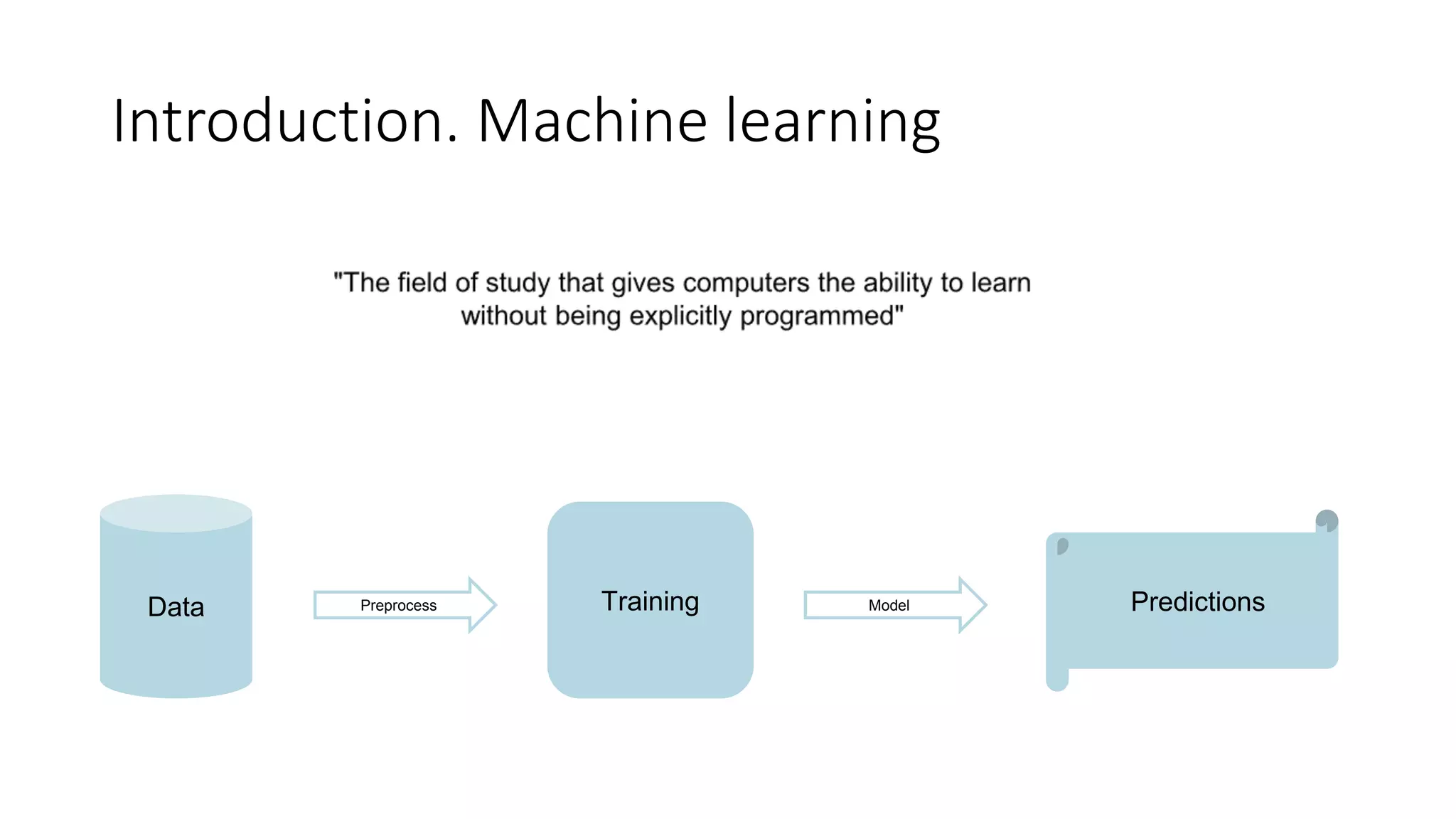
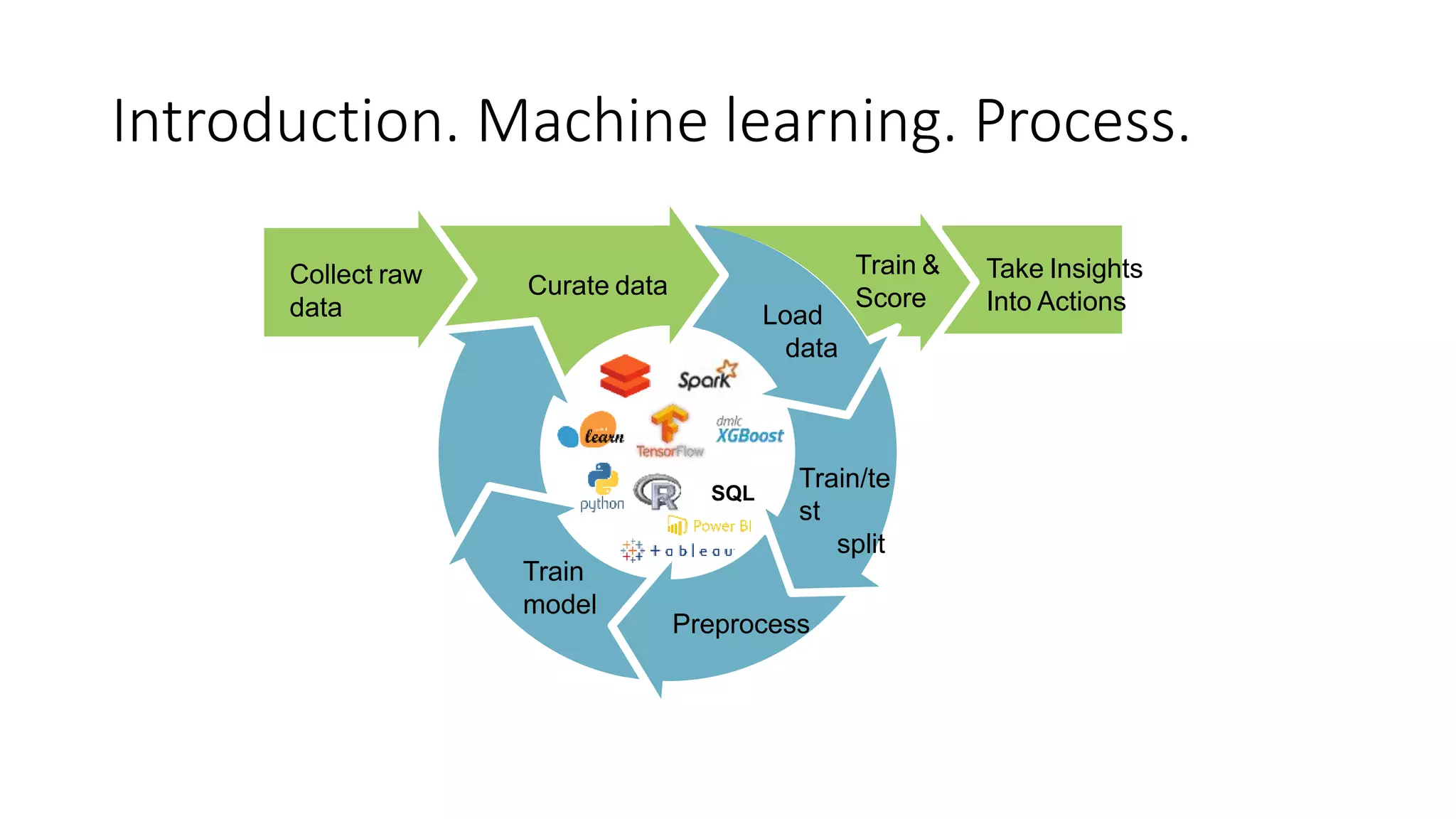
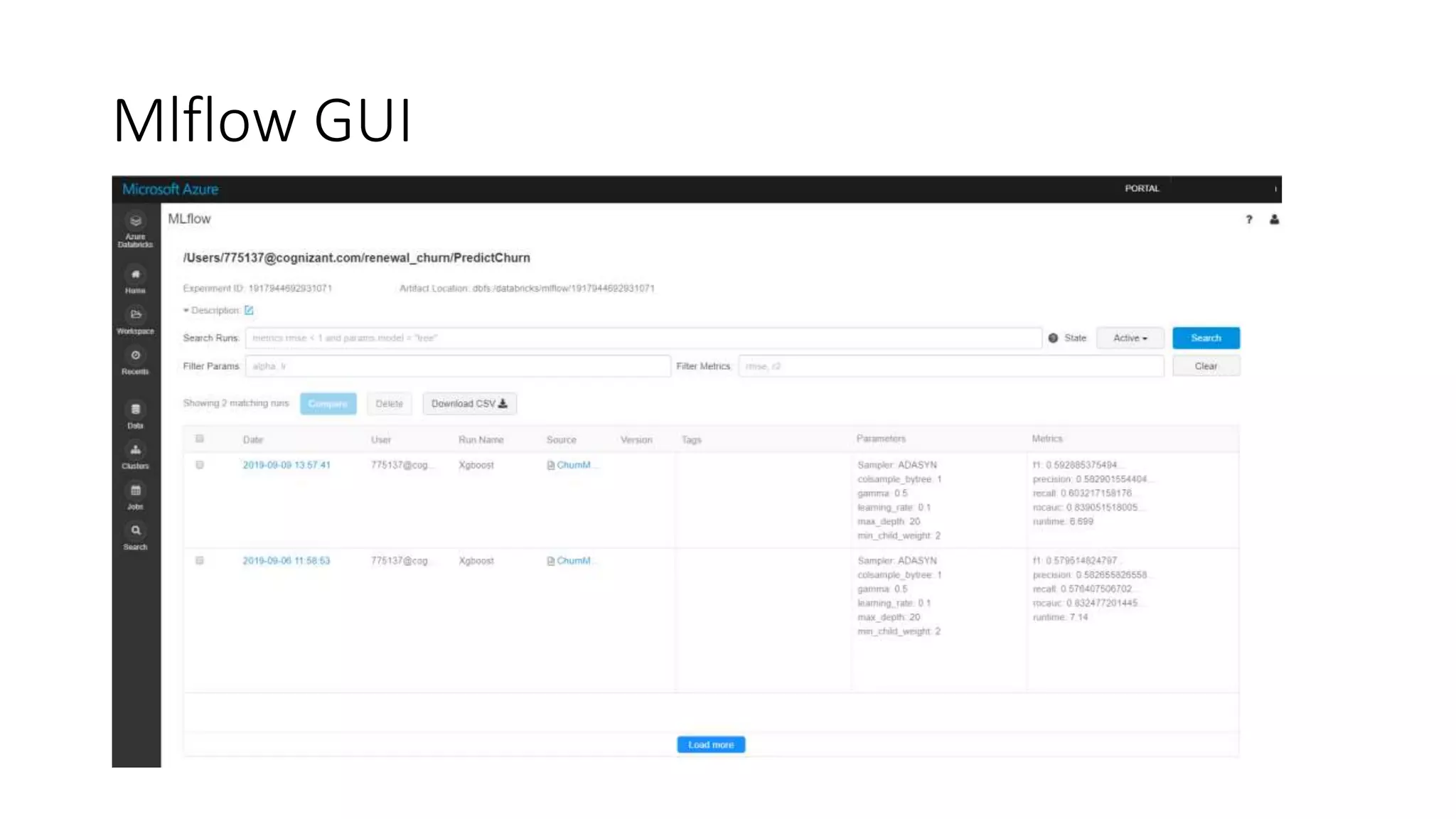
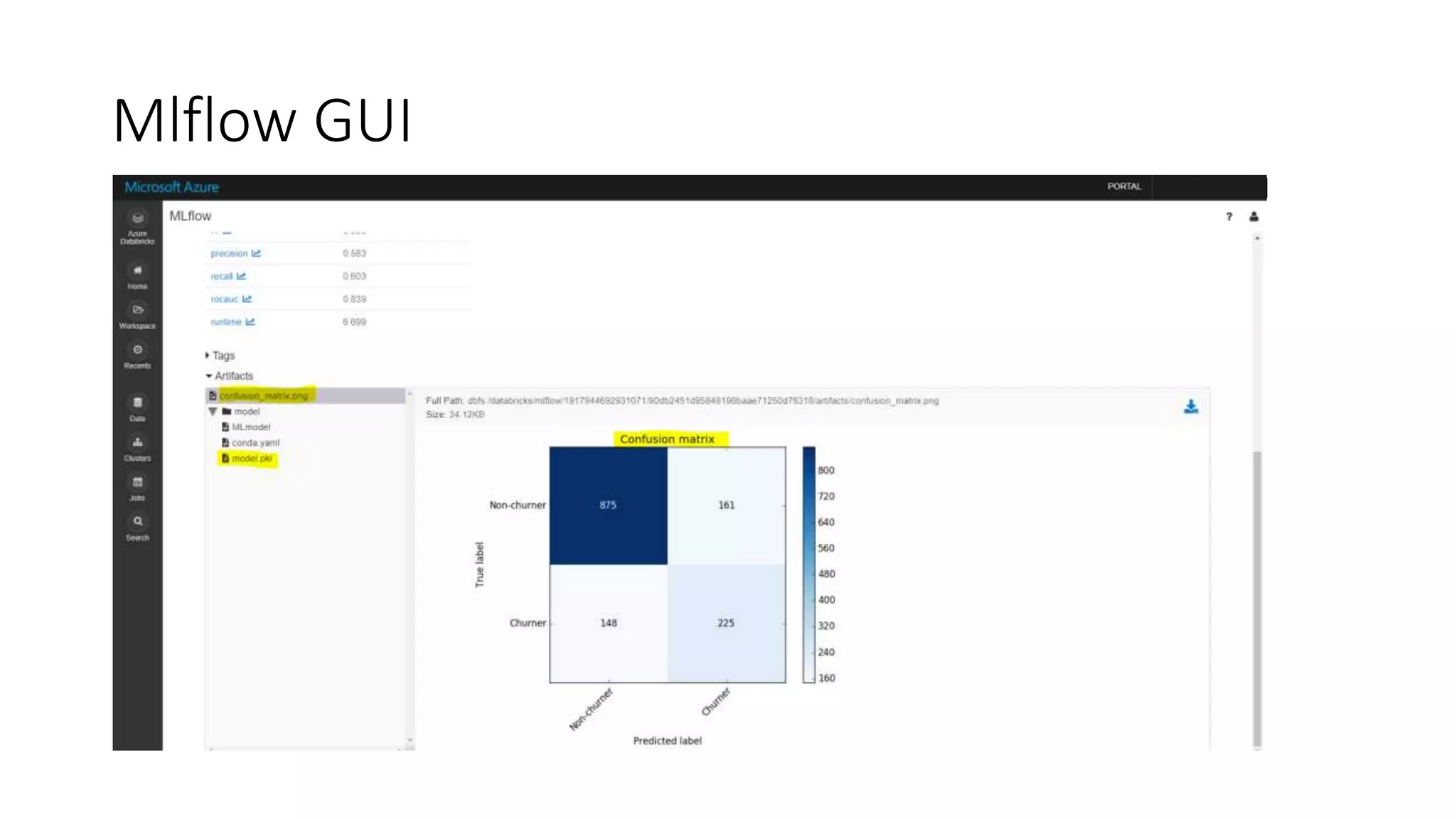
This document discusses predicting customer churn using machine learning models built with Azure Databricks, Scikit-learn, and Mlflow. It involves collecting customer data, preprocessing the data through steps like encoding, scaling, sampling to address class imbalance, and splitting into train and test sets. Various classification models are trained and evaluated on the training data using metrics like f1 score, precision, and recall. Hyperparameter optimization is performed to improve model performance. The best model is stored and tracked using Mlflow for scoring new data and predicting customer churn probabilities. SHAP is used to explain the model predictions.