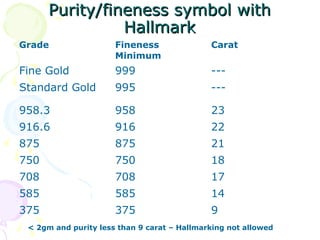
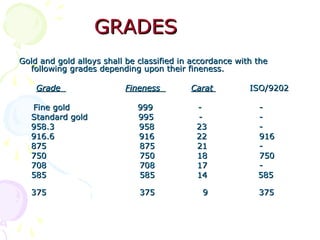
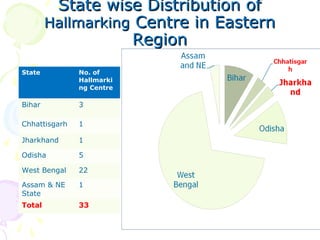
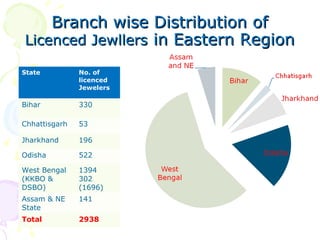
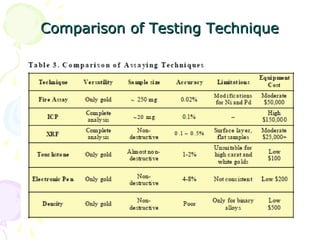
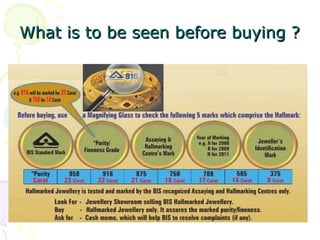
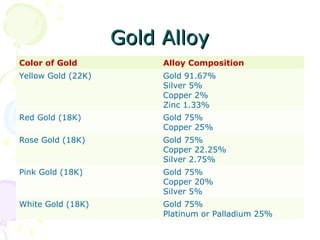
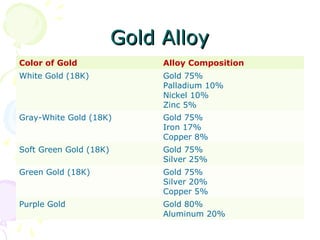
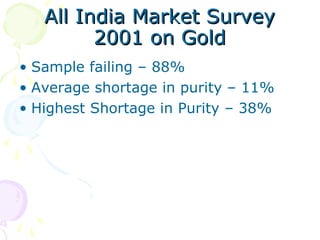
The document discusses hallmarking standards for gold and silver jewelry in India. It provides details on gold alloys, their compositions and colors. Hallmarking guarantees the purity and proportion of precious metals. Standards specify grades of gold and silver, marking requirements, and assaying methods to test purity. Hallmarks must be applied by BIS-recognized centers and include purity grade, assay center mark, year and maker's mark. Regular non-compliance was found in market surveys prior to strict hallmarking laws.




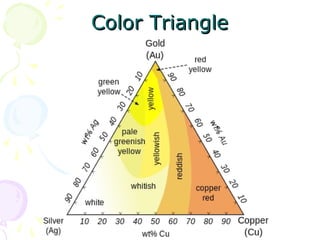









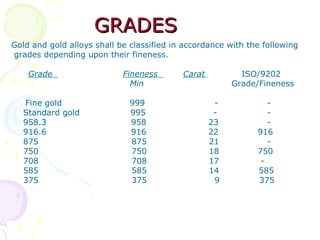







![GRADESGRADES
– Grade Fineness Fineness
» (ISO 9202)
– 9999 ] 999.9 --
– 9995 ] Fine silver 999.5 --
– 999 ] 999.0
– 990 ] 990.0 --
– 970 ] 970.0 --
– 925 ] Silver alloys 925.0 925.0
– 900 ] for jewellery 900.0 --
– 835 ] artefacts 835.0 835.0
– 800 ] 800.0 800.0
–](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hallmarkingpresentation-150421075306-conversion-gate01/85/Presentation-on-BIS-Hallmarking-Scheme-26-320.jpg)