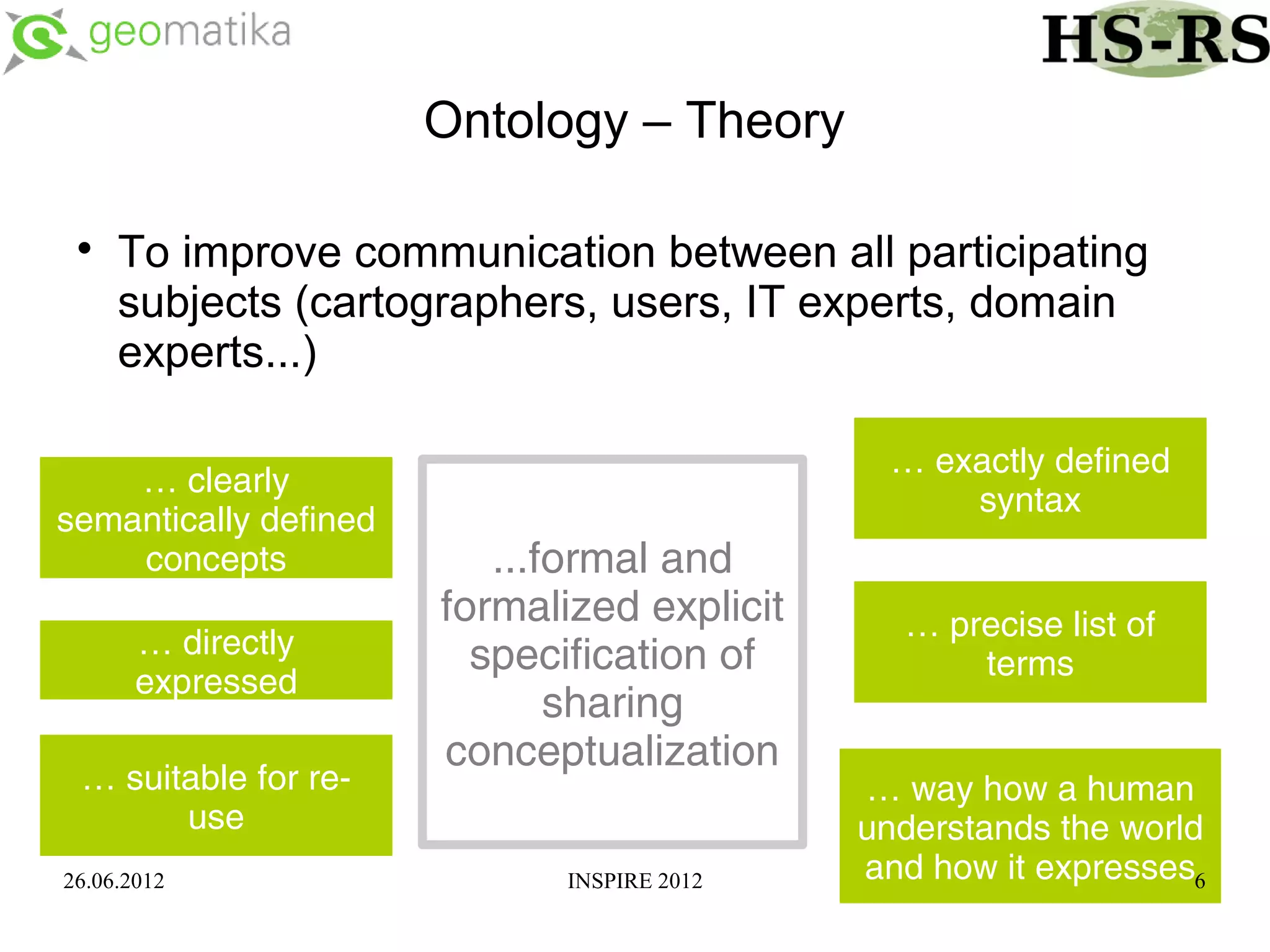
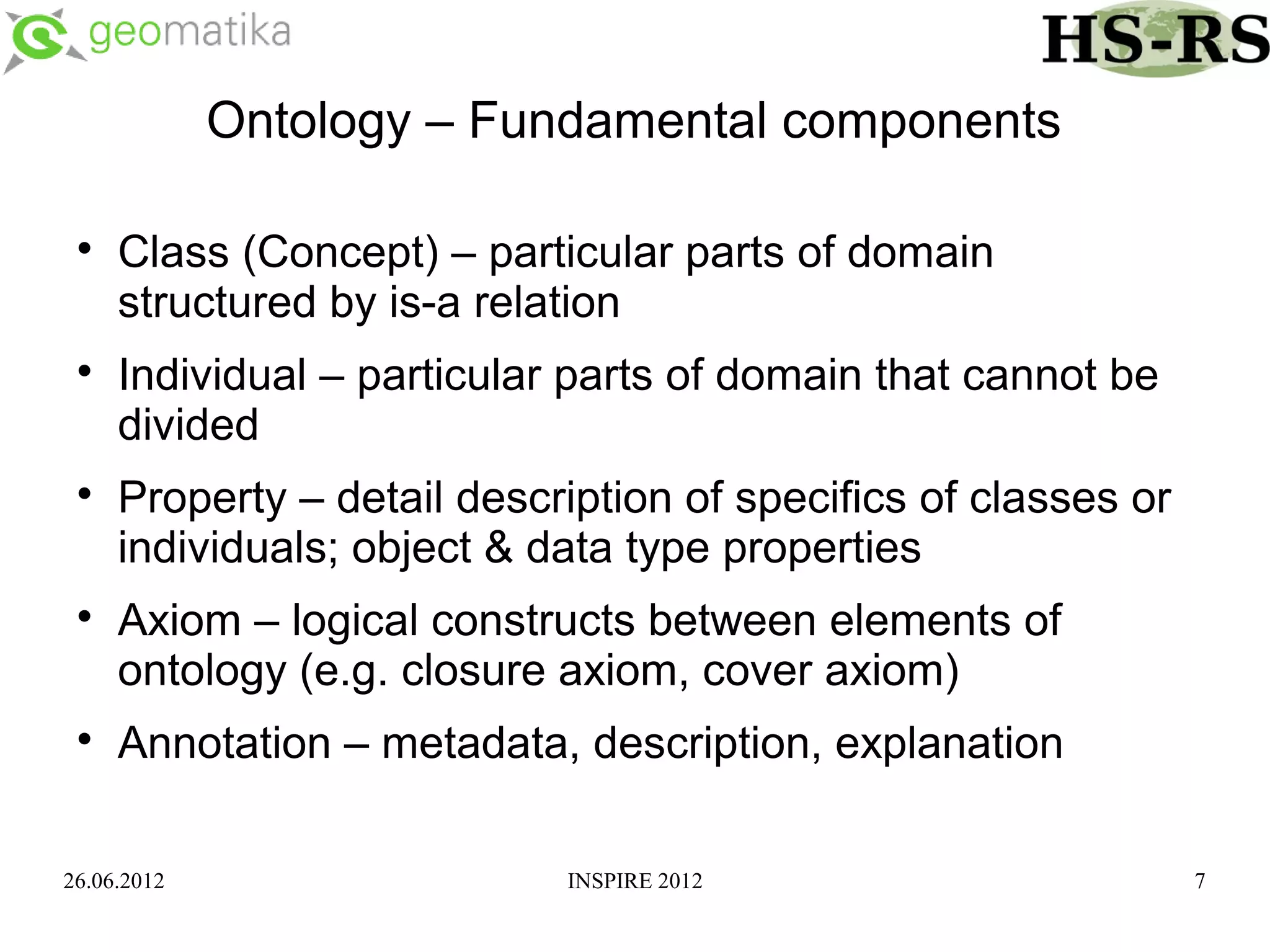
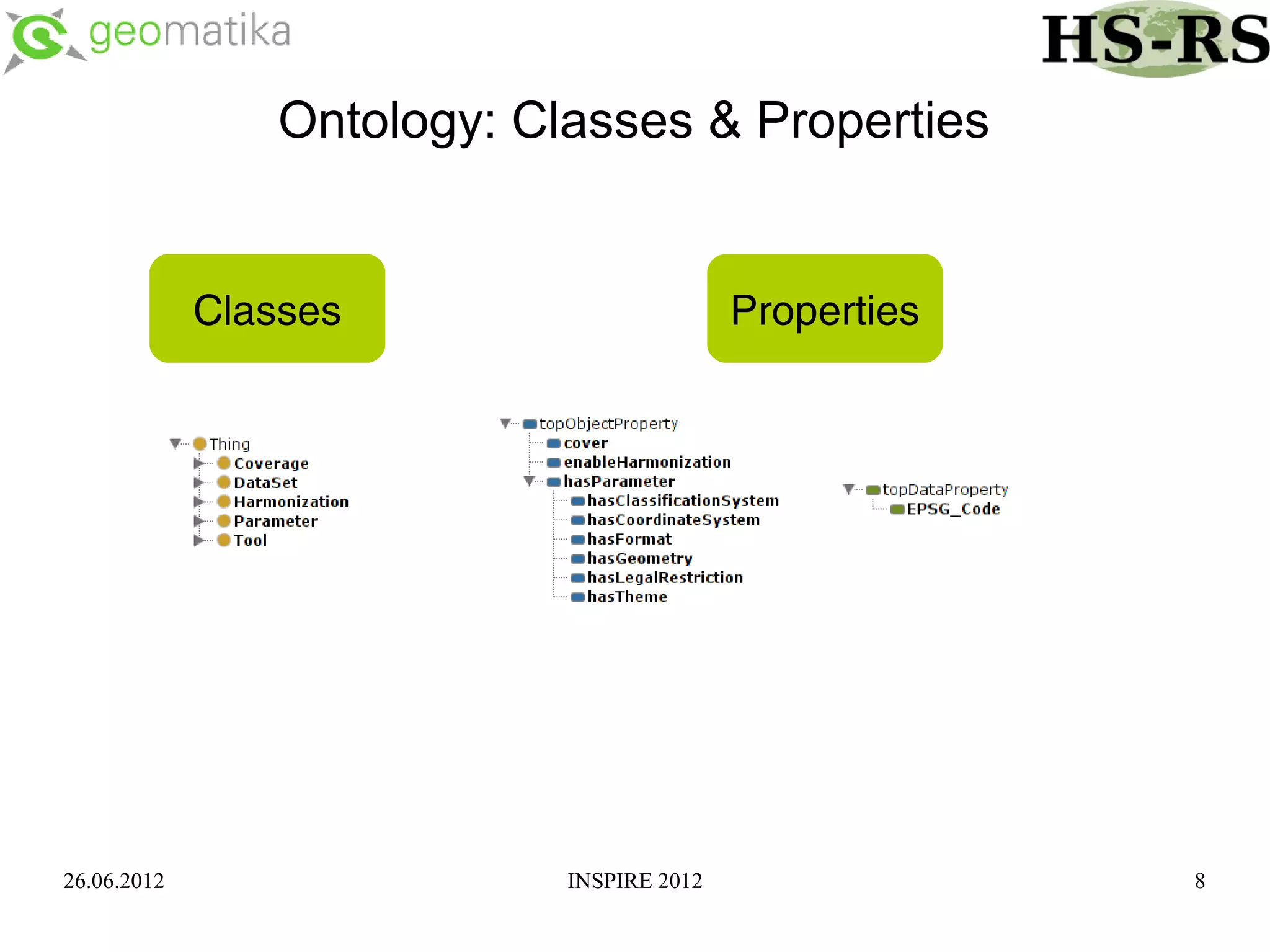
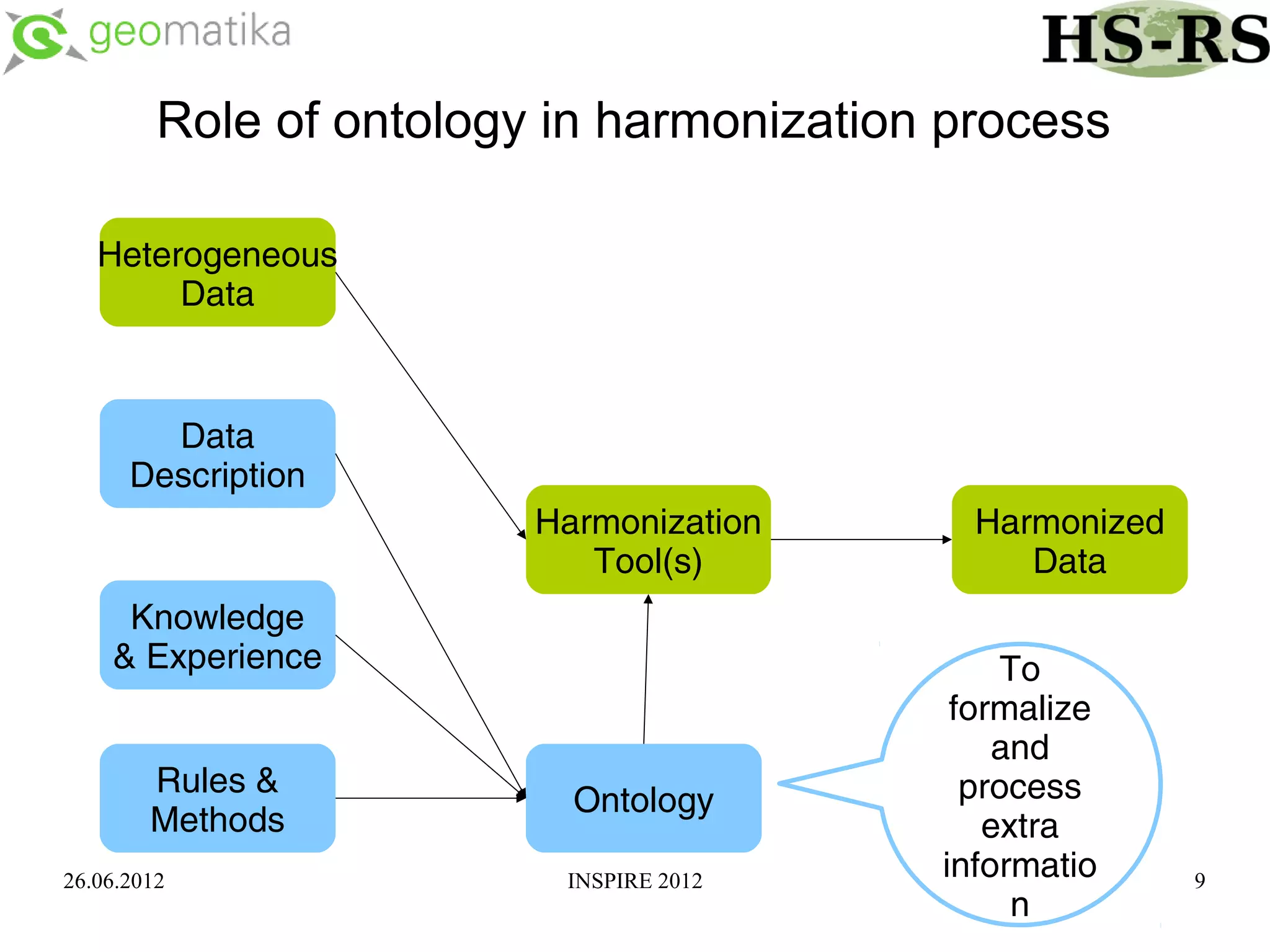
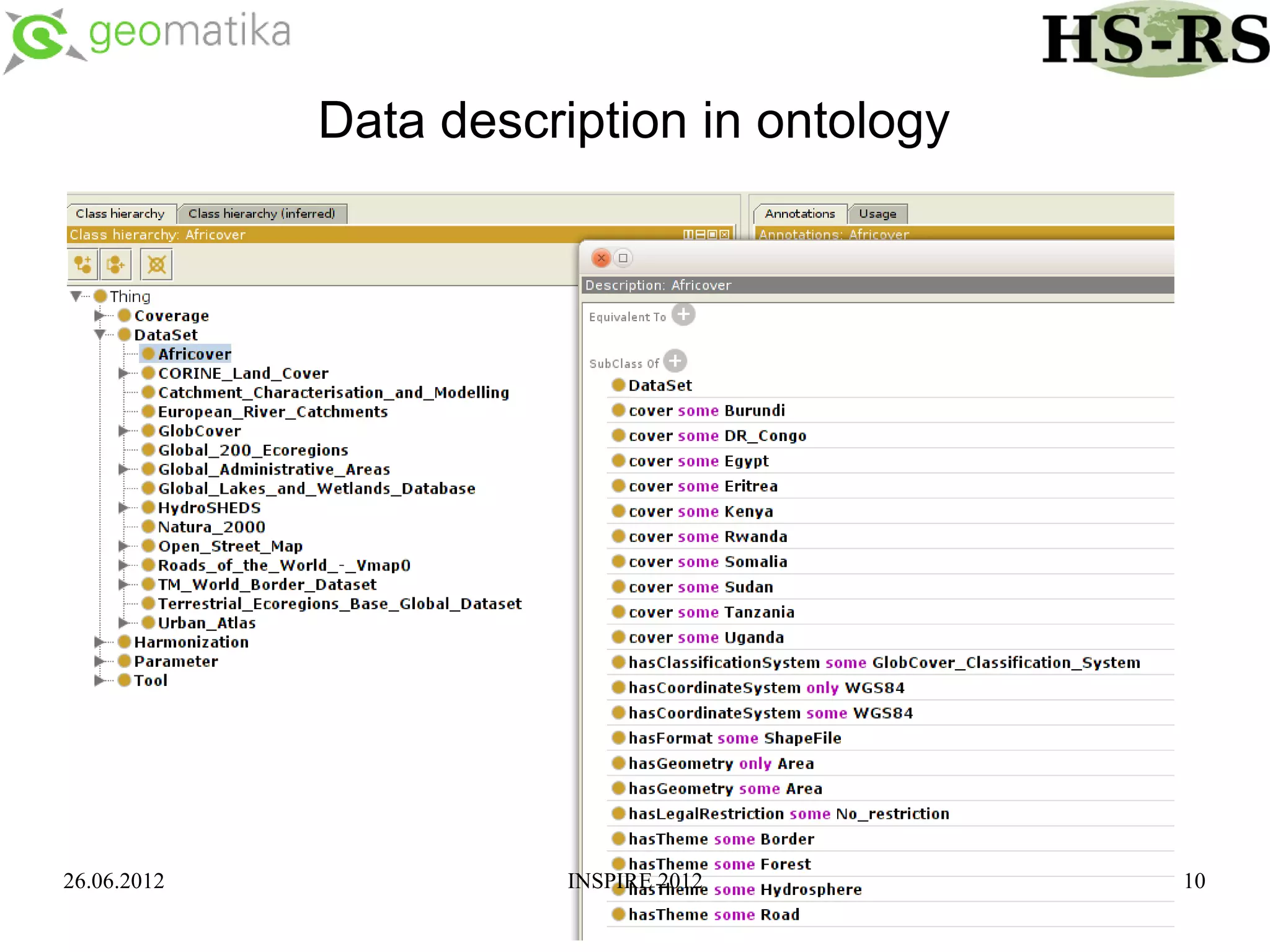
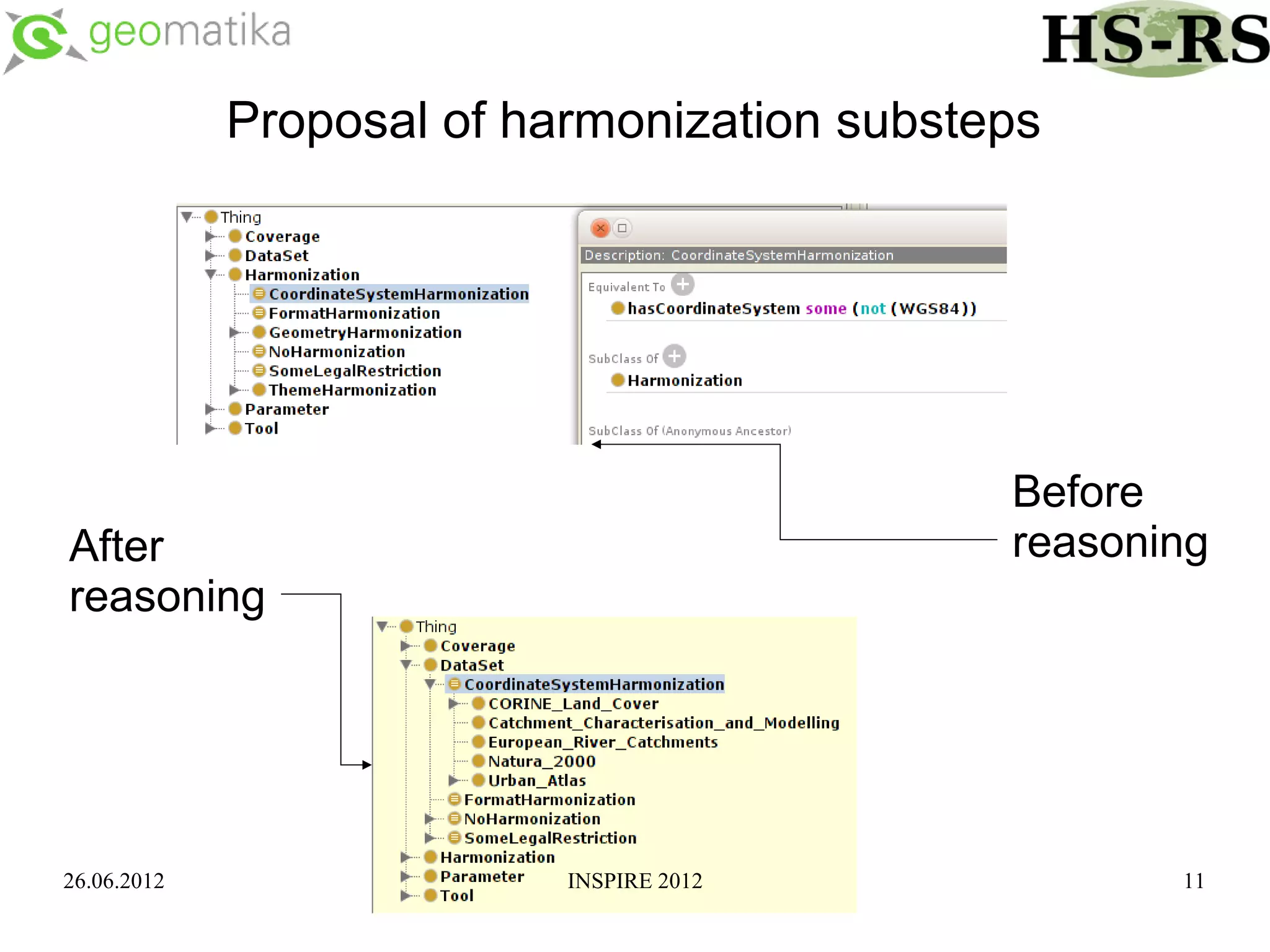
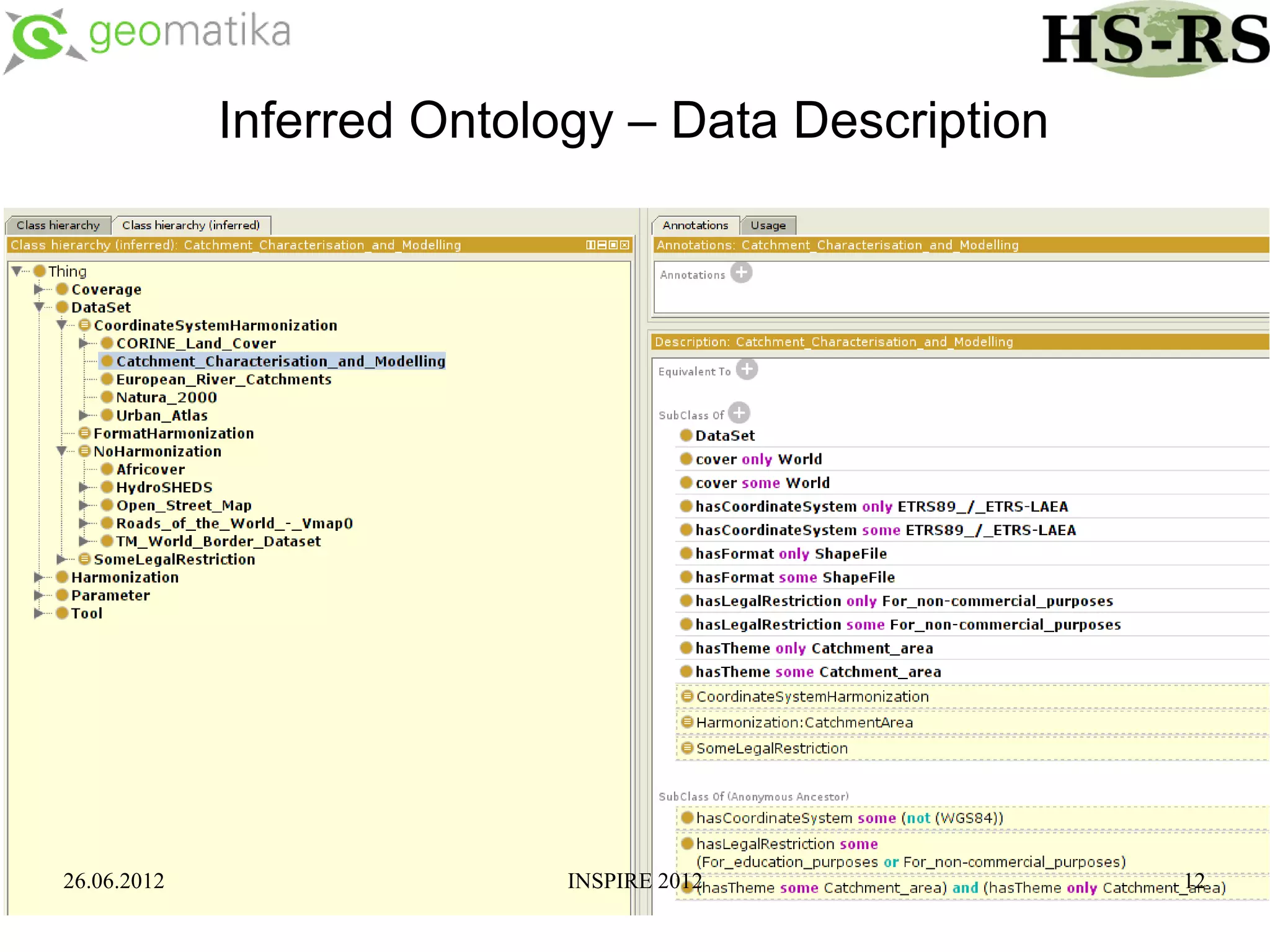
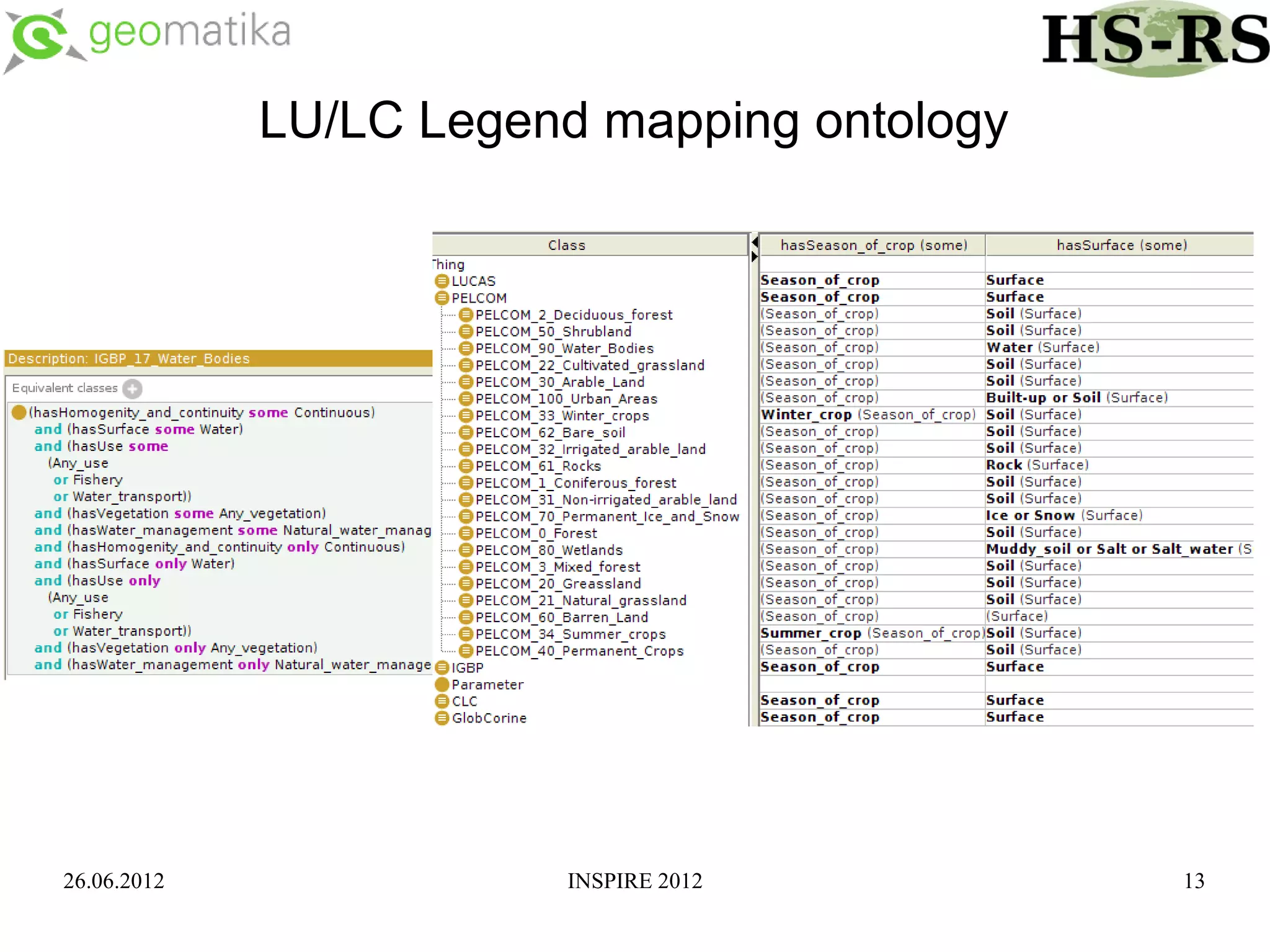
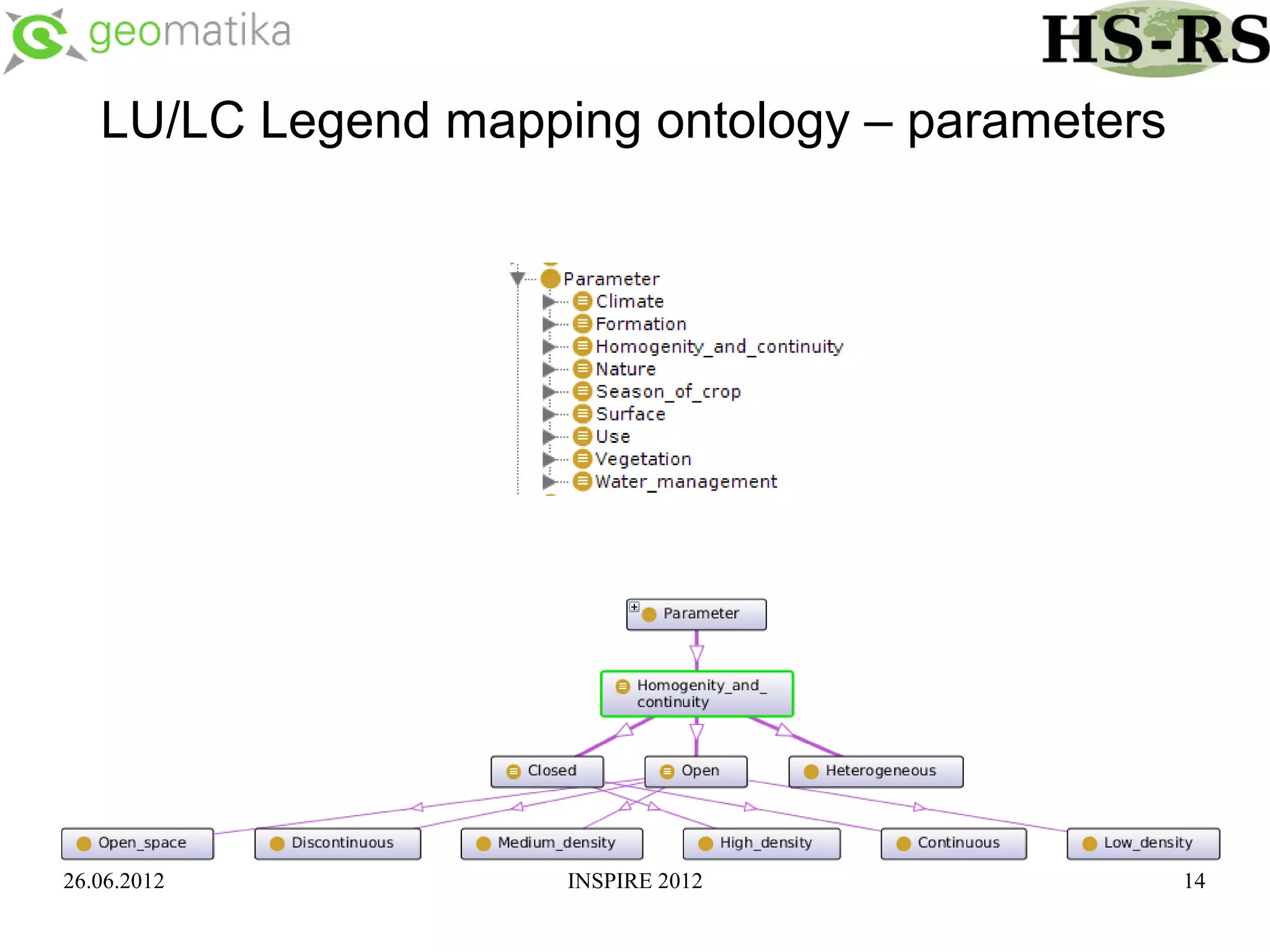
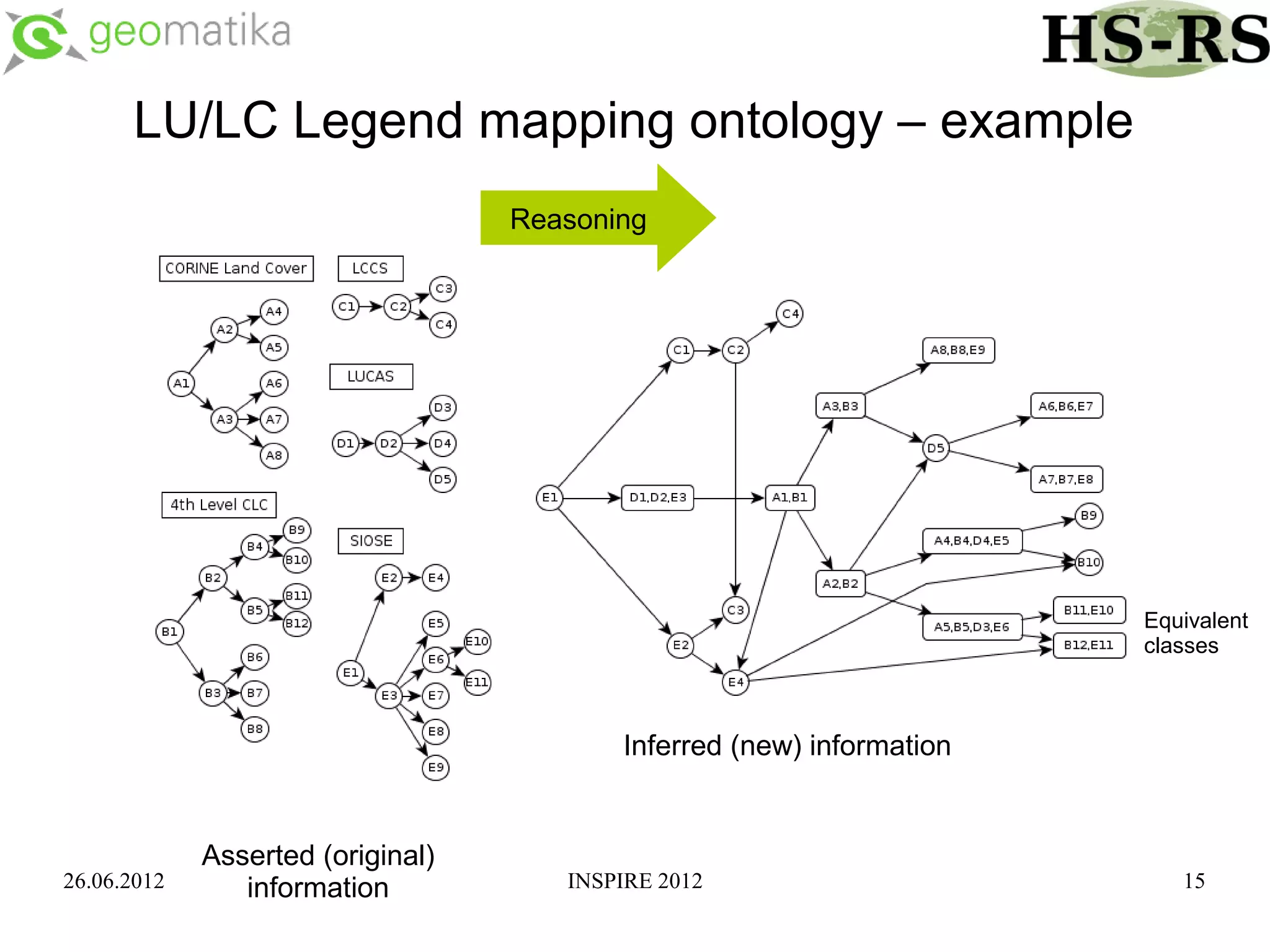
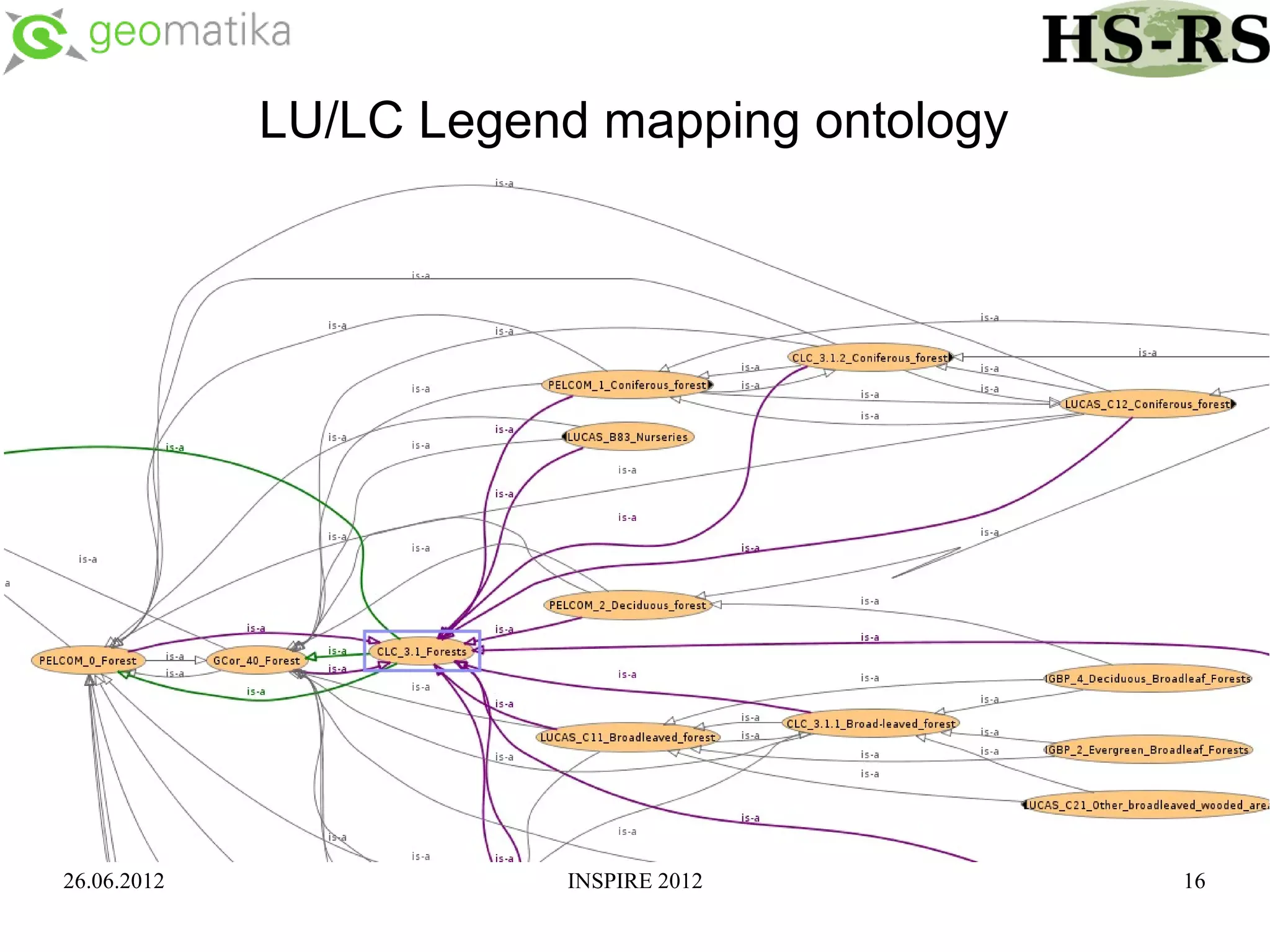
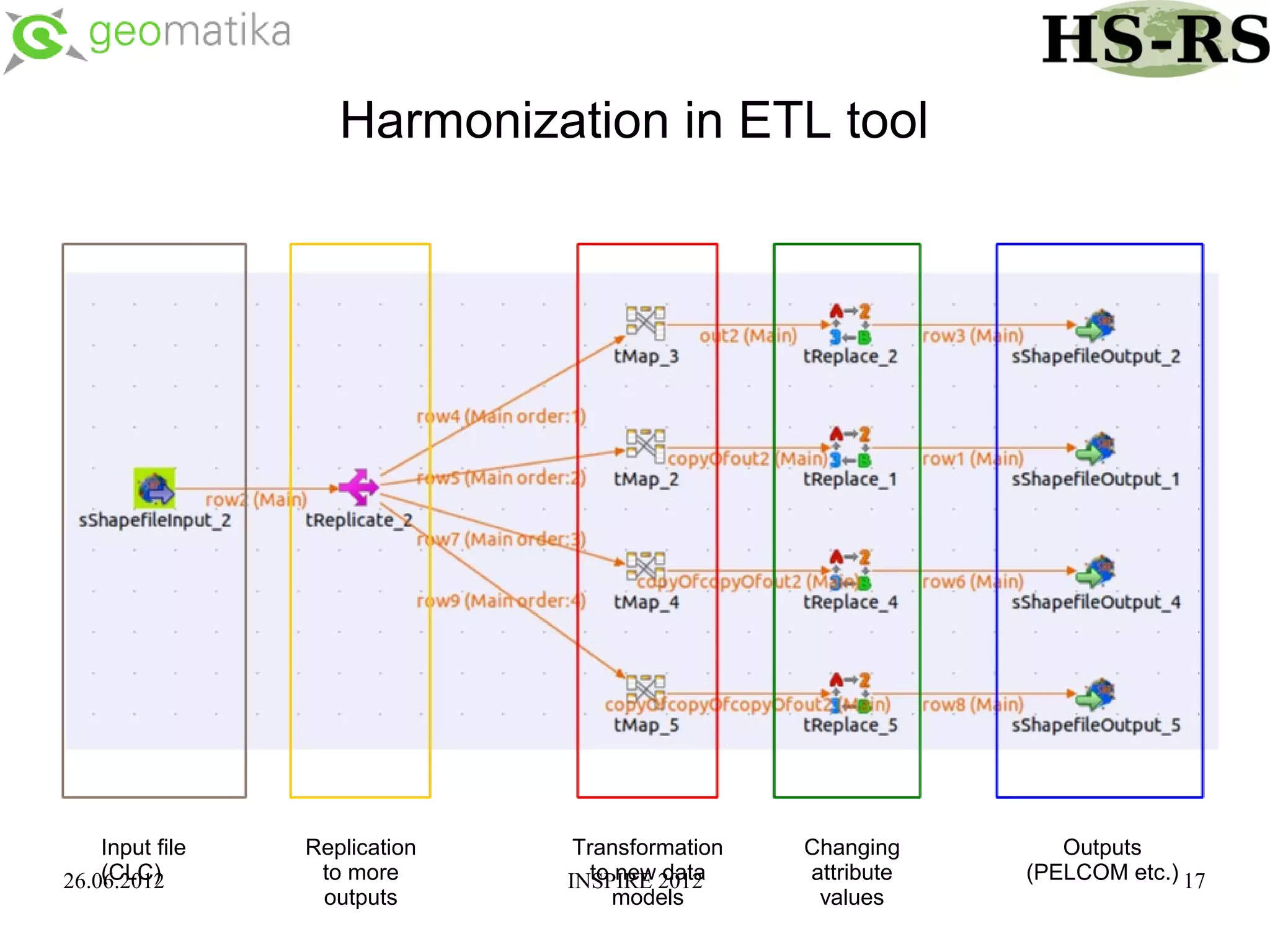
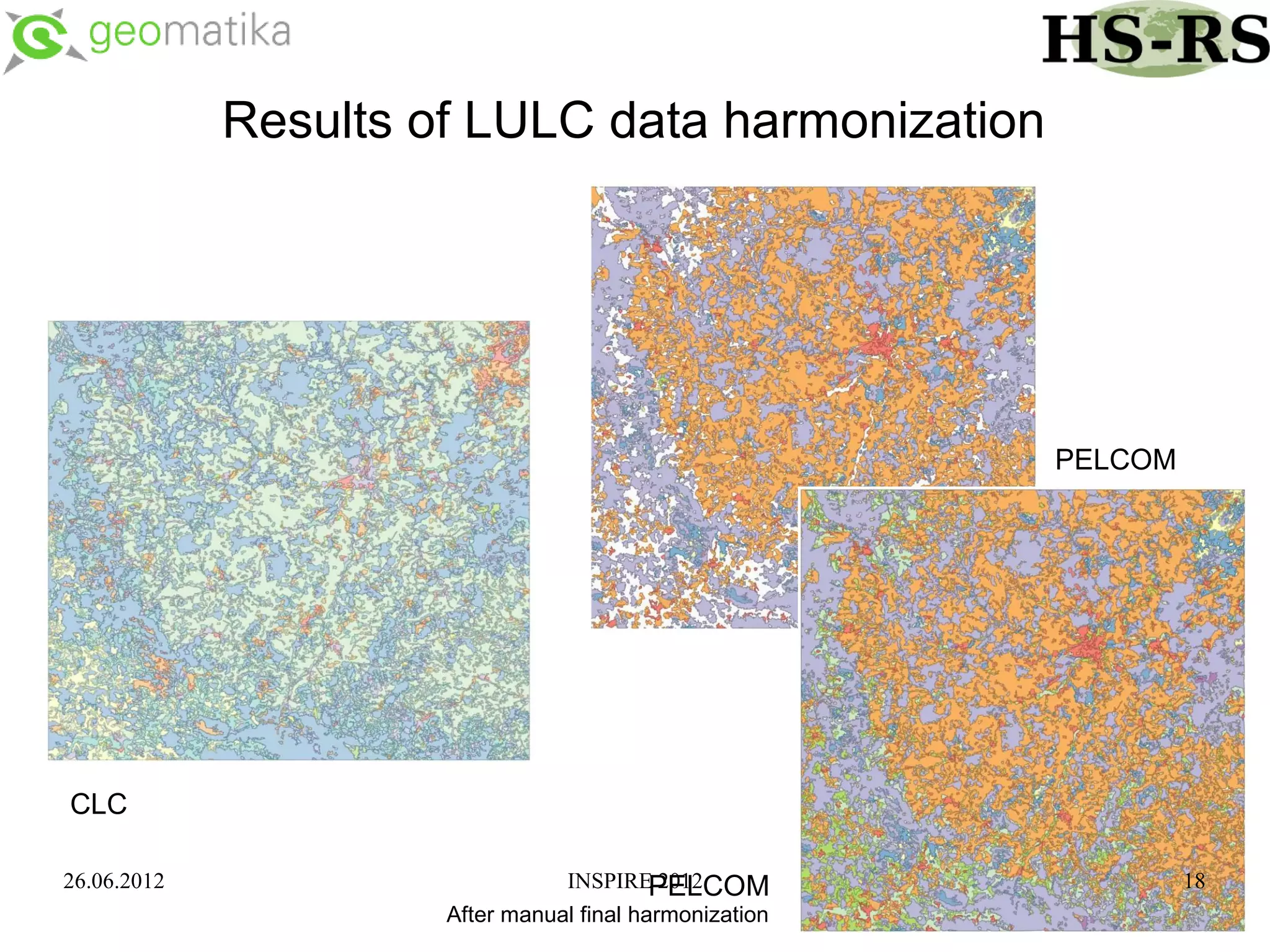
This document discusses using ontologies as the basis for spatial data harmonization. It defines spatial data harmonization as the process of eliminating heterogeneities in spatial data properties to support interoperability. An ontology provides a formal representation of concepts and their relationships in a domain that can be used to describe data and map between different classifications and legends. The document proposes using an ontology to formalize the knowledge and rules for harmonizing land use/land cover data from different sources through an extraction, transformation, and loading tool.