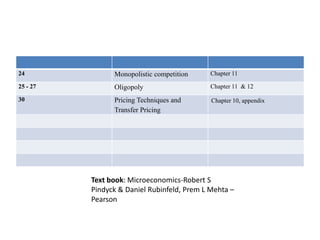
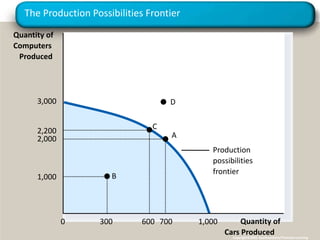
This document provides the session plan and syllabus for a Managerial Economics course. It outlines the topics to be covered each week, including introductions to economics, supply and demand analysis, production and costs, profit maximization, and different market structures. It also schedules evaluations, exams, presentations and the grading breakdown. Key topics of microeconomics that will be discussed are scarcity, efficiency, tradeoffs and the role of prices. Theories, models and the production possibilities frontier will also be examined.