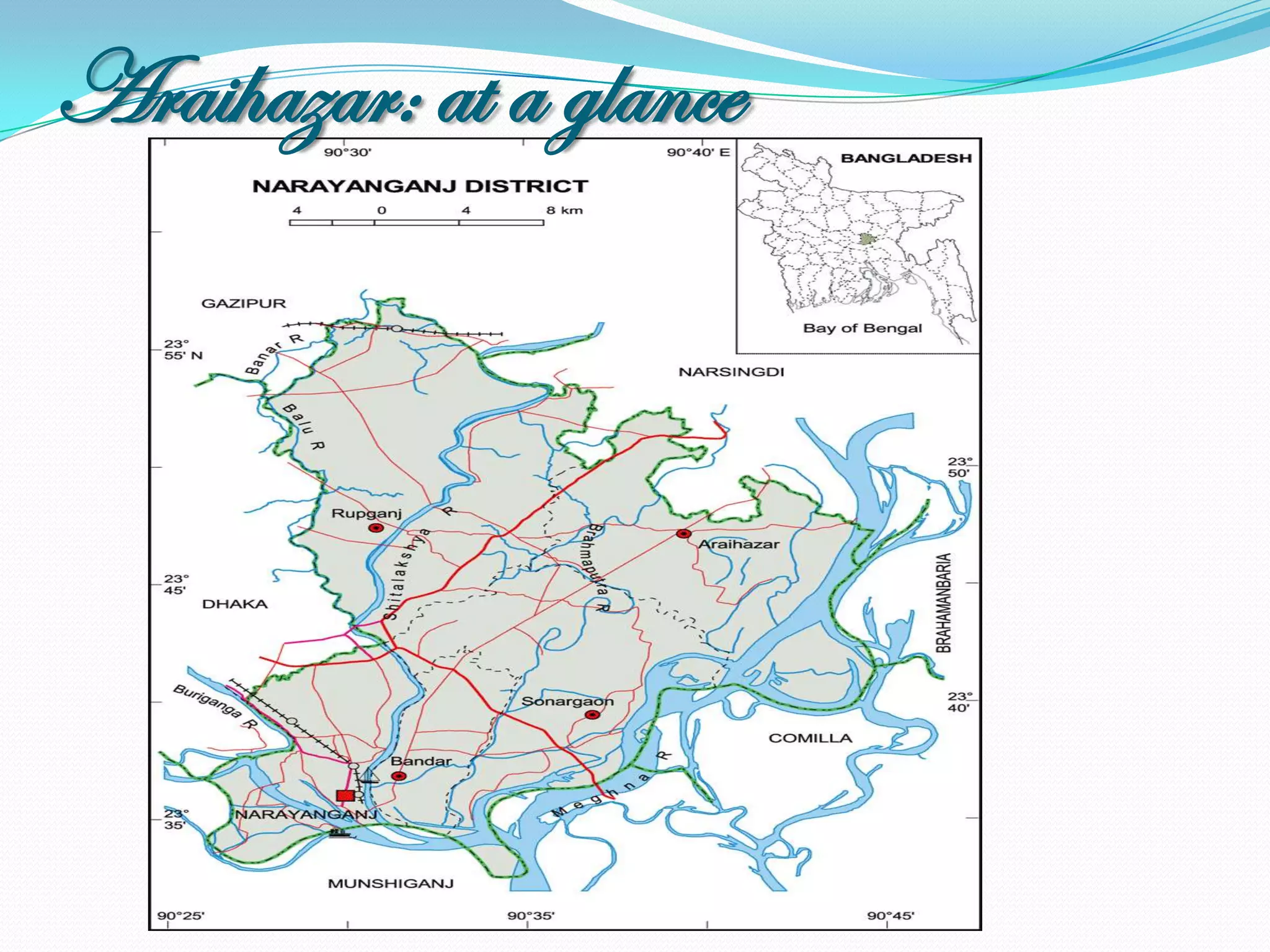
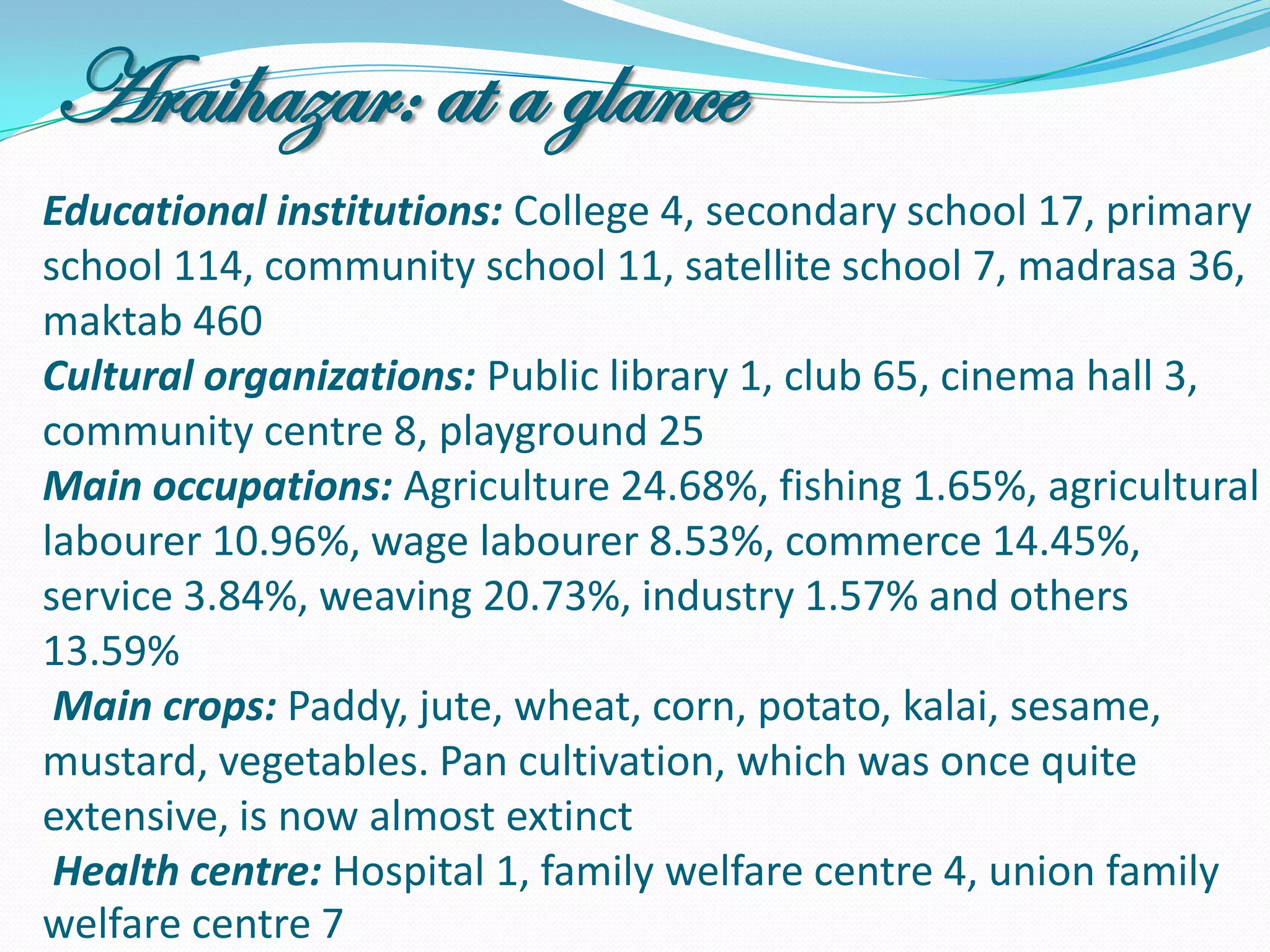
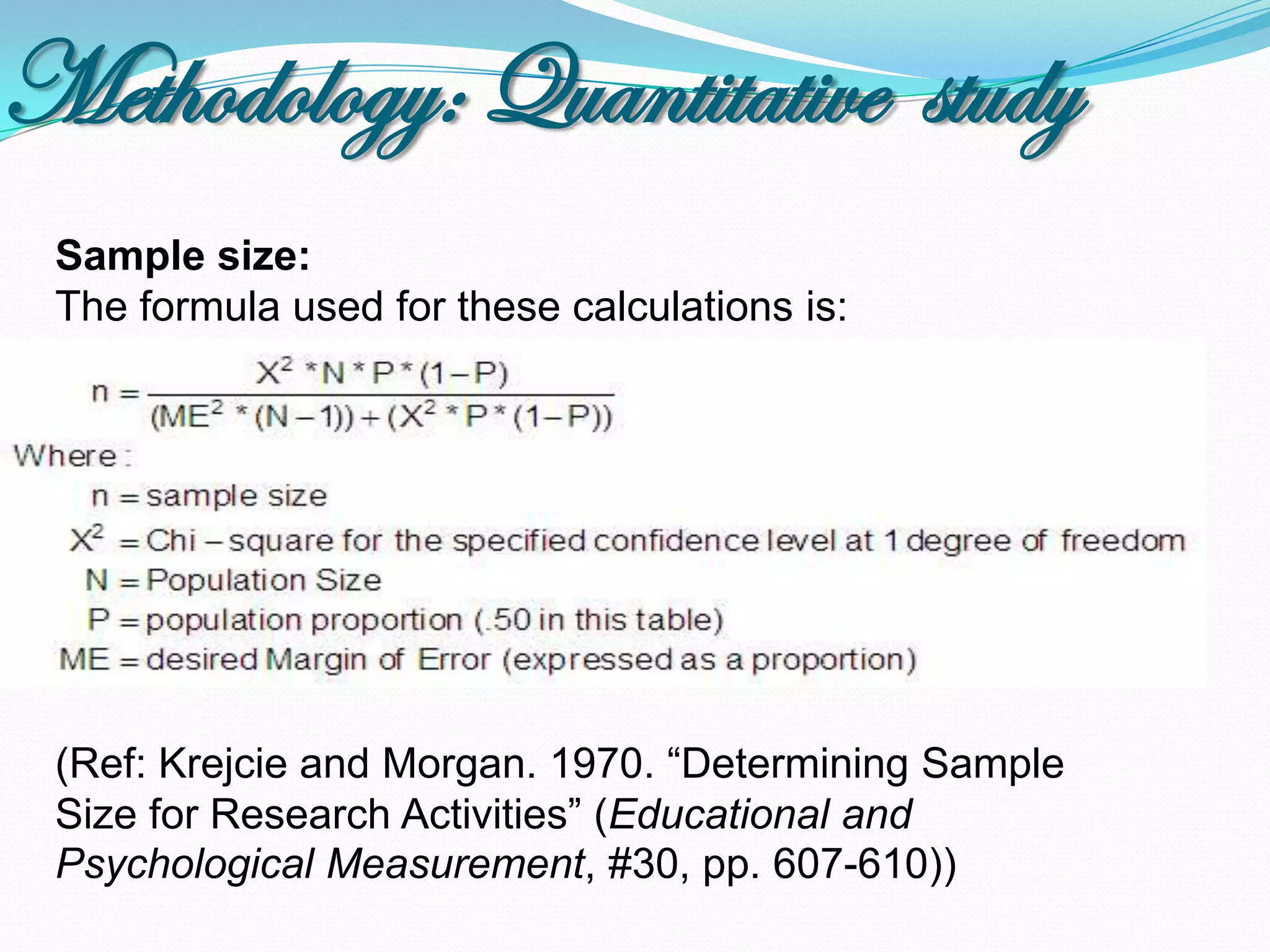
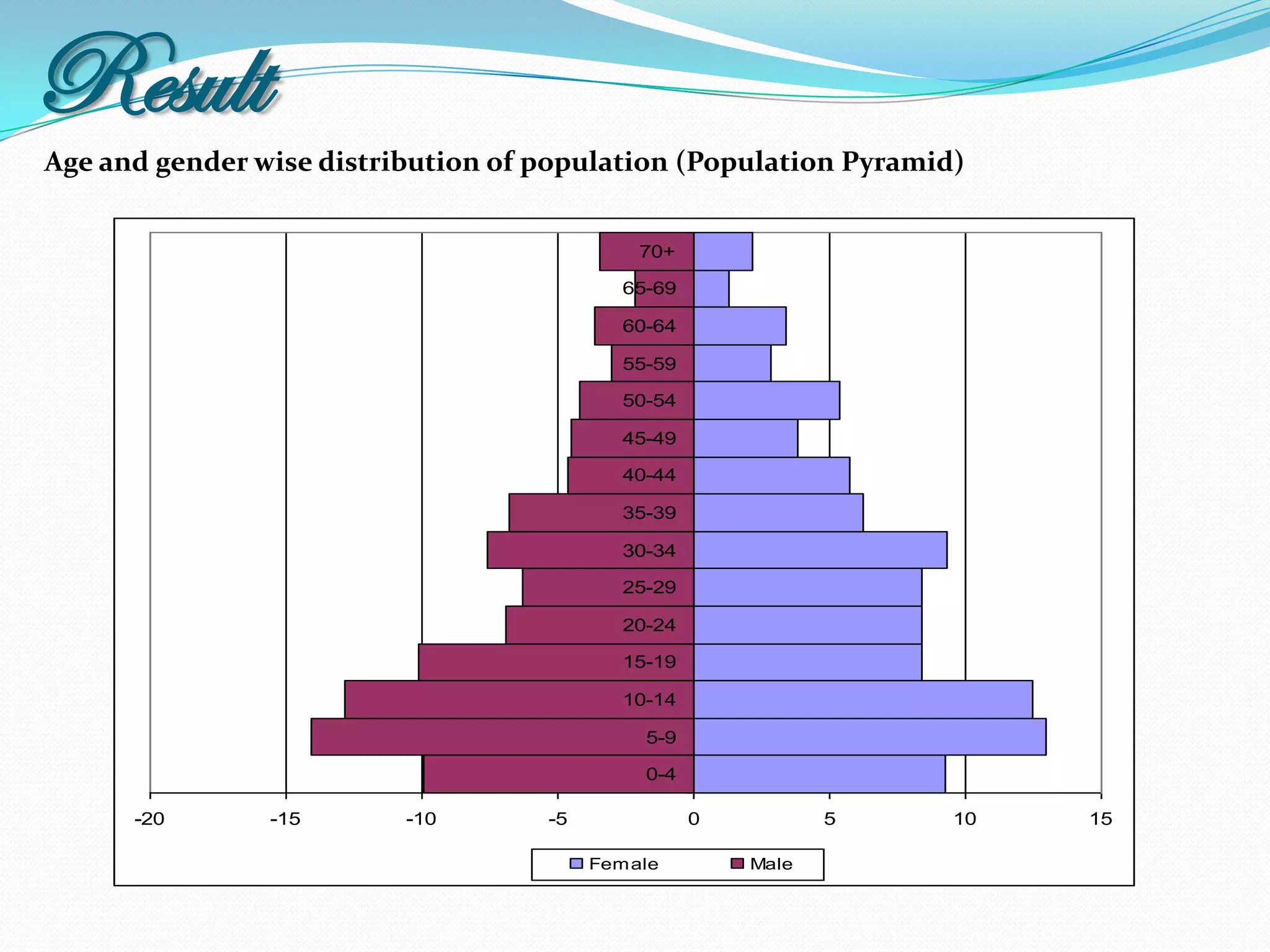
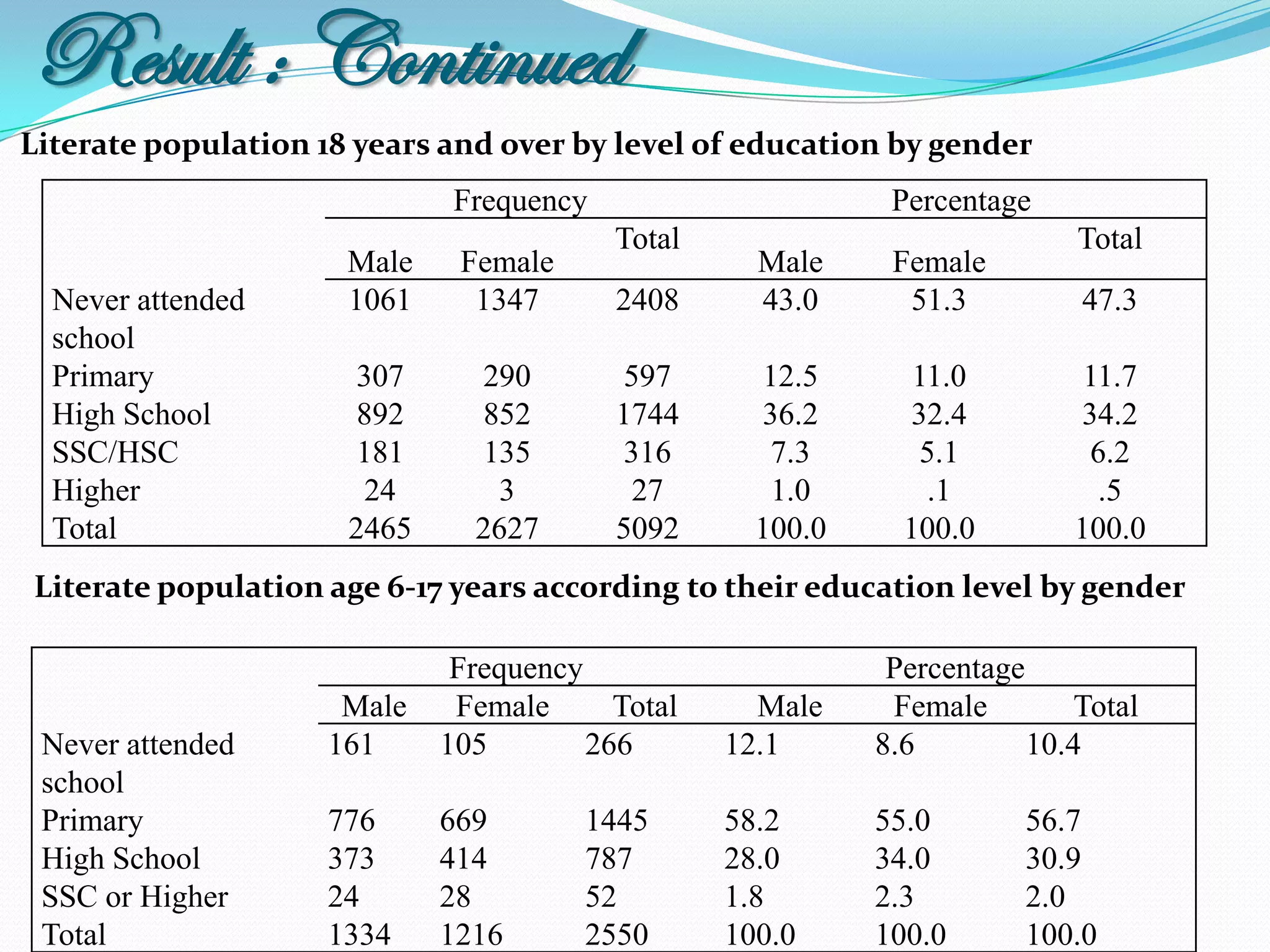
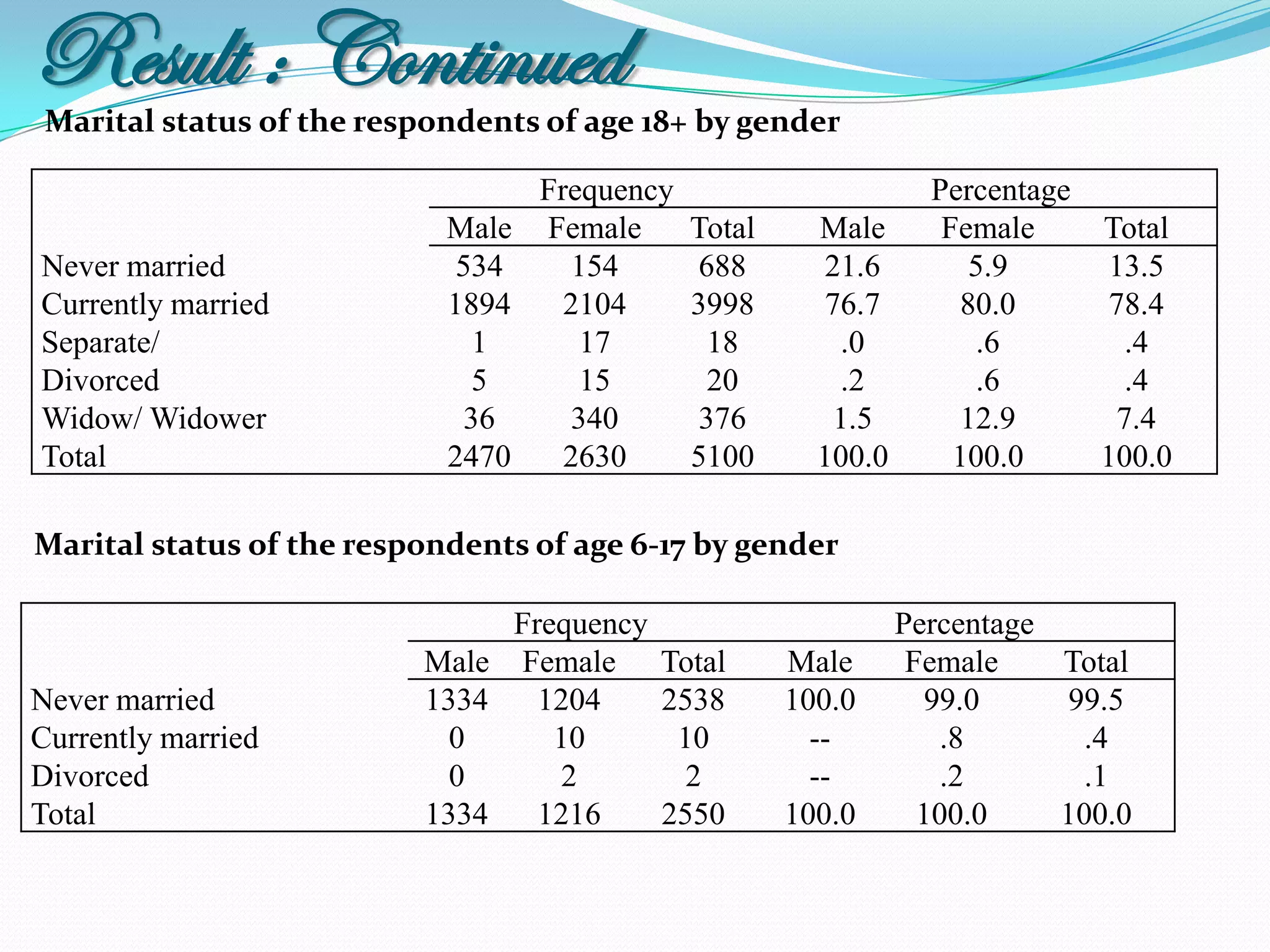
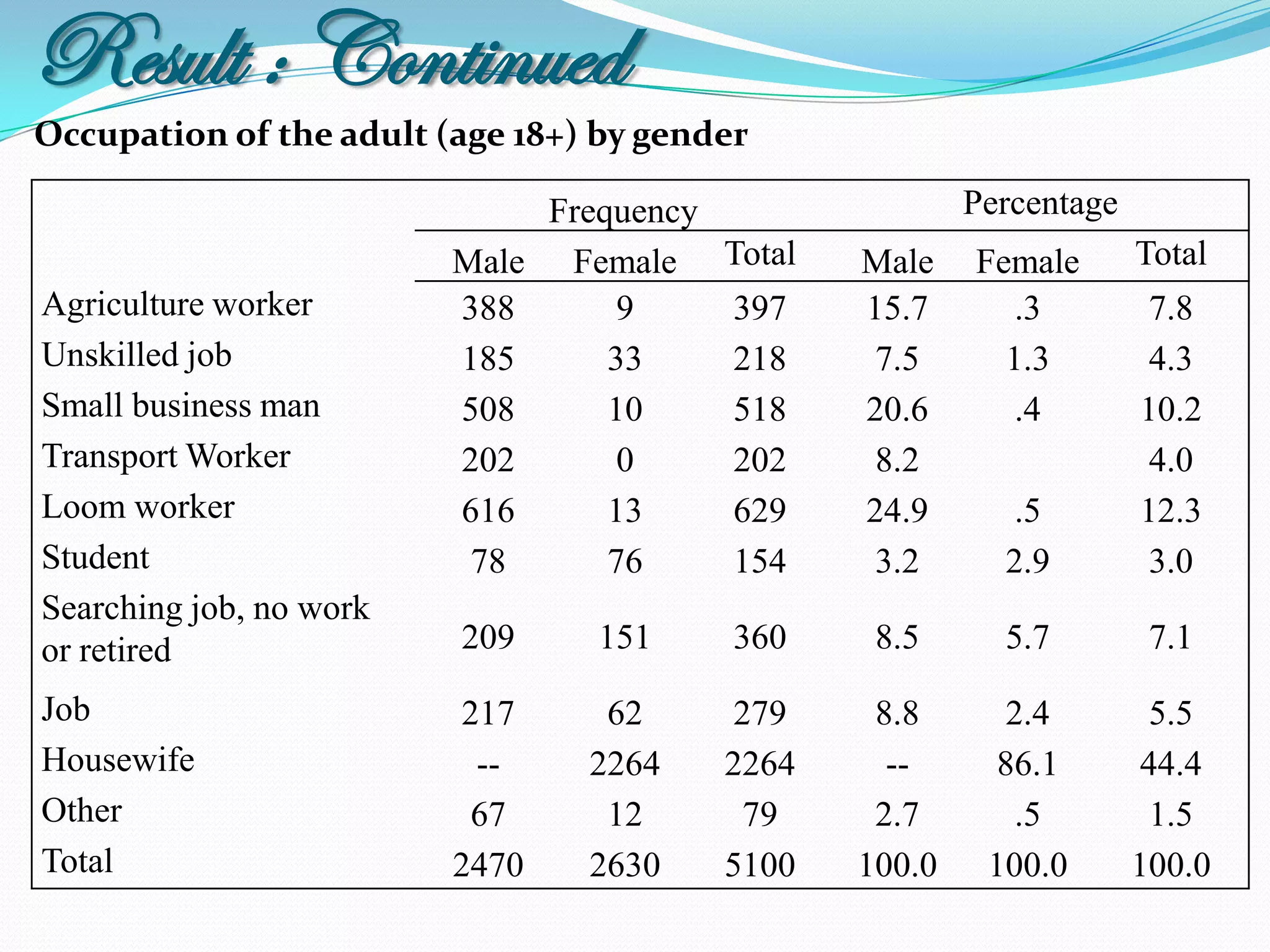
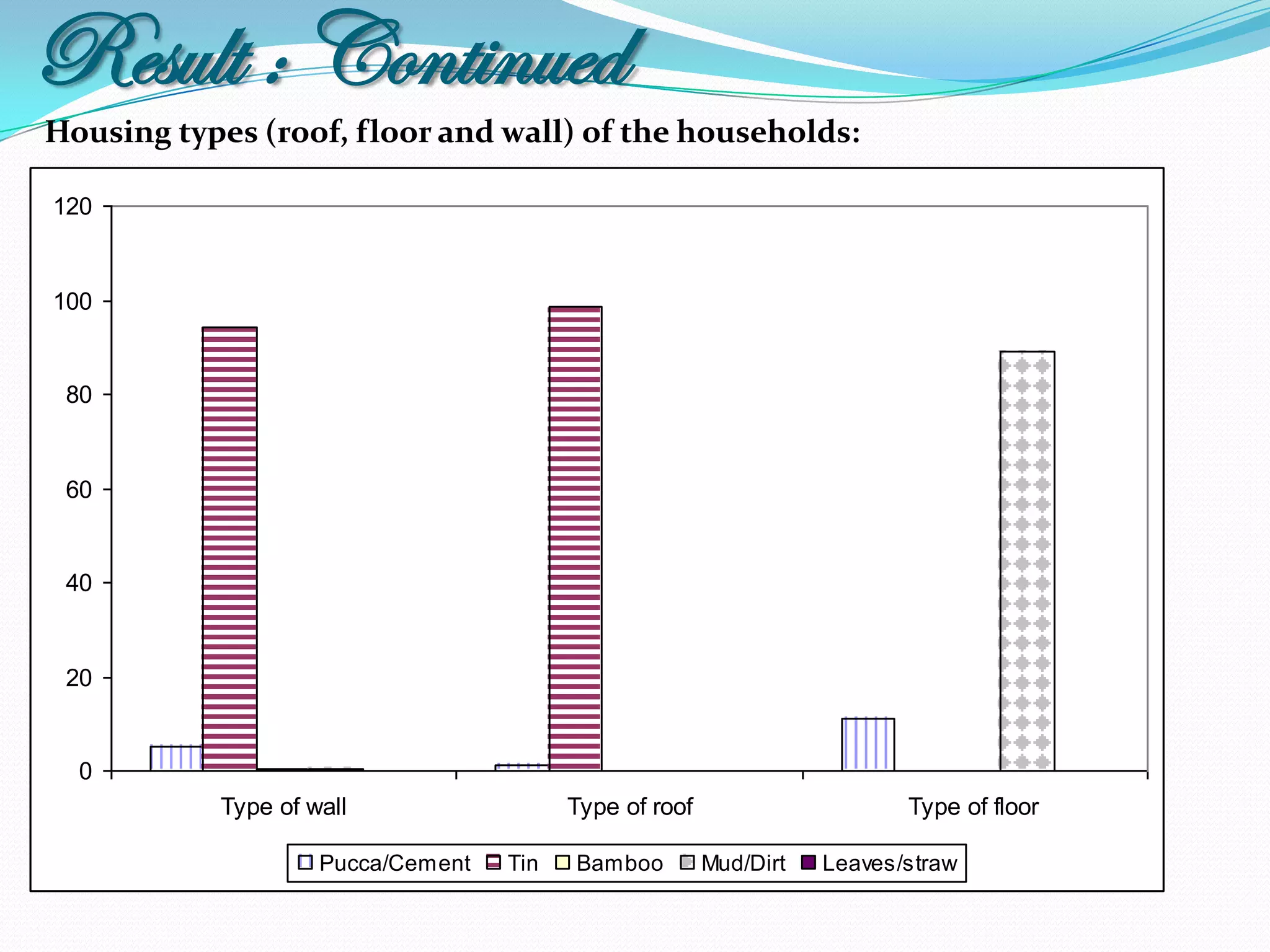
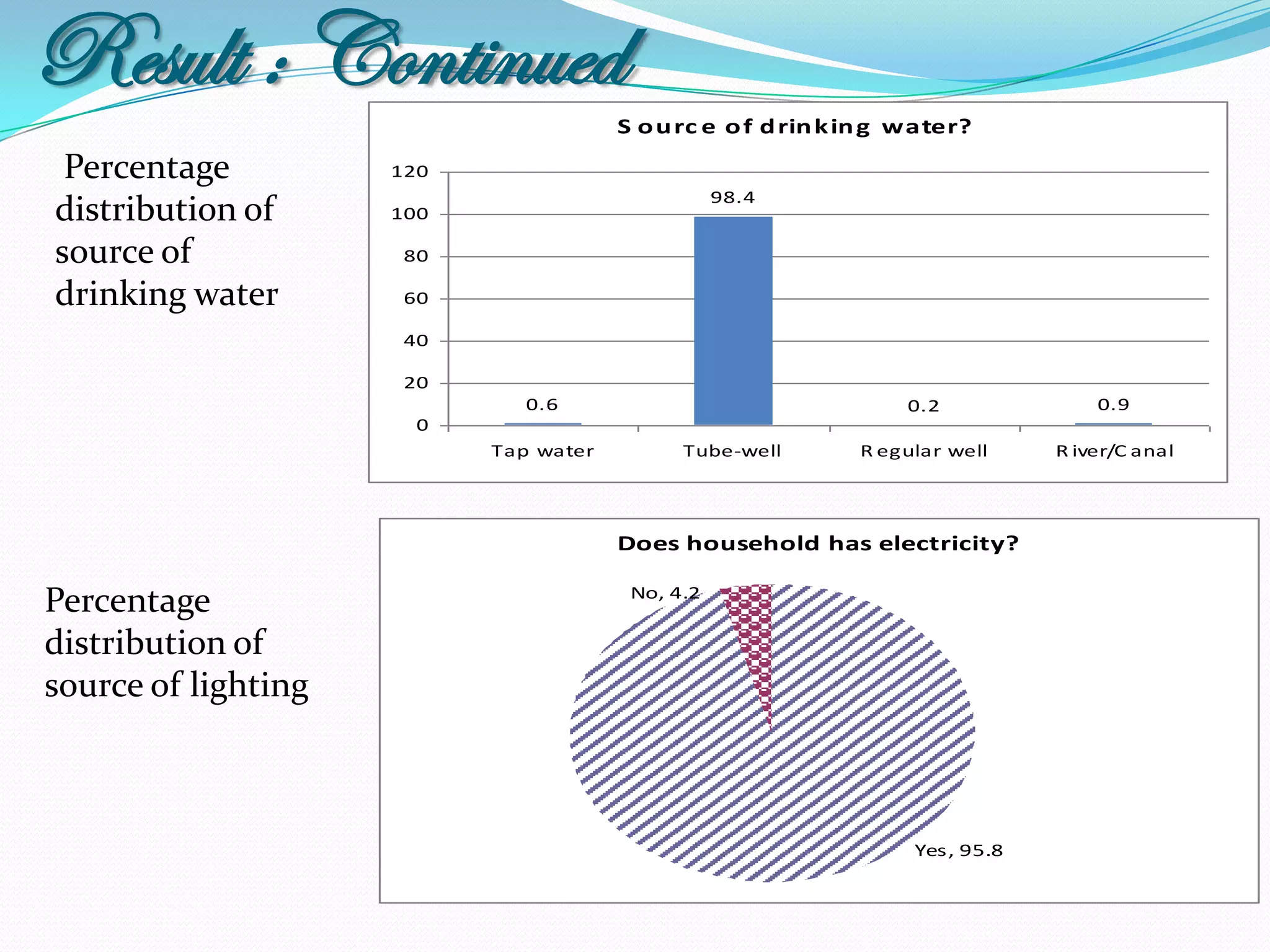
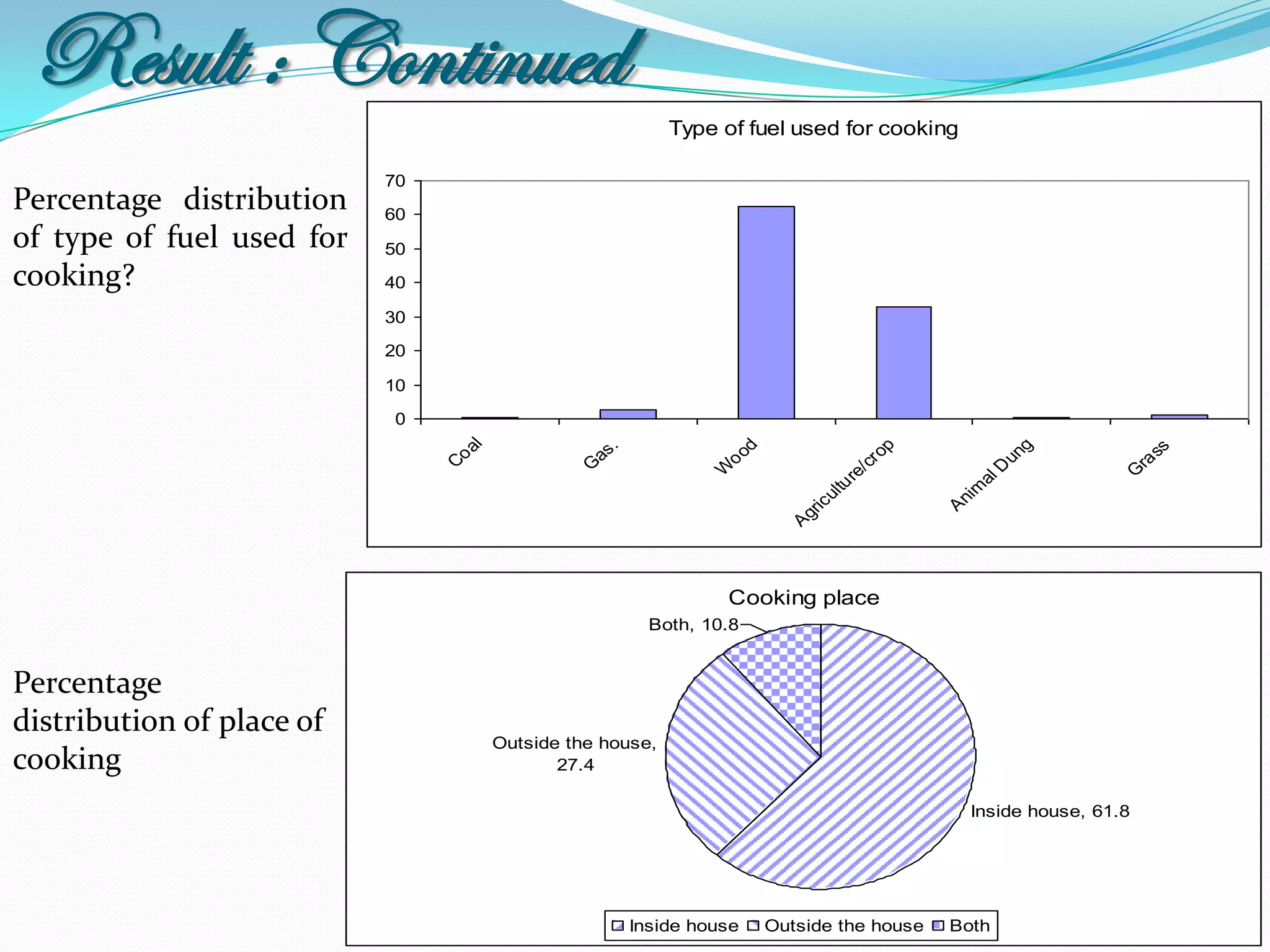
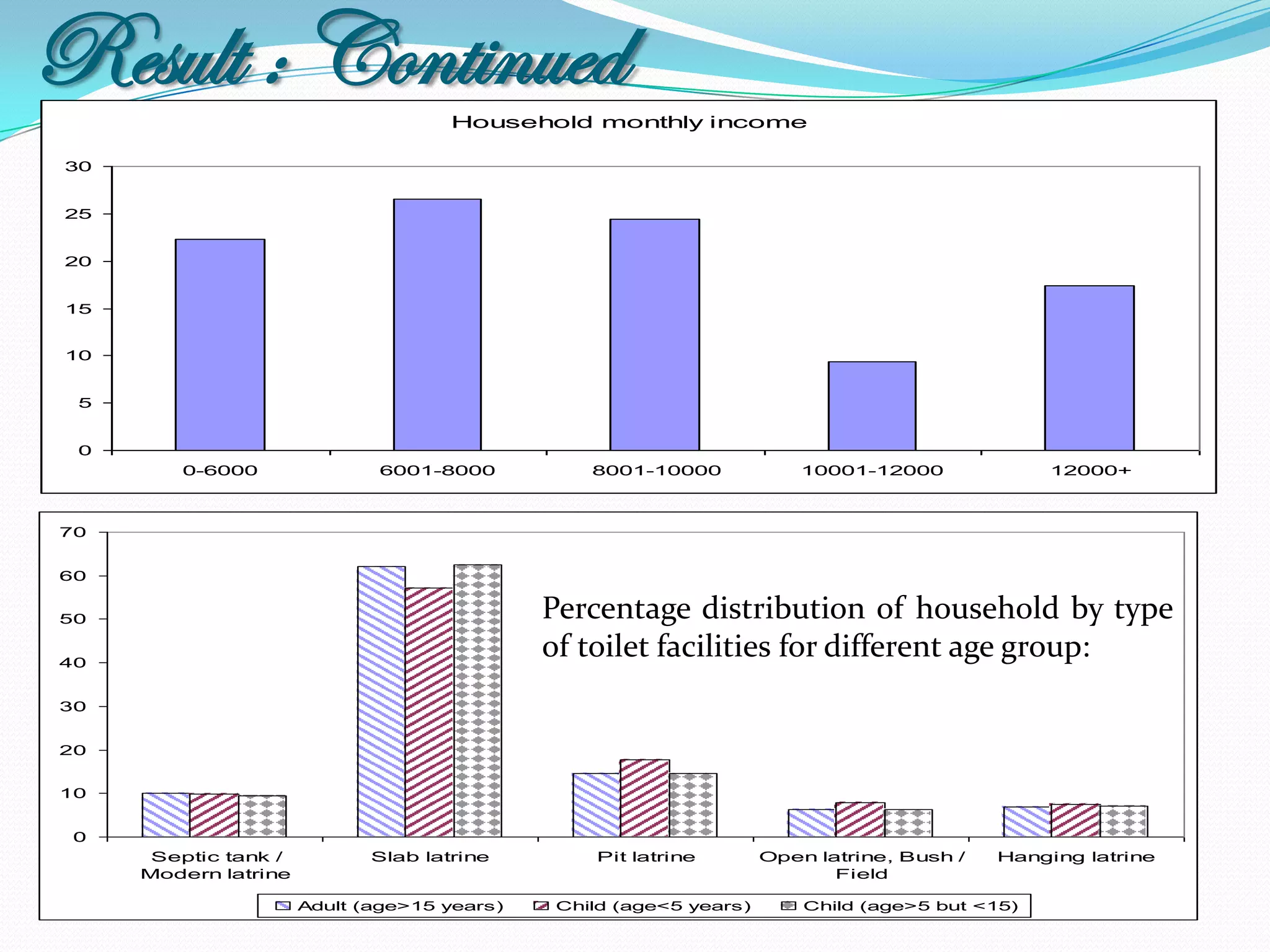
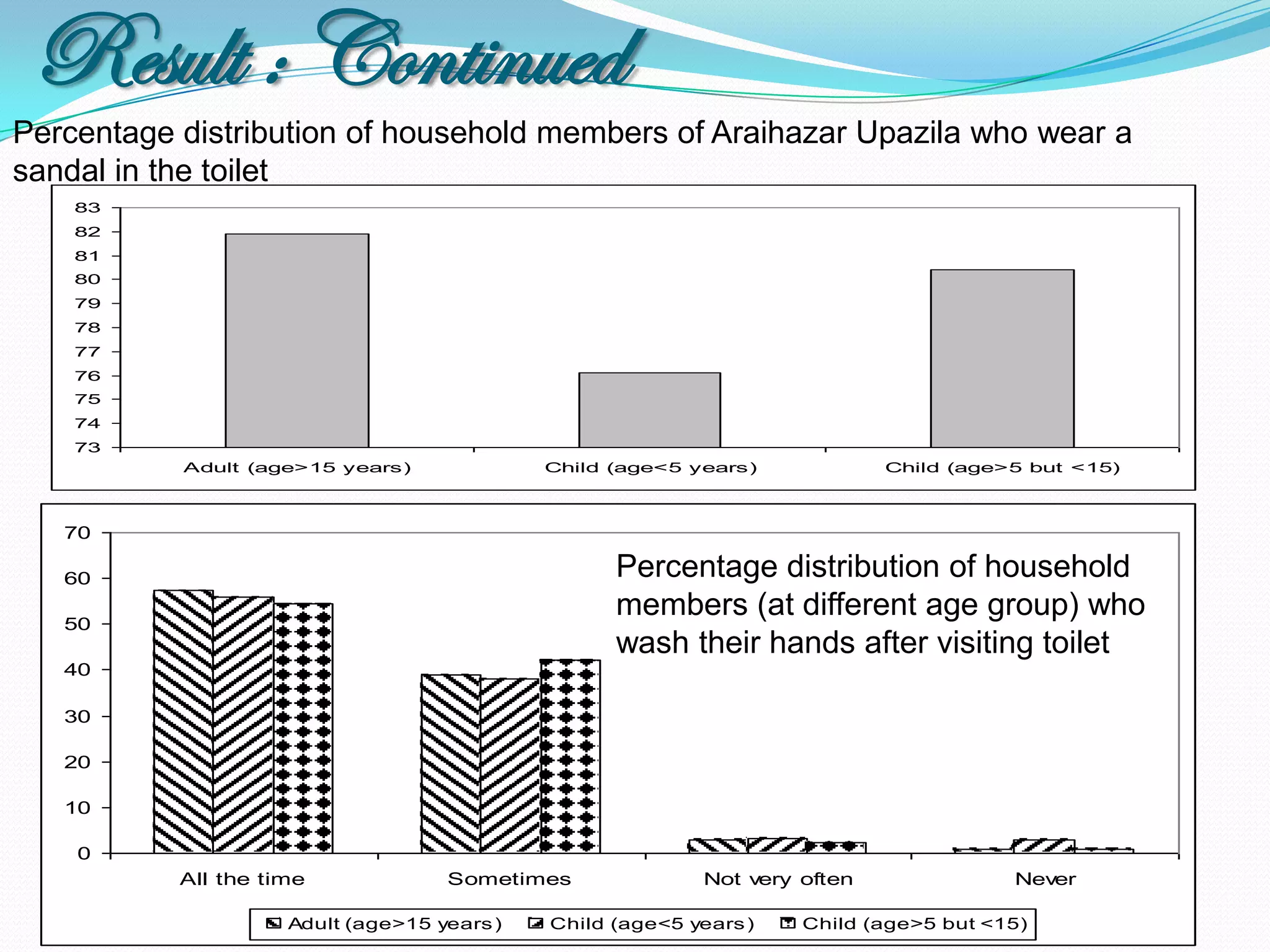
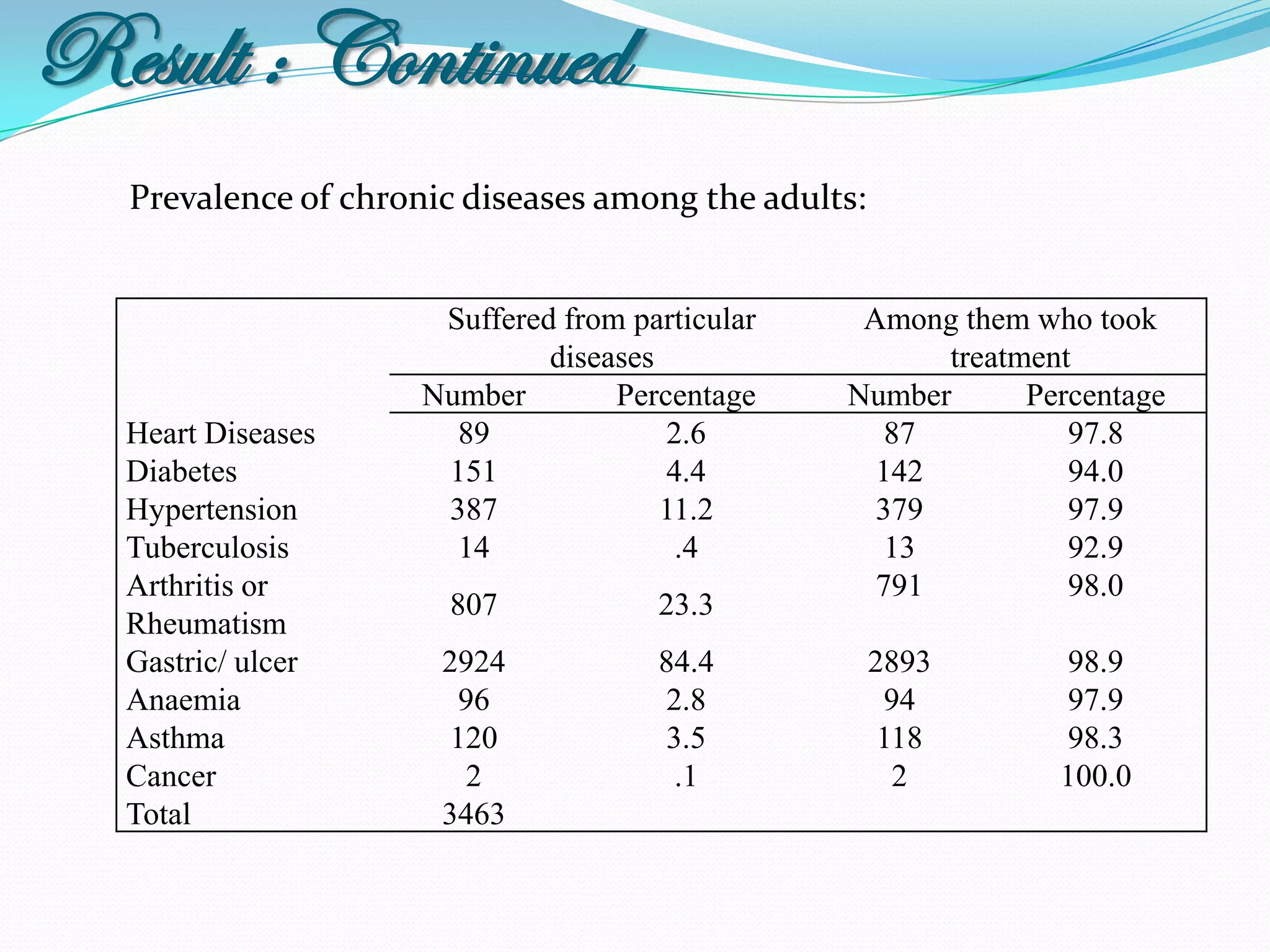
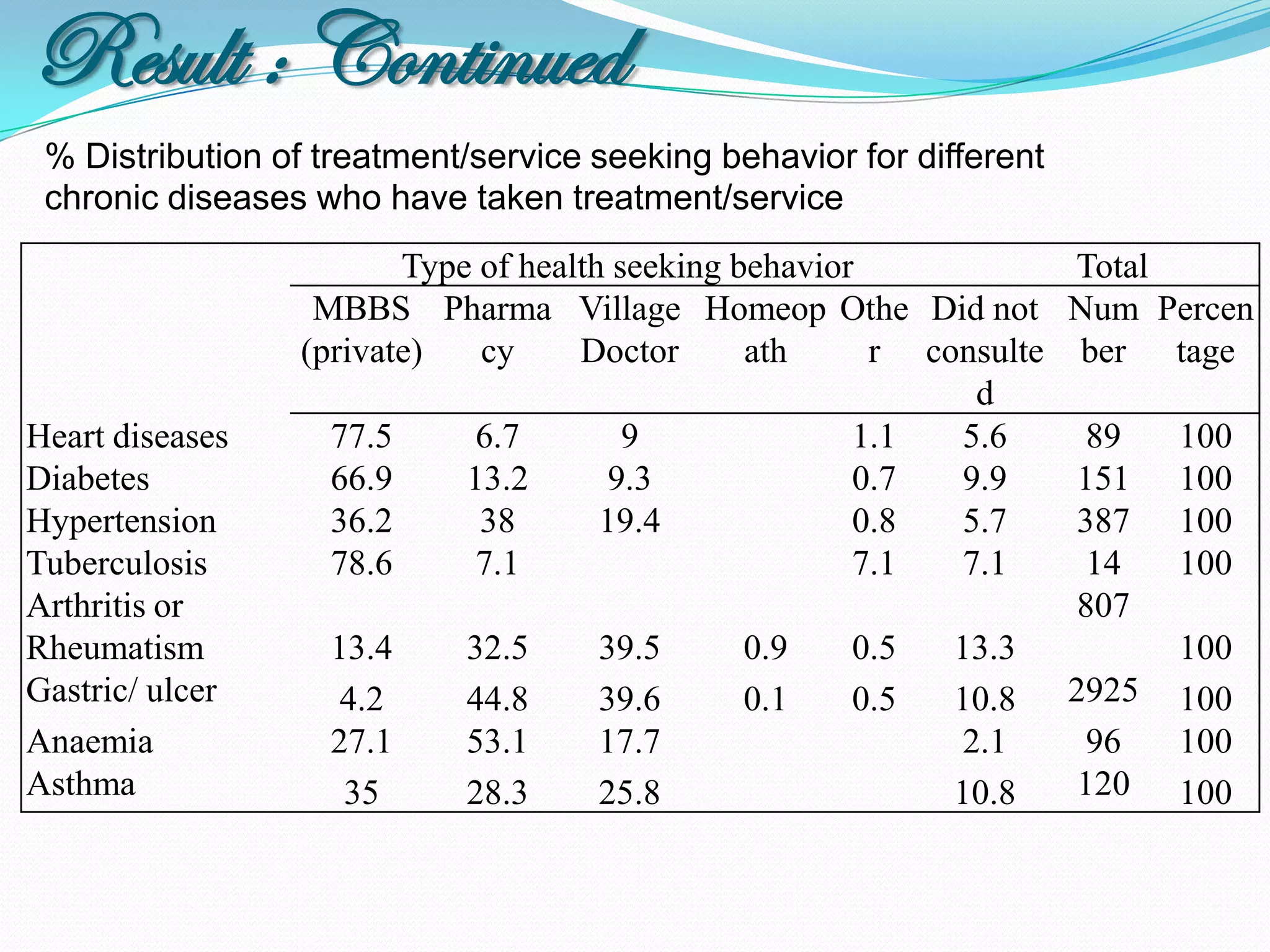
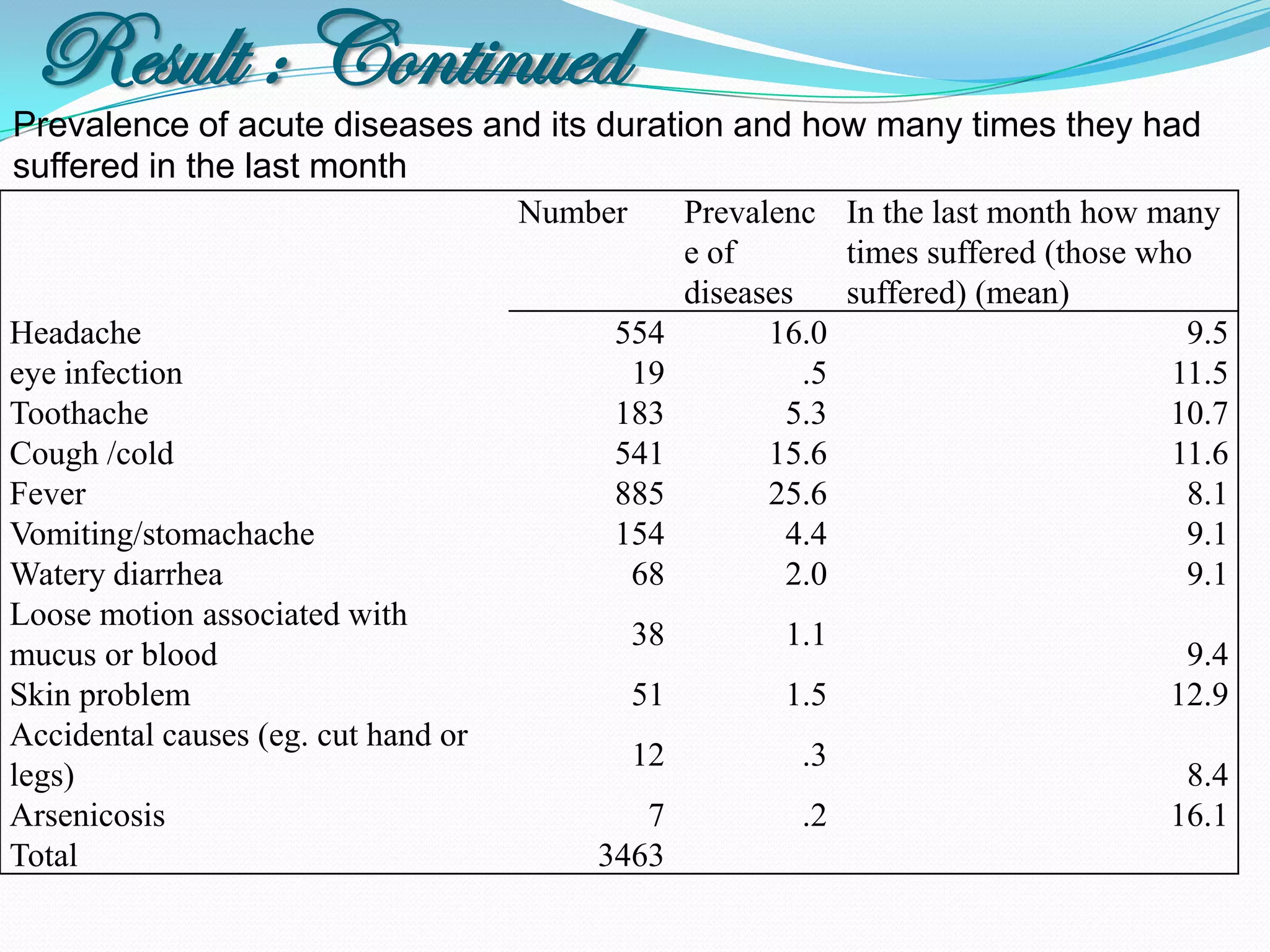
The document outlines a study in Araihazar, Bangladesh, focusing on the socio-economic and health impacts of industrial pollution due to rapid industrialization and urbanization, highlighting issues such as untreated industrial waste and its detrimental effects on local water sources and human health. Findings indicate a high awareness among the population regarding pollution but poor practices in waste management and environmental care. Recommendations include stricter regulations for industries and active involvement of industry owners in raising awareness about pollution and health.