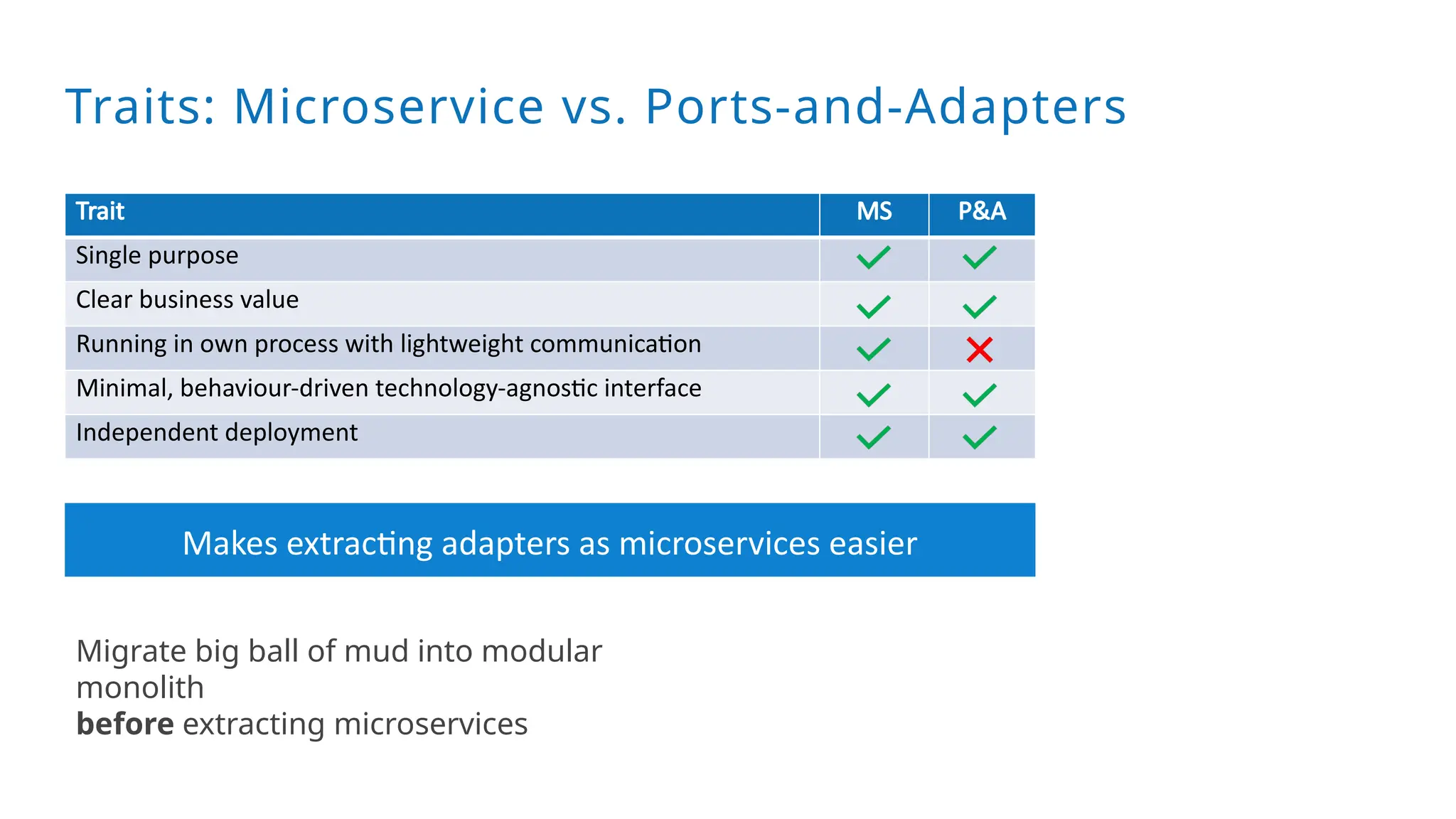
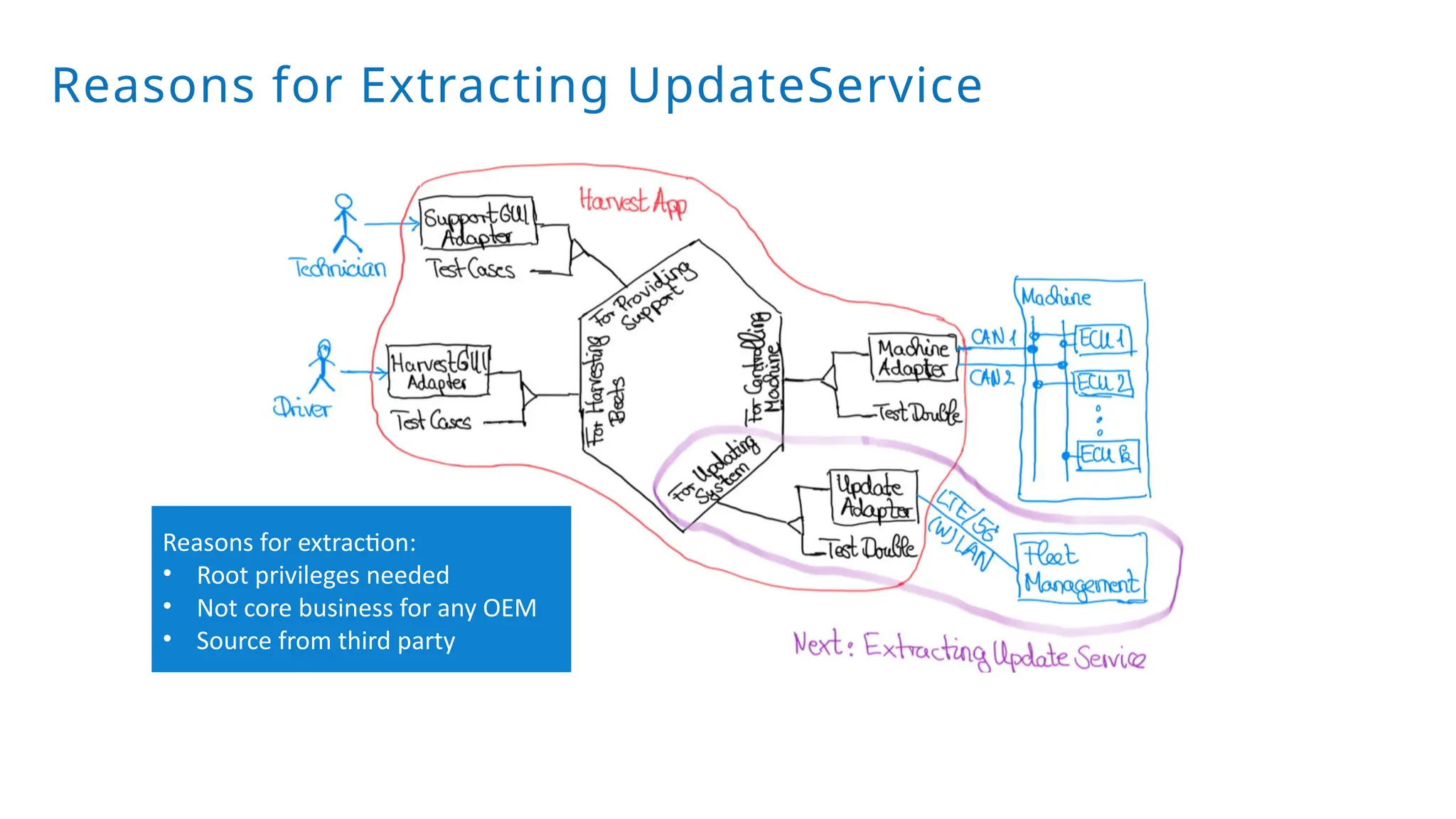
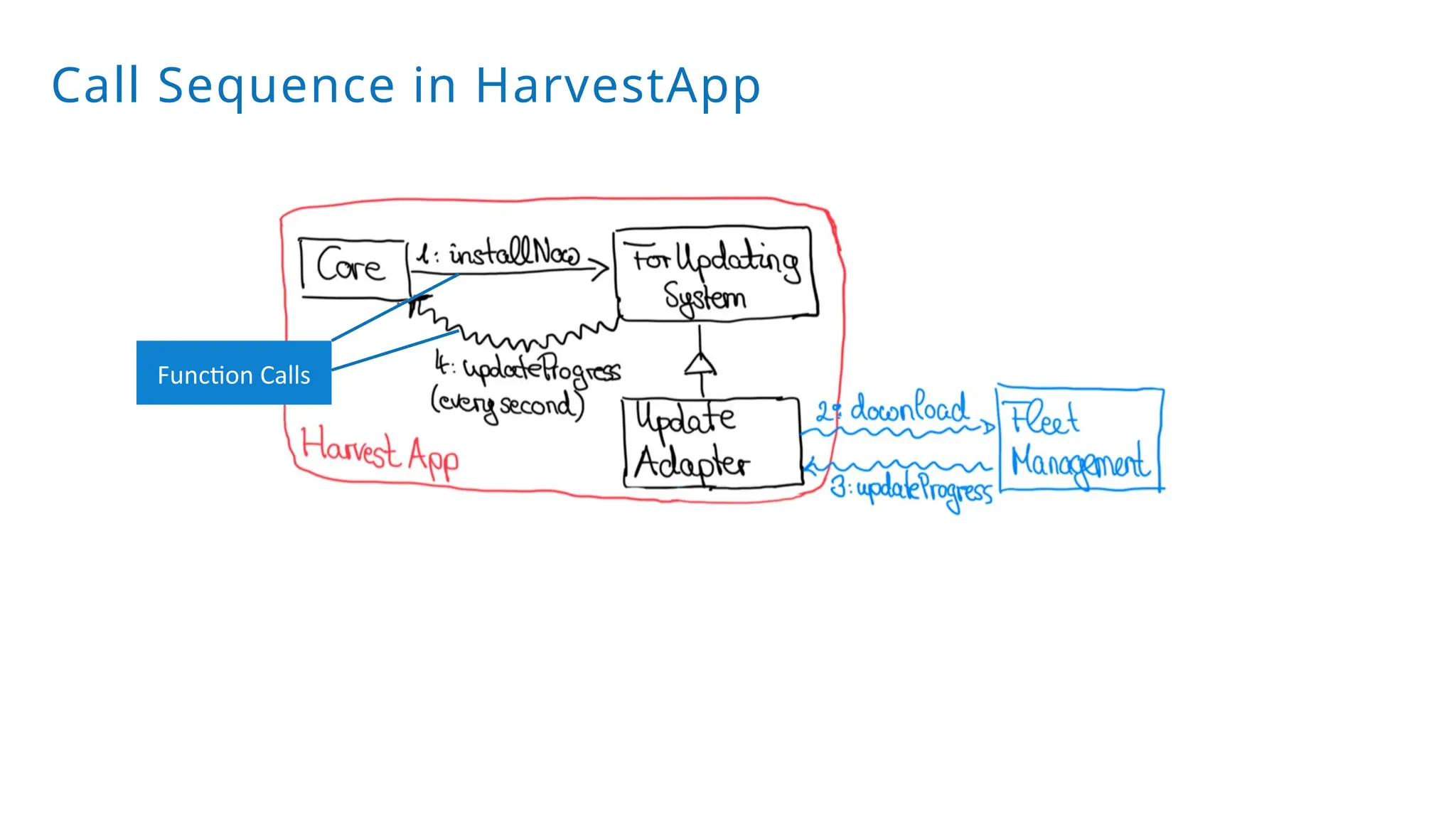
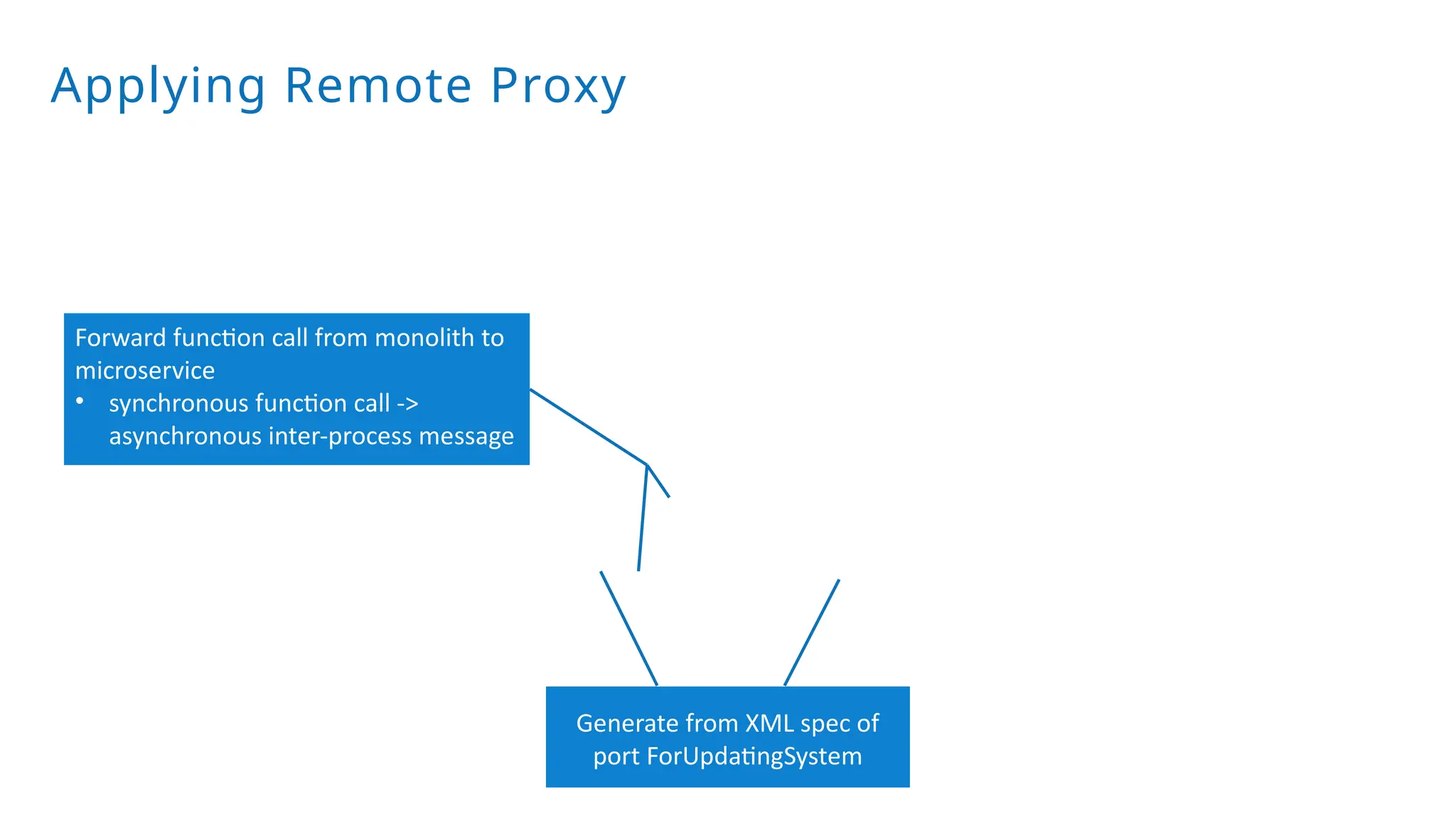
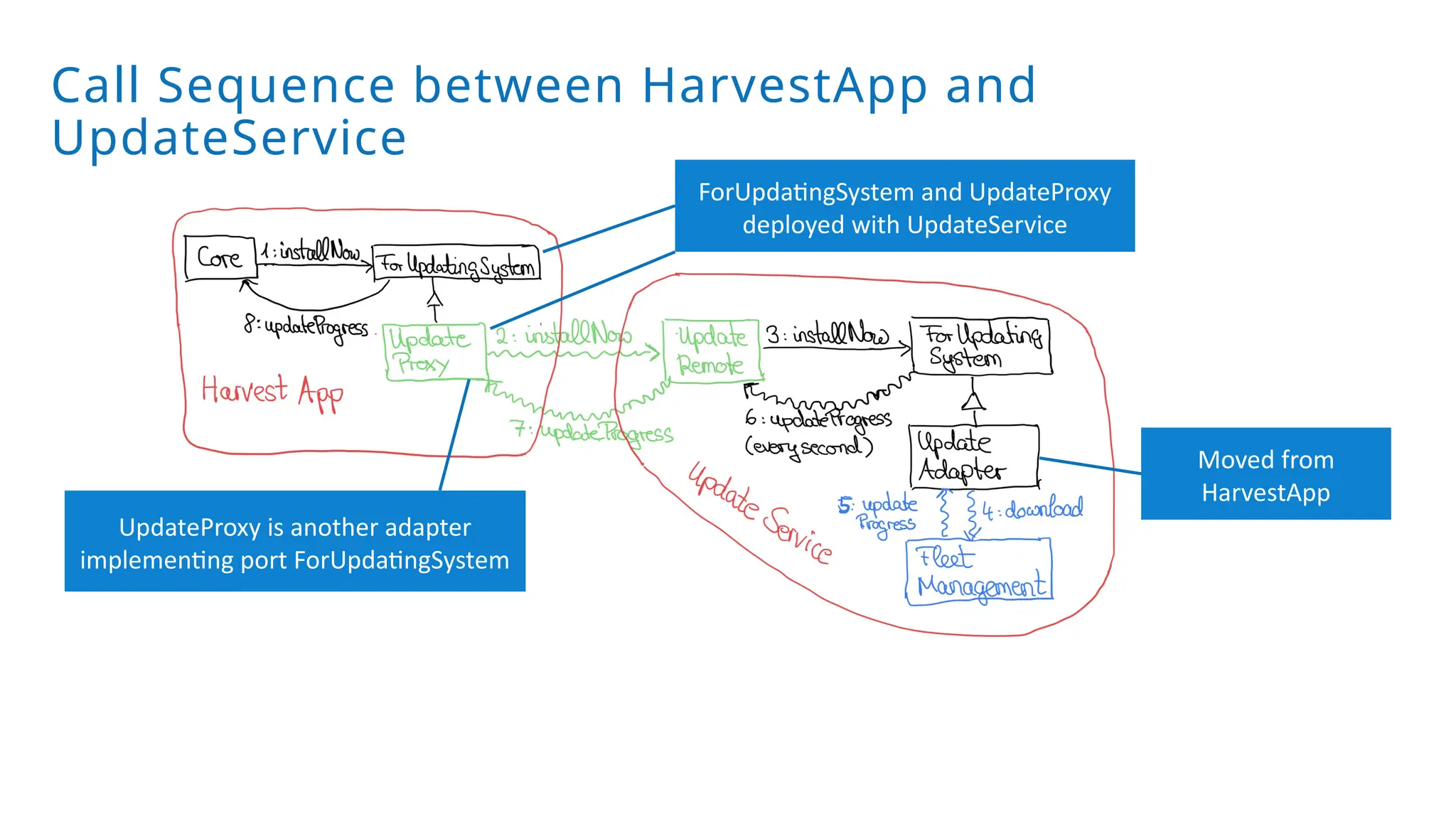
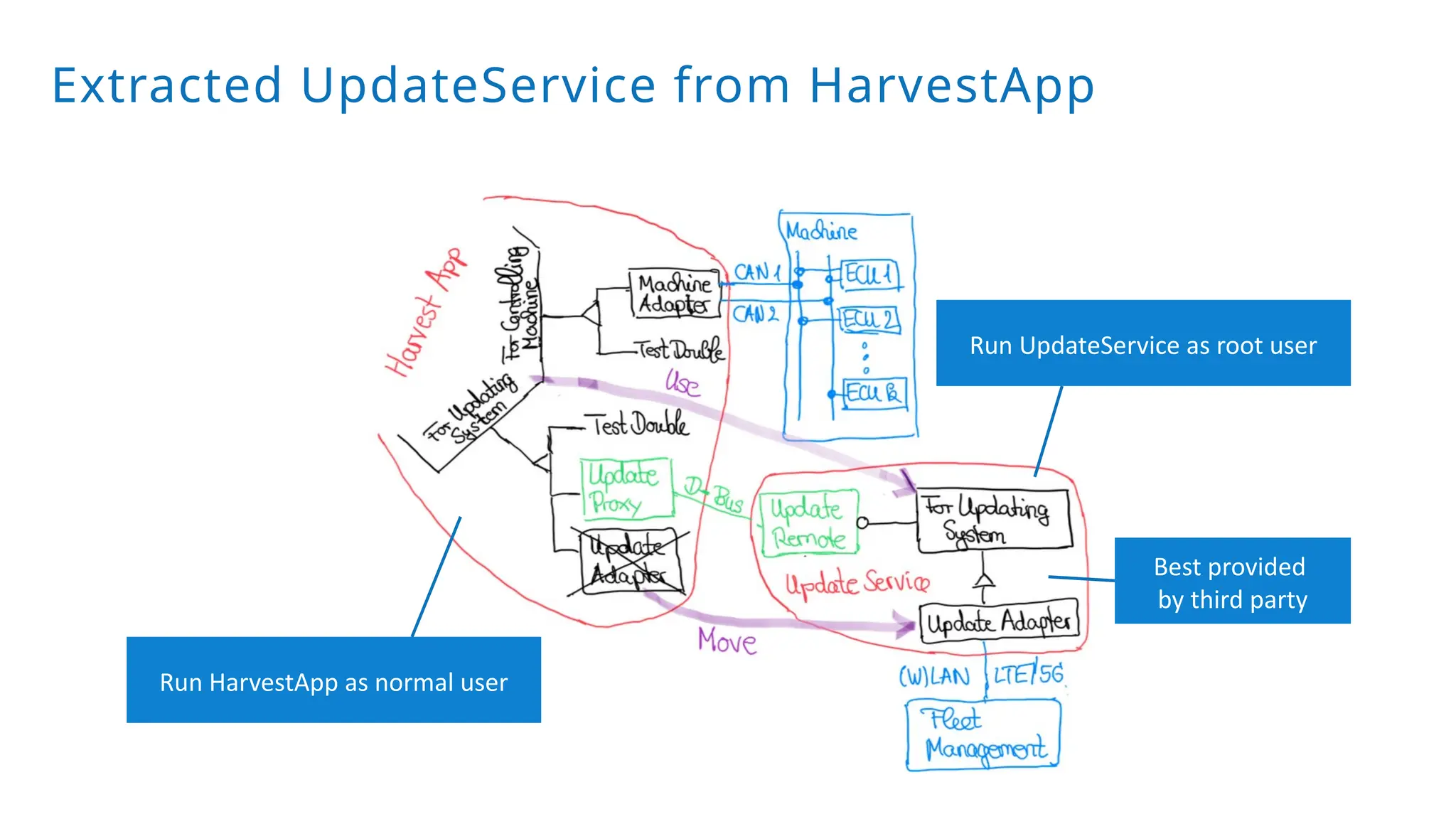
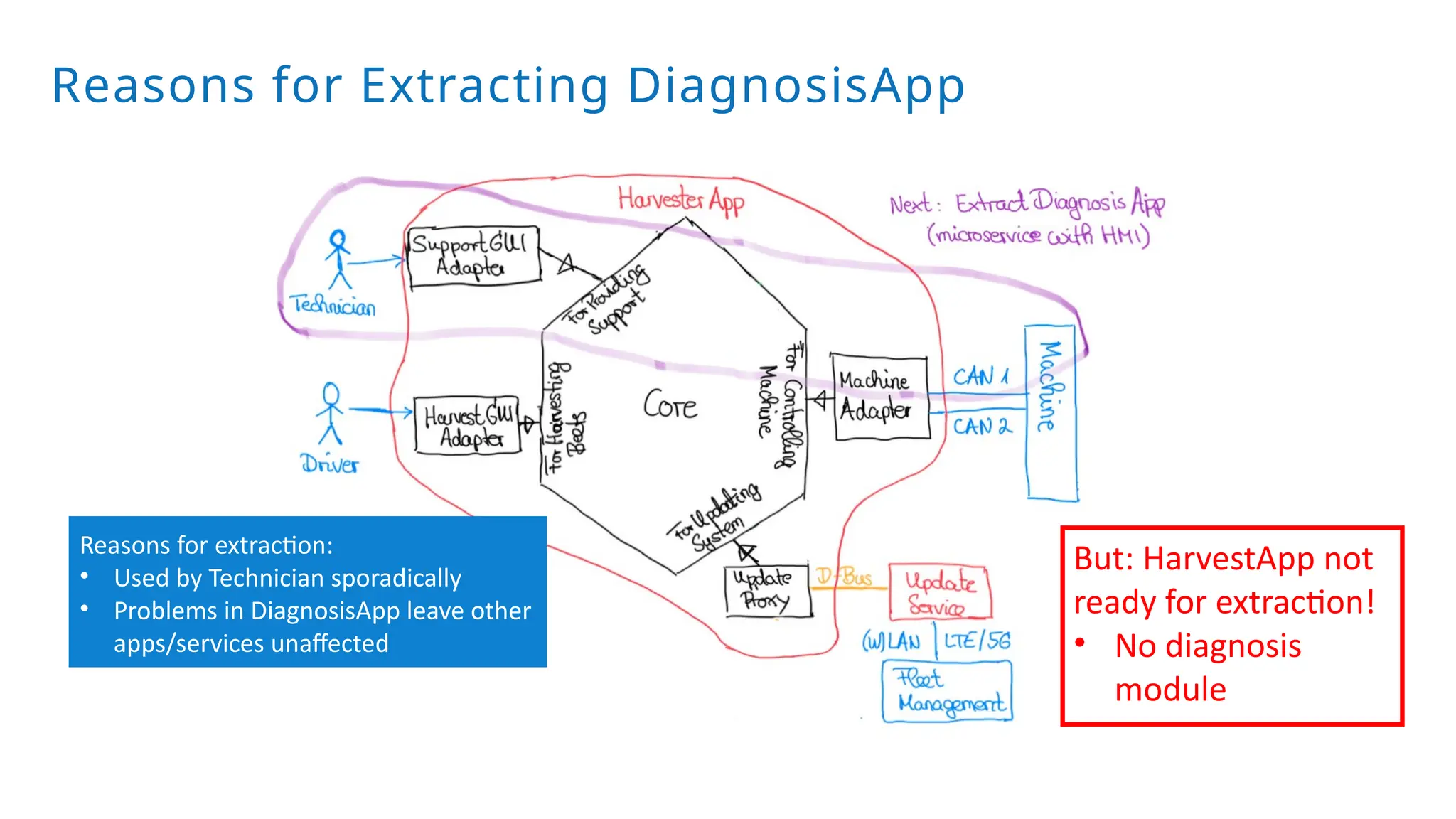
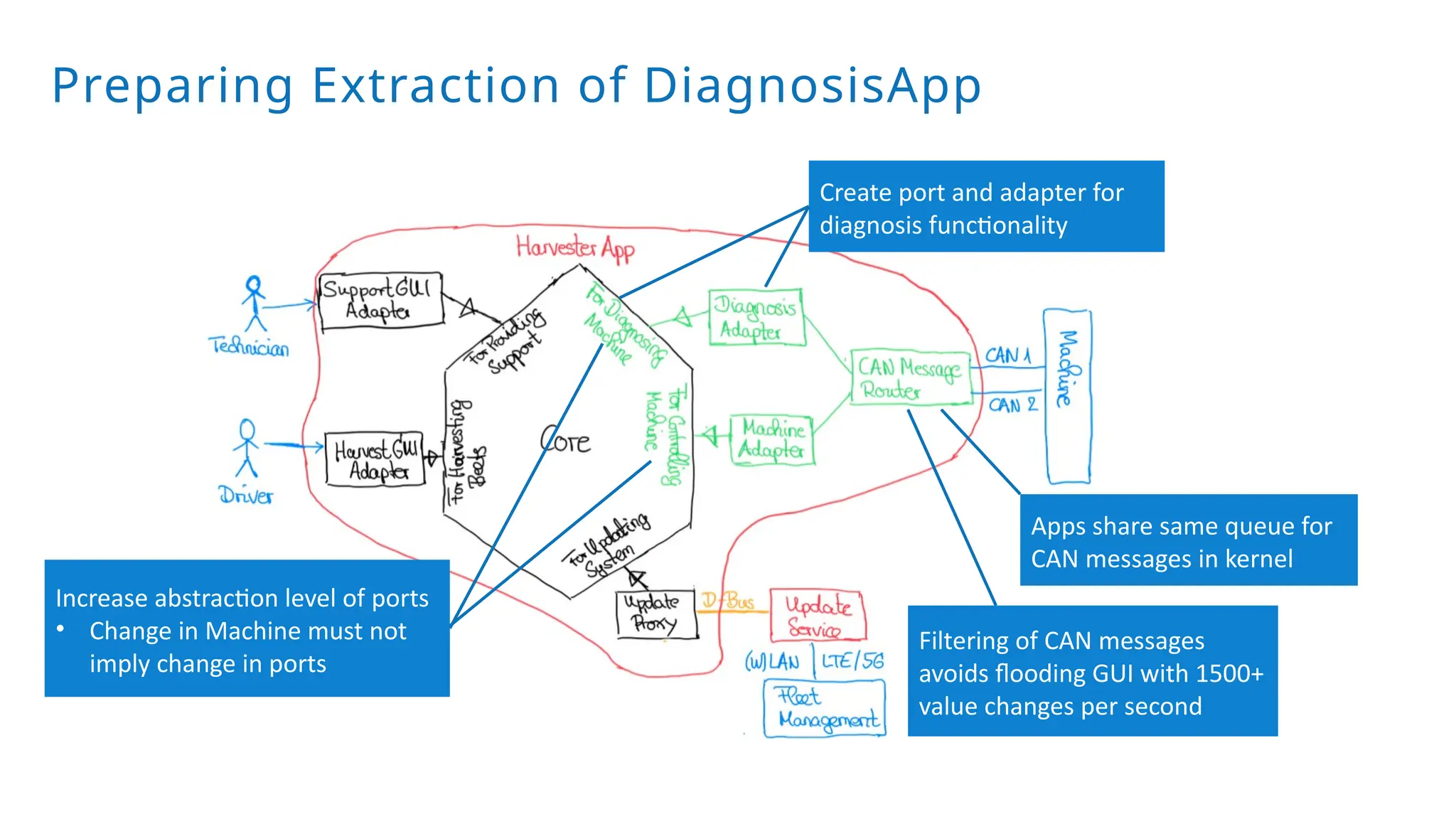
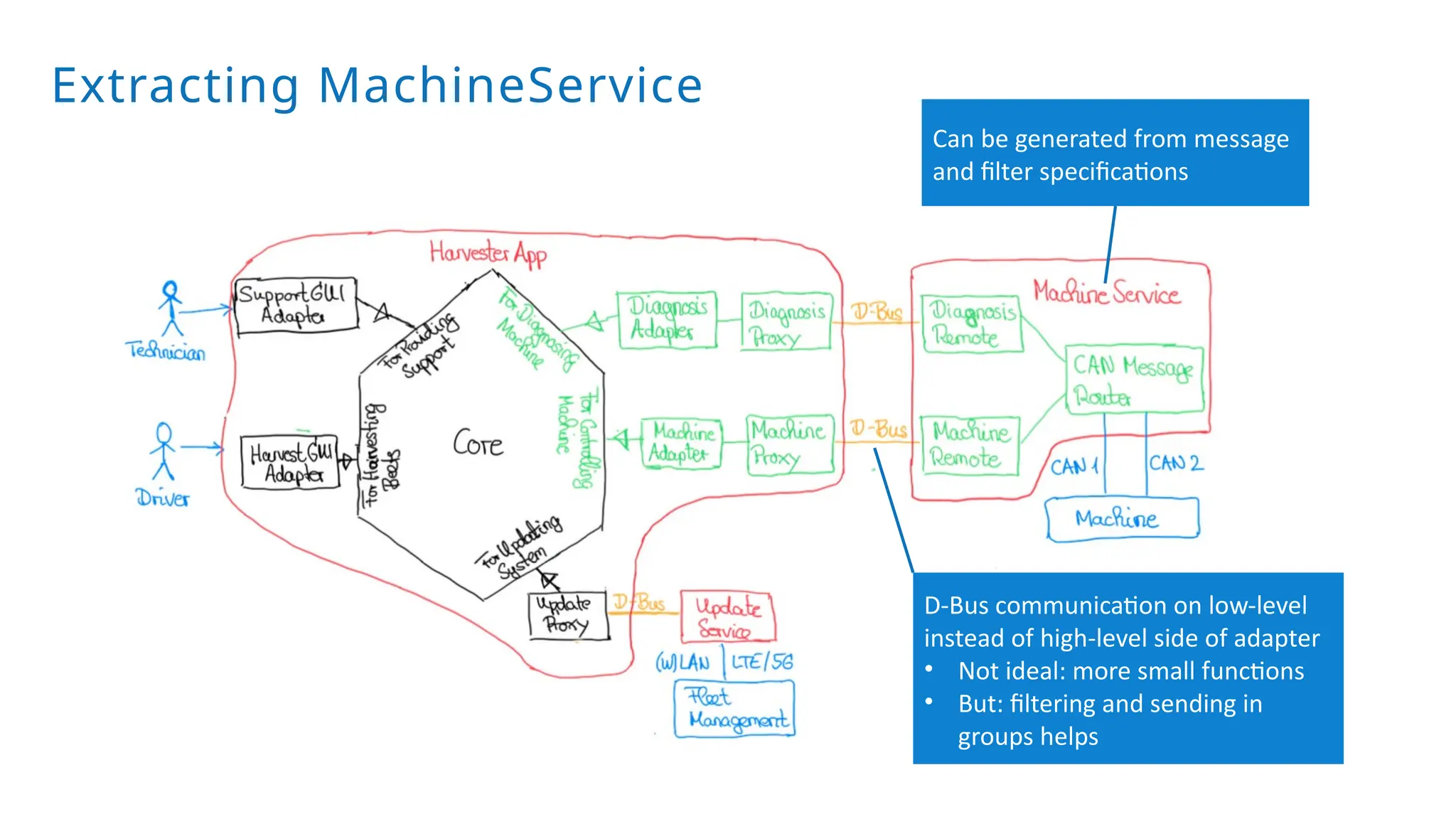
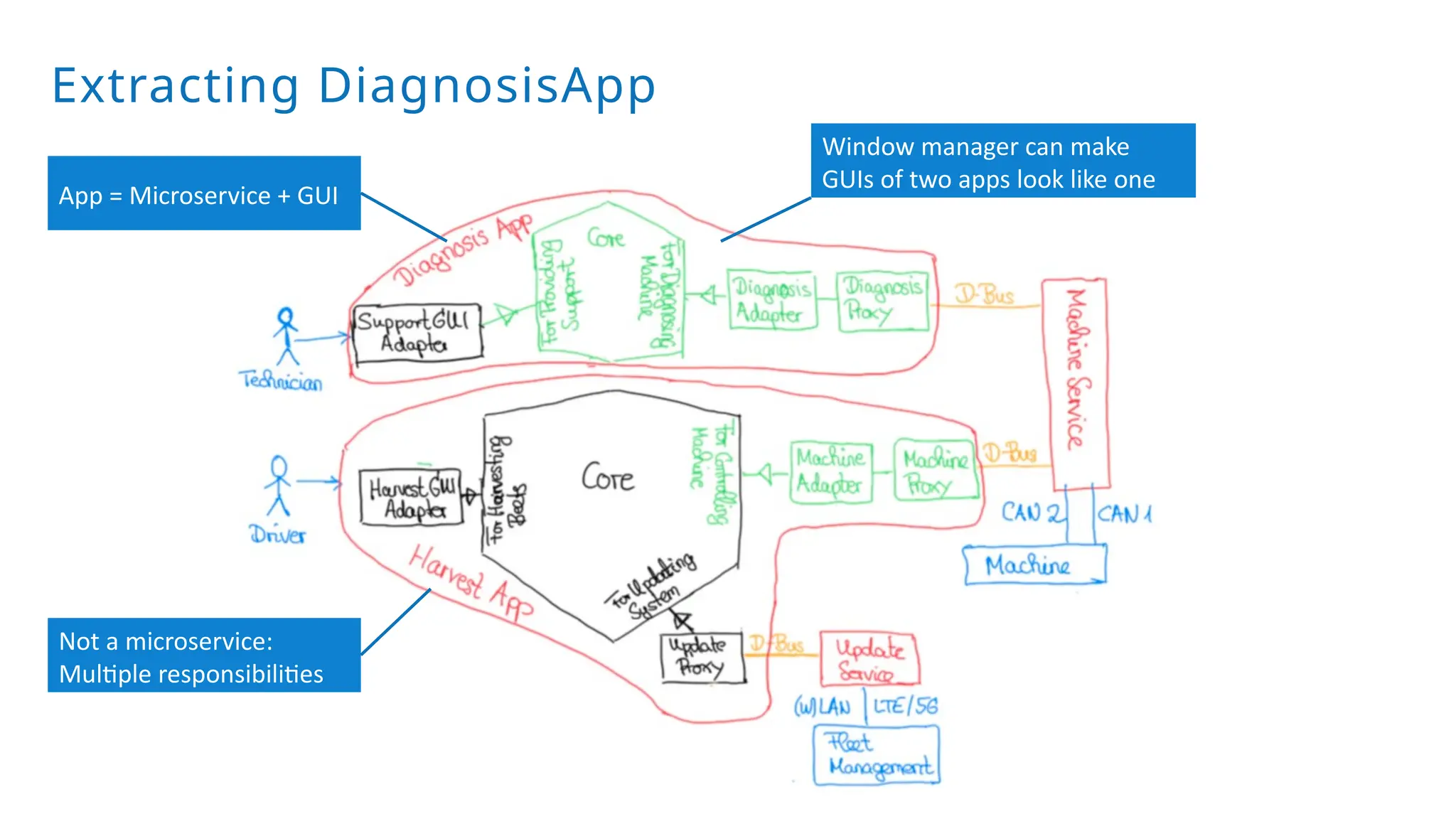
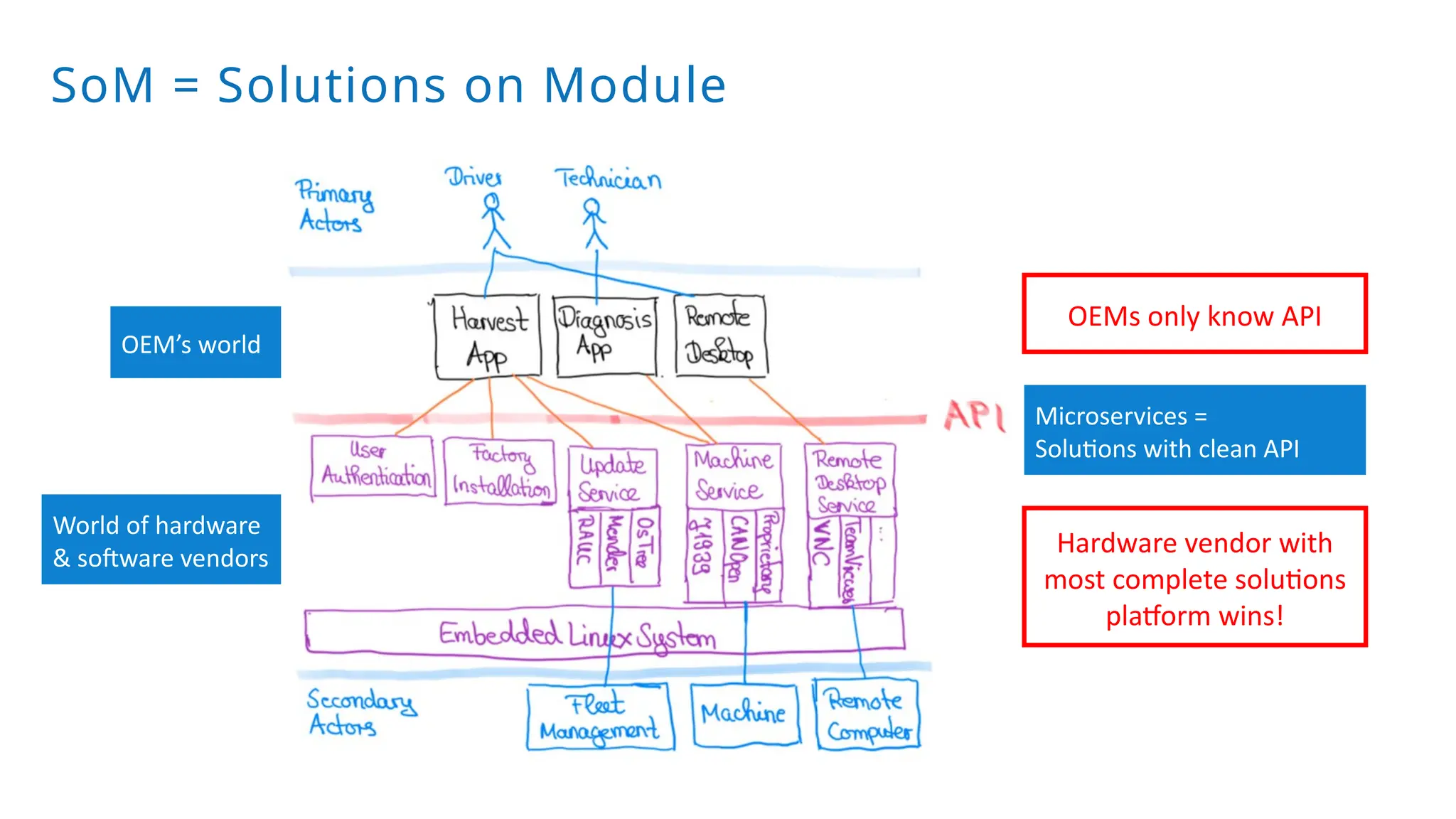
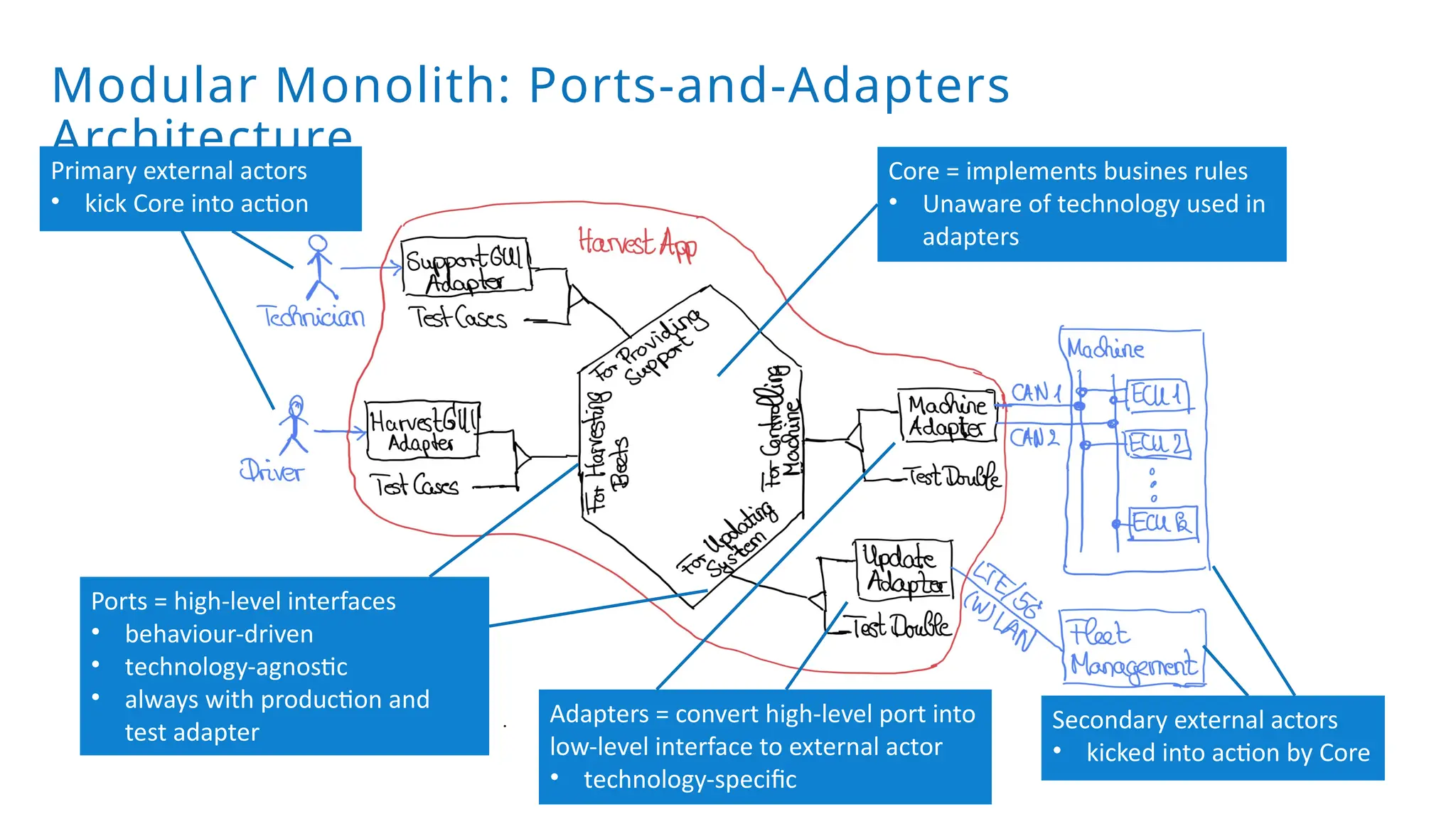
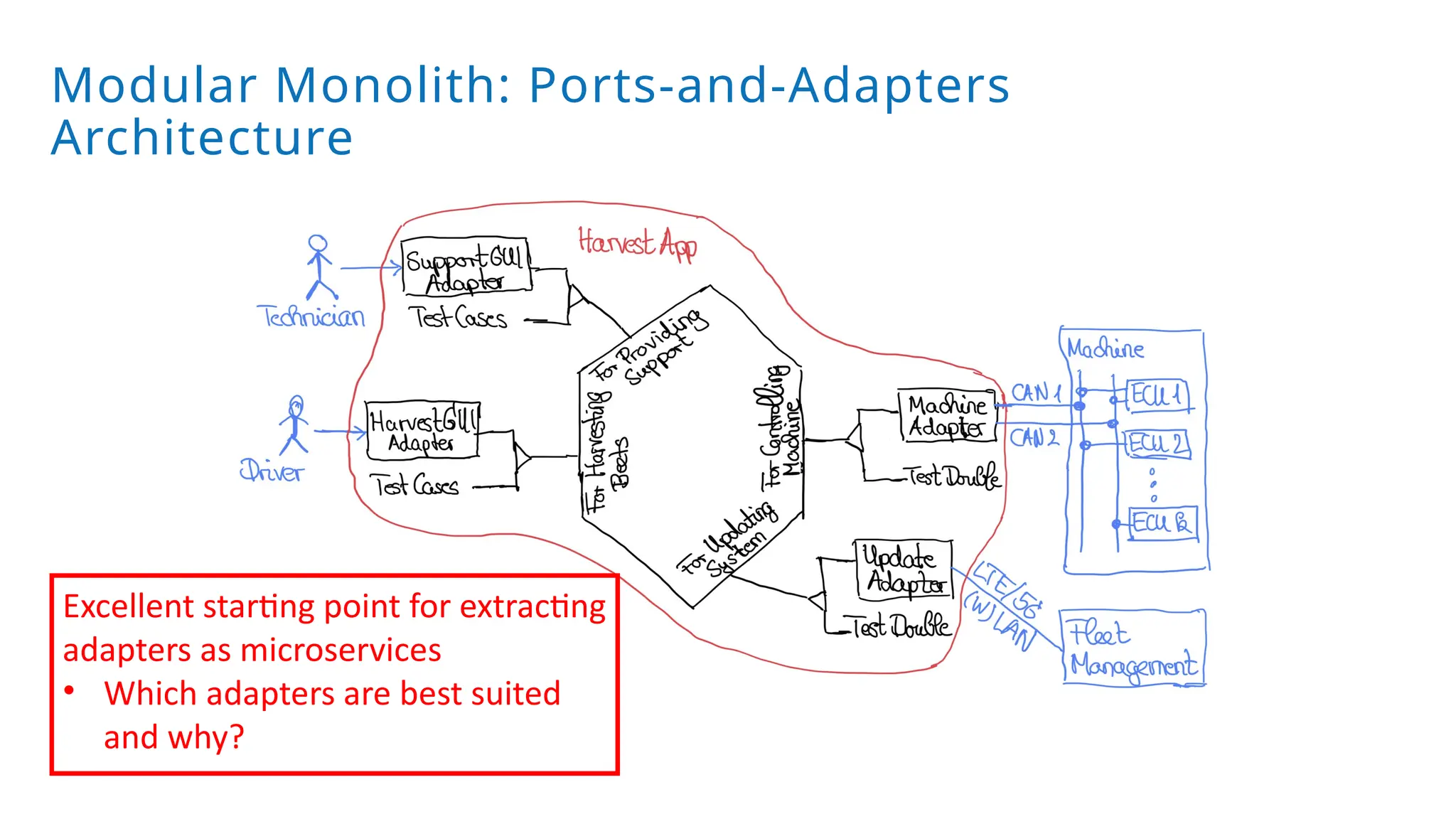
A modular monolith based on the ports-and-adapters architecture is an excellent starting point for extracting microservices. A microservice shares the same traits as an adapter together with its port – and additionally runs in its own process. Introducing a microservice should have a good reason, because it comes with some extra complexity. We extract an update and diagnostic service from a driver terminal of a harvester.



![Definition: Microservice
James Lewis, Martin Fowler:
Microservices – a definition of this new archit
ectural style
, 2014:
“In short, the microservice architectural style is an
approach to developing a single application as a
suite of small services, each running in its own
process and communicating with lightweight
mechanisms […]. These services are built
around business capabilities and
independently deployable by fully automated
deployment machinery.”
Microservice:
• Single purpose
• Clear business value
• Running in its own process with
lightweight communication
• Minimal, behaviour-driven, technology-
agnostic interface
• Independent deployment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stubert-eoc2025-extracting-microservice-from-a-modular-monolith-251101225110-f317062c/75/Presentation-Extracting-Microservices-from-a-Modular-Monolith-at-Embedded-Online-Conference-2025-8-2048.jpg)