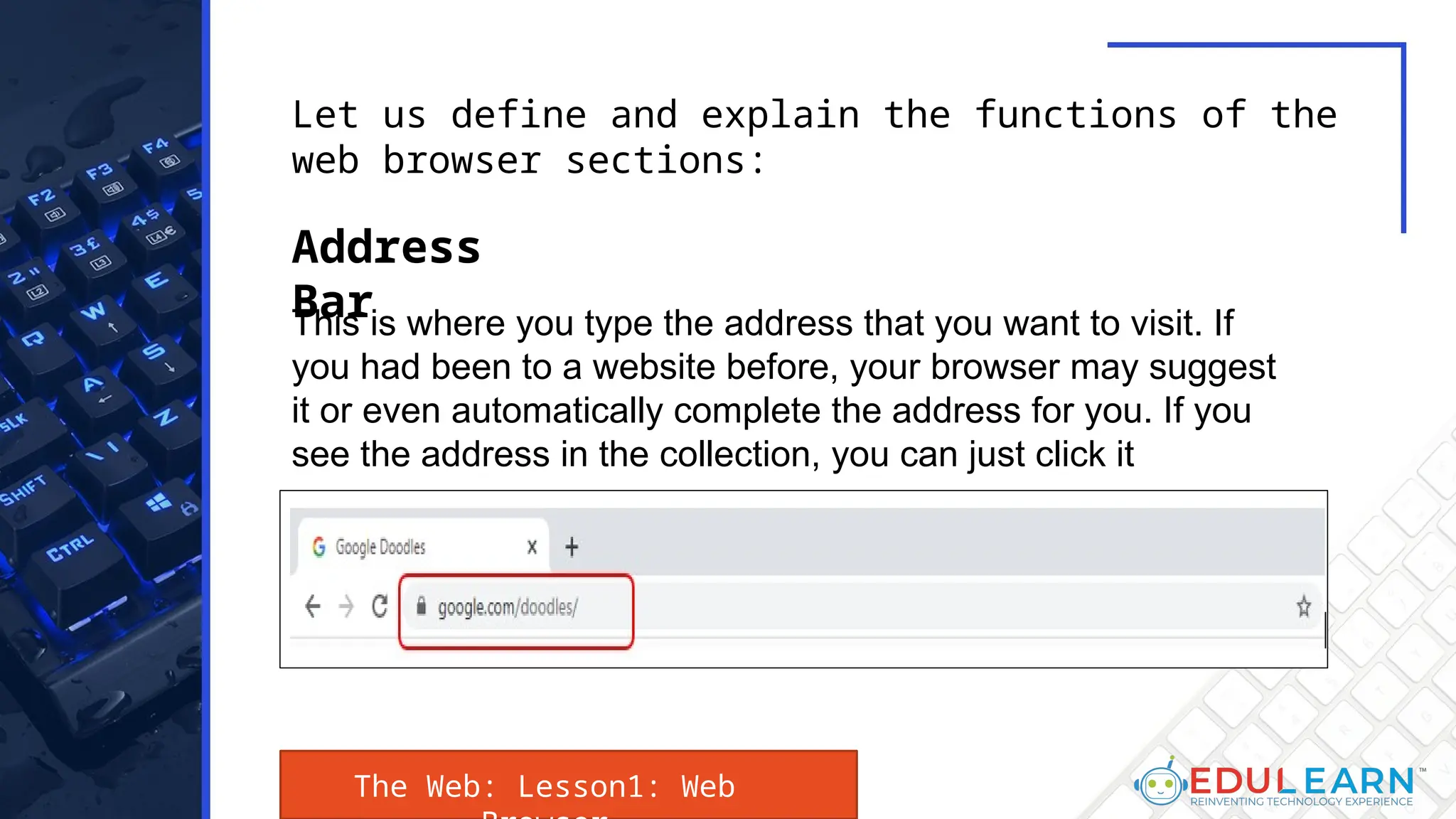
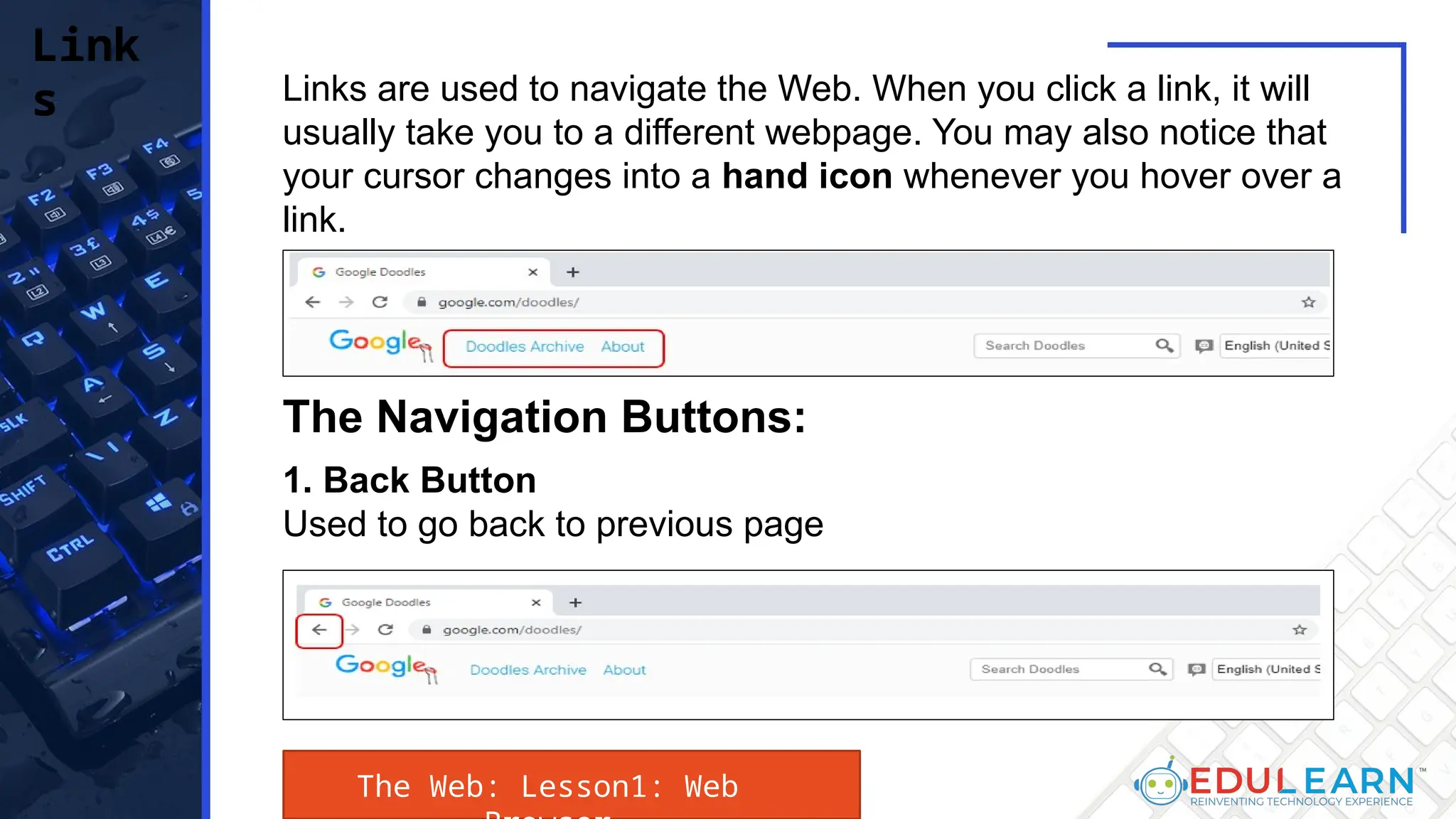
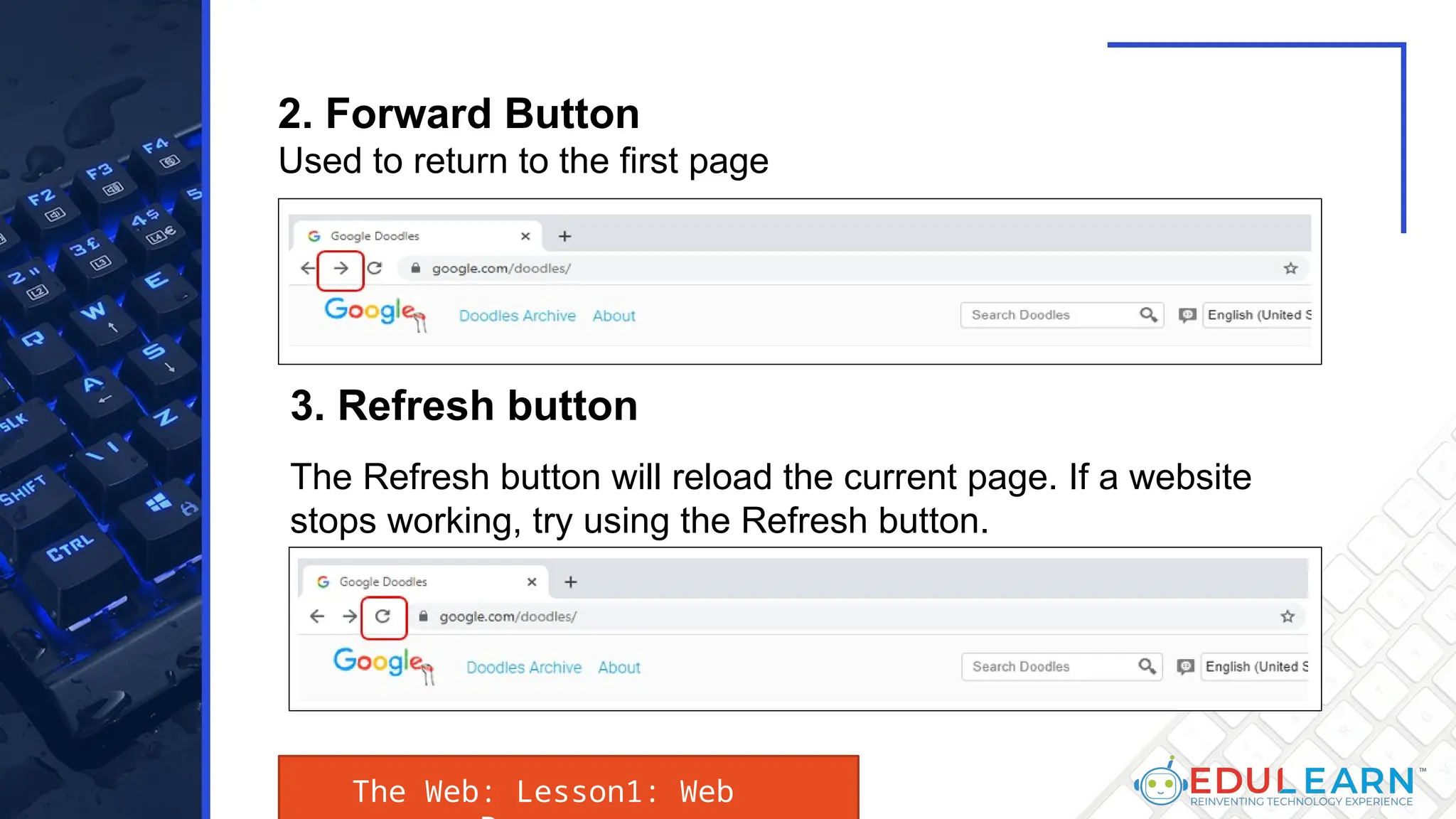
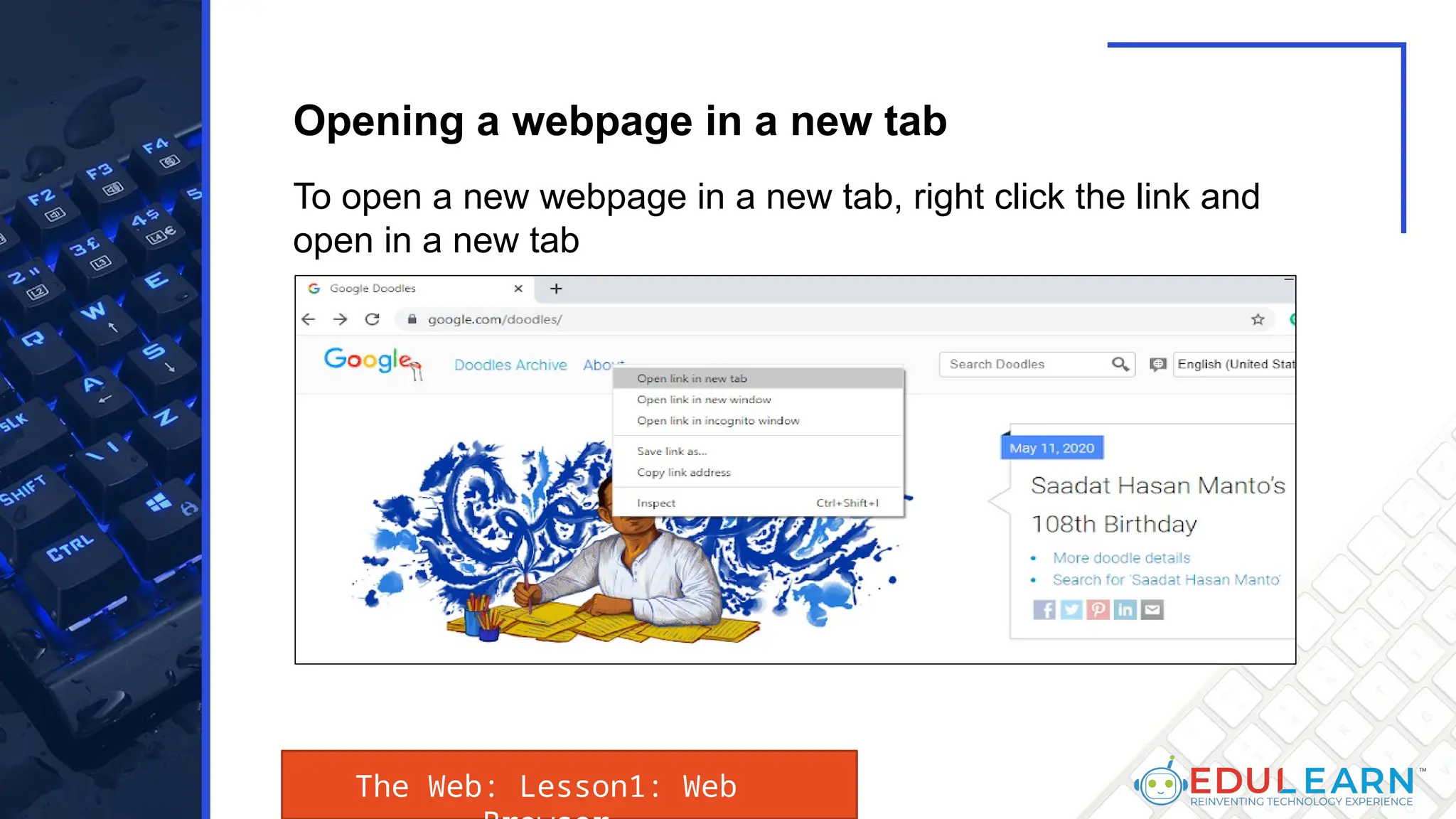
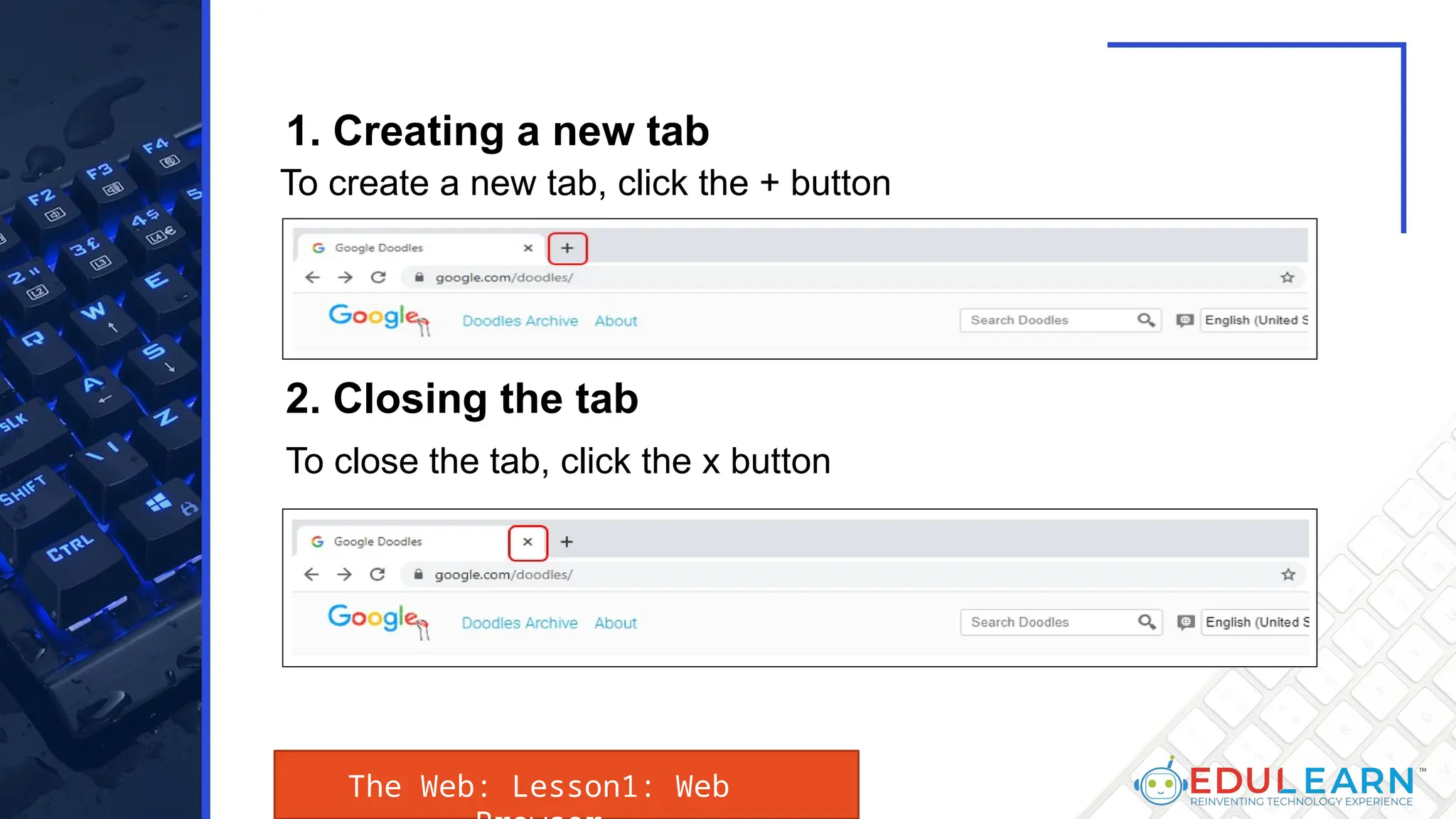
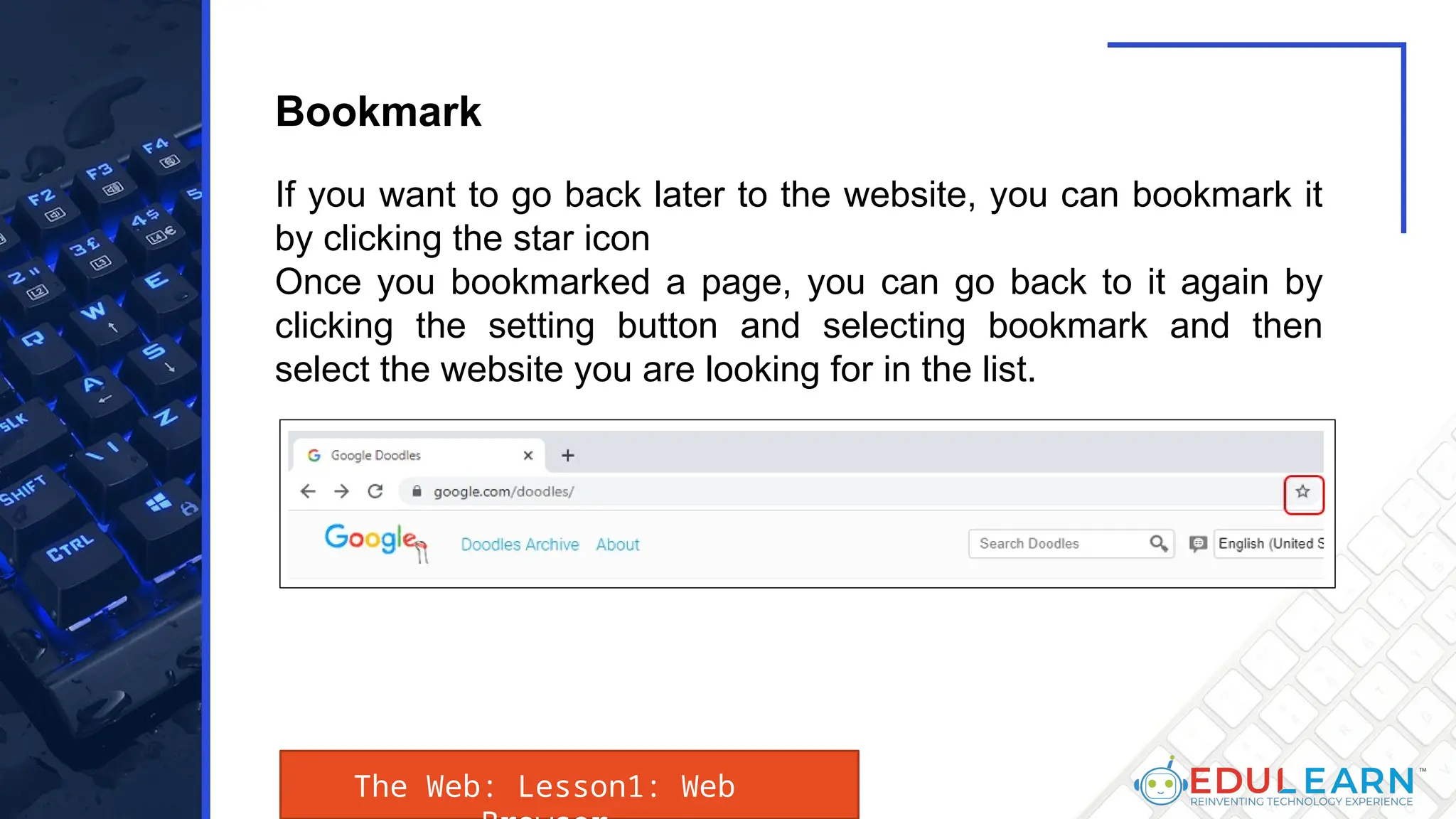
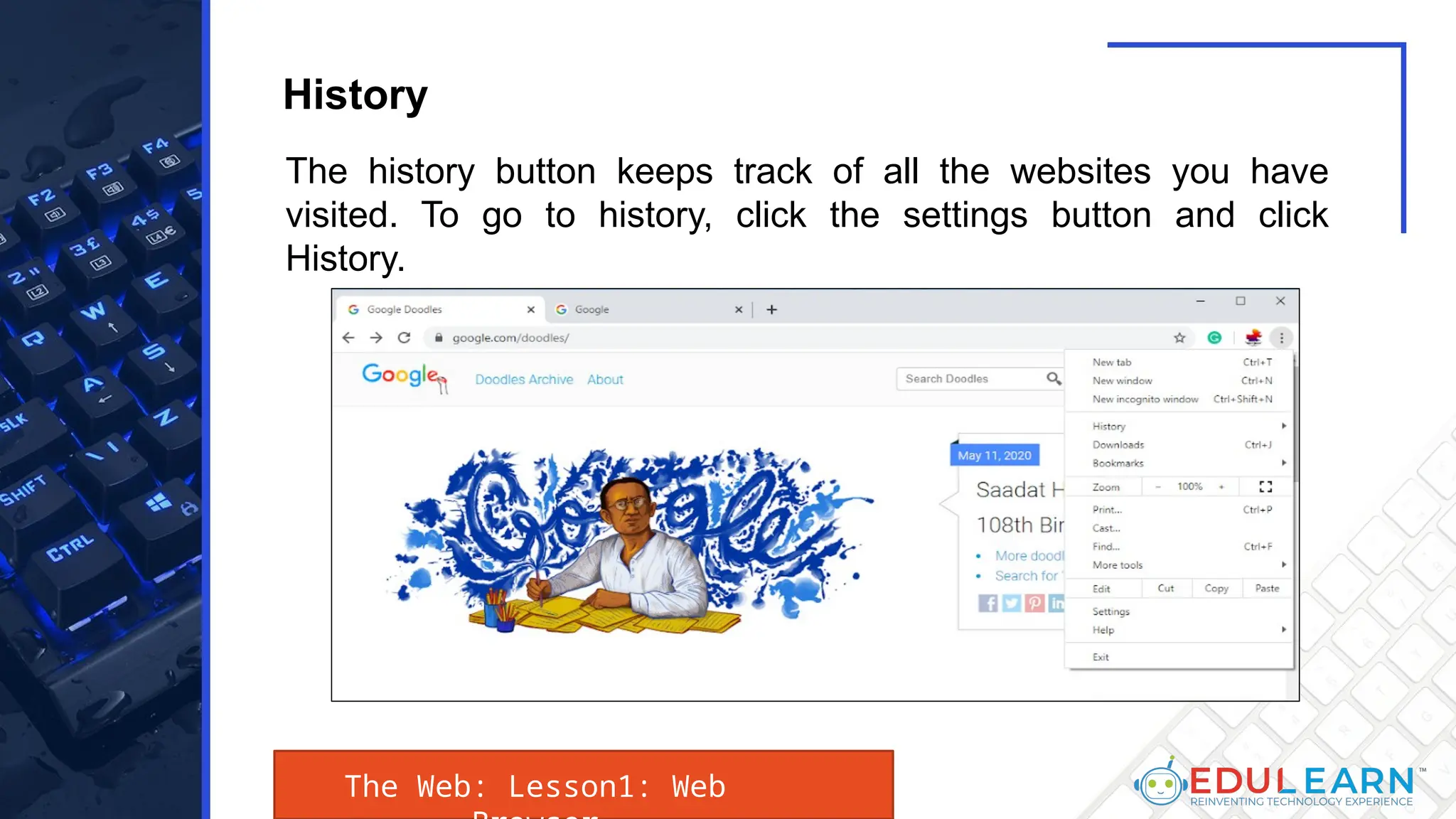
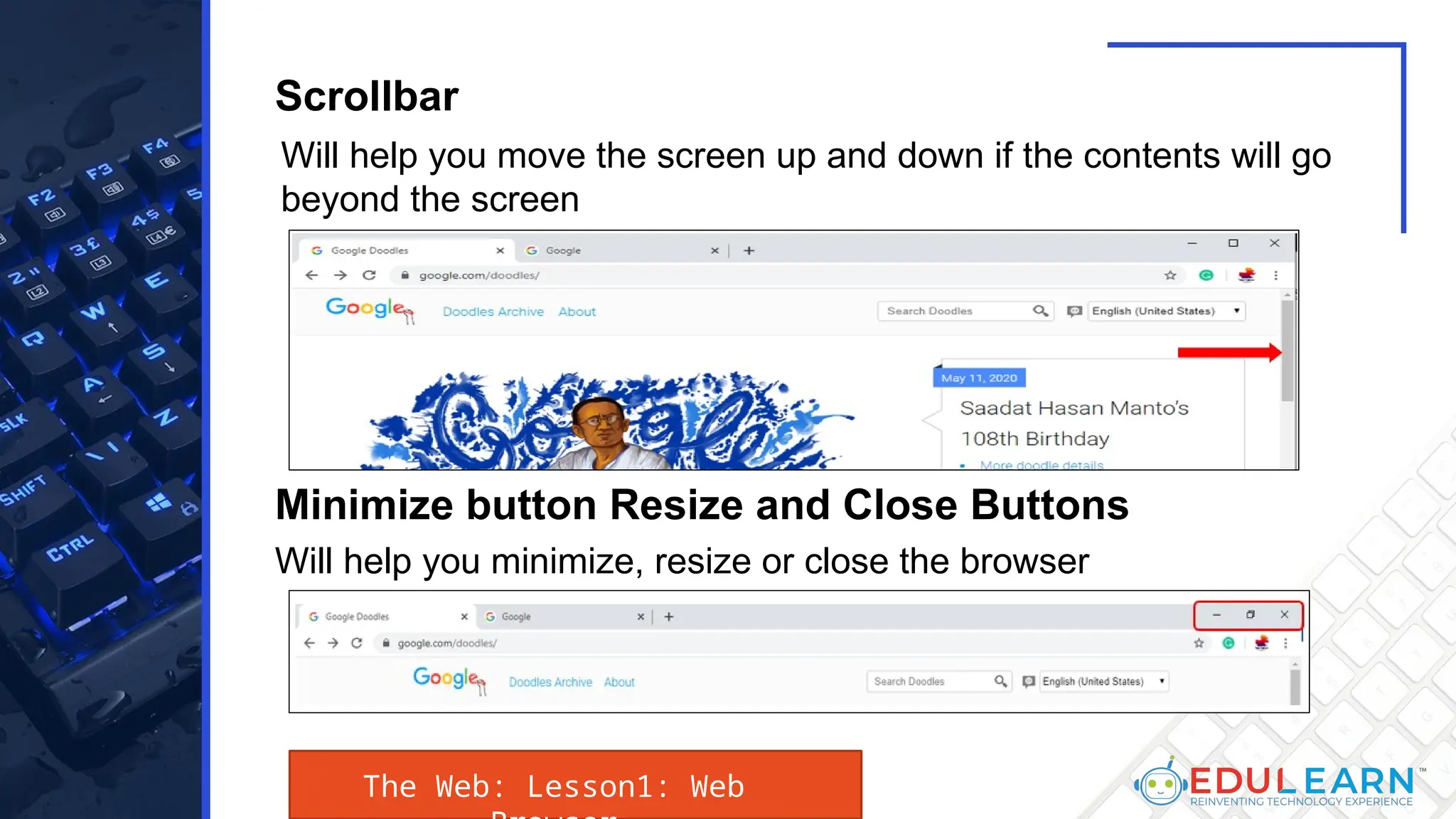
This document provides an overview of web browsers, including their functionality and different types, such as Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Apple Safari, and Opera. Key features discussed include browser operations, user interface elements, security options, and the role of the URL in accessing web pages. The document also highlights how browsers vary in design and purpose, catering to diverse user needs.