The document discusses the bin-packing problem, particularly focusing on the knapsack variant where the objective is to maximize the value of packed items within a specified weight limit. It presents an example of the knapsack problem, illustrating the use of a formula for optimal packing combinations, as well as the implementation of a Python algorithm to solve it. The content highlights the practical application of operational research in decision-making processes through advanced analytical methods.





![Knapsack Problem
Output function f(i,w)
f(i,w)=Max[ xi + f(i,w-wi) ; f(i-1,w) ]
ONE Item i + optimum
combination of weight w-wi
NO Item i + optimum
combination items 1 to i-
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationofknapsack-181102082223/85/Presentation-of-knapsack-7-320.jpg)

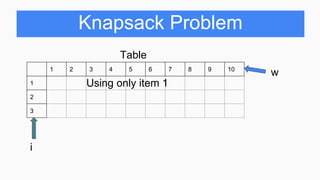
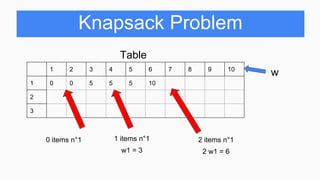
![Knapsack Problem
Table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1 0 0 5 5 5 10 10 10 15 15
2 0 0 5 7
3
w-w2 =
5 - 4 = 1
f(i,w)=Max[ xi + f(i,w-wi) ; f(i-1,w) ]
+ x2(=7)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationofknapsack-181102082223/85/Presentation-of-knapsack-13-320.jpg)
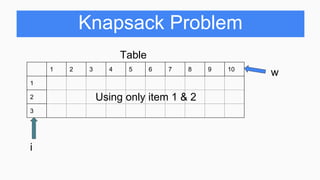
![Knapsack Problem
Table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1 0 0 5 5 5 10 10 10 15 15
2 0 0 5 7 7
3
f(i,w)=Max[ xi + f(i,w-wi) ; f(i-1,w) ]
+ x2(=7)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationofknapsack-181102082223/85/Presentation-of-knapsack-14-320.jpg)
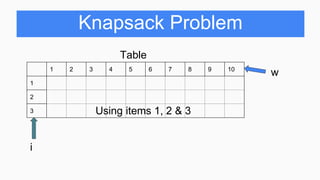
![Knapsack Problem
Table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1 0 0 5 5 5 10 10 10 15 15
2 0 0 5 7 7
3
w-w2 =
6 - 4 = 2
f(i,w)=Max[ xi + f(i,w-wi) ; f(i-1,w) ]
+ x2(=7)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationofknapsack-181102082223/85/Presentation-of-knapsack-15-320.jpg)
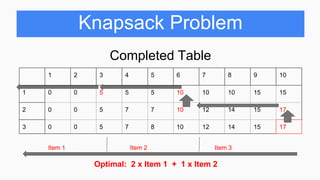
![Knapsack Problem
Table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1 0 0 5 5 5 10 10 10 15 15
2 0 0 5 7 7 10
3
f(i,w)=Max[ xi + f(i,w-wi) ; f(i-1,w) ]
+ x2(=7)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationofknapsack-181102082223/85/Presentation-of-knapsack-16-320.jpg)
![Python code for Knapsack problem
from ortools.algorithms import pywrapknapsack_solver
def main():
# Create the solver.
solver = pywrapknapsack_solver.KnapsackSolver(
pywrapknapsack_solver.KnapsackSolver.
KNAPSACK_MULTIDIMENSION_BRANCH_AND_BOUND_SOLVER,
'test')
values = [360, 83, 59, 130, 431, 67, 230, 52, 93,
125, 670, 892, 600, 38, 48, 147, 78, 256,
63, 17, 120, 164, 432, 35, 92, 110, 22,
42, 50, 323, 514, 28, 87, 73, 78, 15,
26, 78, 210, 36, 85, 189, 274, 43, 33,
10, 19, 389, 276, 312]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationofknapsack-181102082223/85/Presentation-of-knapsack-18-320.jpg)
![weights = [[7, 0, 30, 22, 80, 94, 11, 81, 70,
64, 59, 18, 0, 36, 3, 8, 15, 42,
9, 0, 42, 47, 52, 32, 26, 48, 55,
6, 29, 84, 2, 4, 18, 56, 7, 29,
93, 44, 71, 3, 86, 66, 31, 65, 0,
79, 20, 65, 52, 13]]
capacities = [850]
solver.Init(values, weights, capacities)
computed_value = solver.Solve()
packed_items = [x for x in range(0, len(weights[0]))
if solver.BestSolutionContains(x)]
packed_weights = [weights[0][i] for i in packed_items]
total_weight= sum(packed_weights)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationofknapsack-181102082223/85/Presentation-of-knapsack-19-320.jpg)
![Print the output
or result.
print("Packed items: ", packed_items)
print("Packed weights: ", packed_weights)
print("Total value: ", computed_value)
print("Total weight: ", total_weight)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Packed items: [0, 1, 3, 4, 6, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15,
16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 22, 24, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31,
32, 34, 38, 39, 41, 42, 44, 47, 48, 49]
Packed weights: [7, 0, 22, 80, 11, 59, 18, 0, 3,
8, 15, 42, 9, 0, 47, 52, 26, 6, 29, 84, 2, 4, 18, 7,
71, 3, 66, 31, 0, 65, 52, 13]
Total value: 7534
Total weight: 850
Output of the python
code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationofknapsack-181102082223/85/Presentation-of-knapsack-20-320.jpg)

