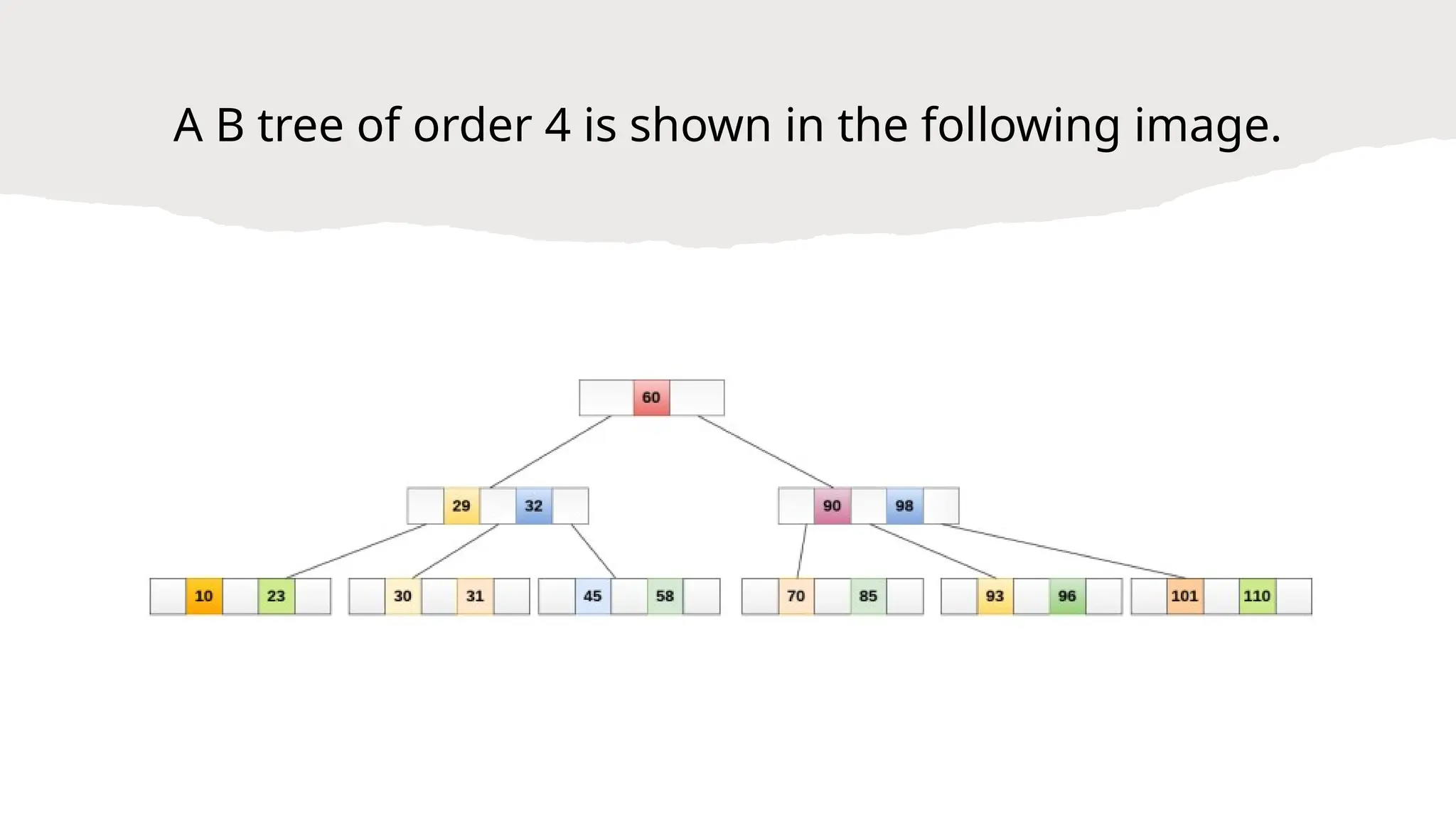
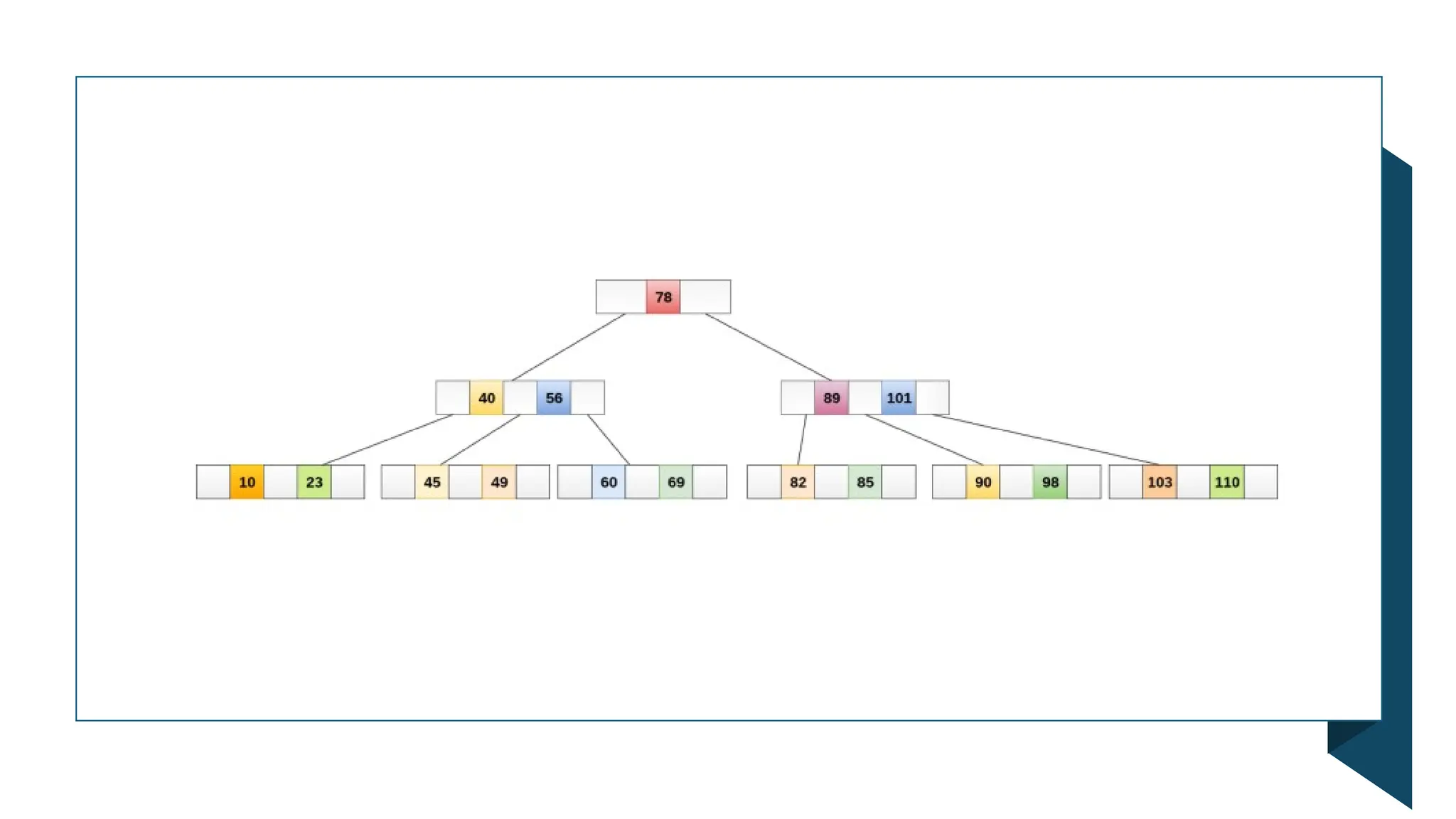
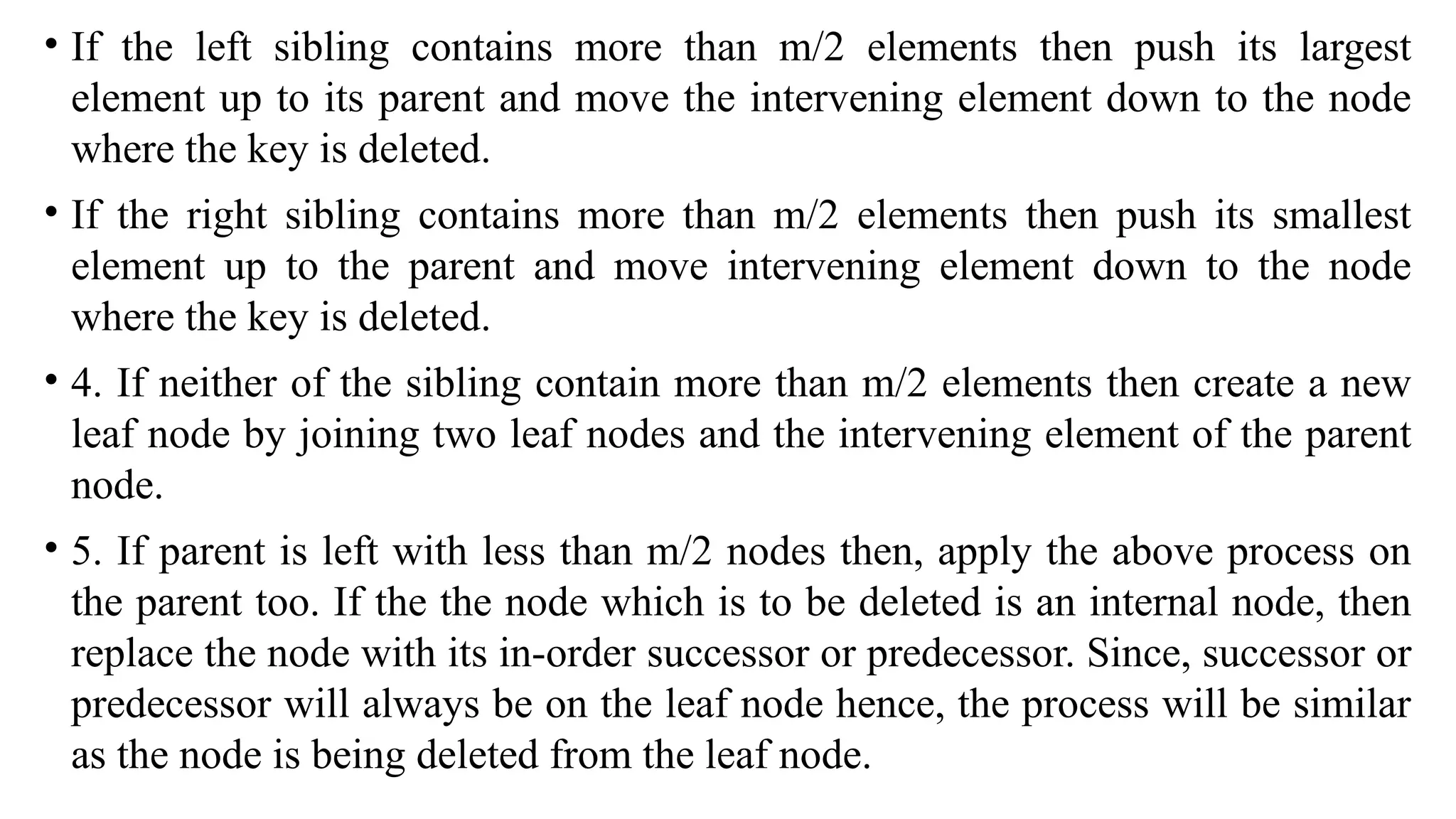
A B-tree is an m-way tree structure optimized for disk access, allowing efficient storage and retrieval of large numbers of keys. It maintains properties such as a maximum number of children per node and ensures all leaf nodes are at the same level, which facilitates operations like searching, inserting, and deleting. B-trees significantly improve the performance of database indexing, enabling search operations to be completed in O(log n) time.