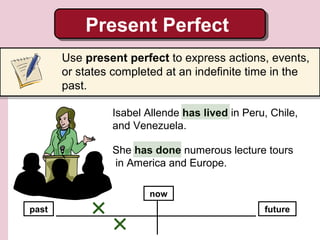
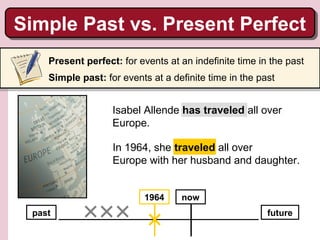
1. Isabel Allende grew up in South America and attended private school in Bolivia in the 1950s. She has lived in several South American countries and has extensively traveled throughout Europe and America.
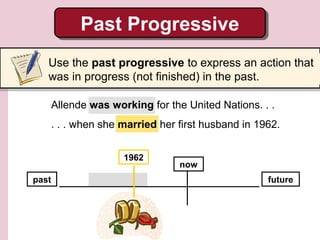
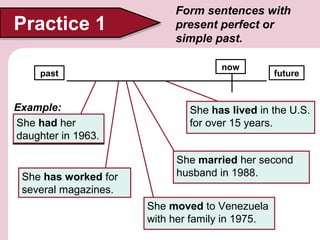
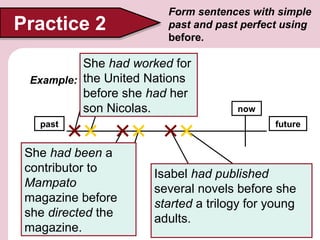
2. Allende worked for magazines and the United Nations before writing her famous novel House of Spirits. She had published many articles and started a young adult trilogy before moving to Venezuela in 1975.
3. Allende was going to stay in Chile but had to flee after the 1973 military coup. She was going to write a letter that instead turned into her first novel. Allende and her husband were going to separate but she returned to him in 1978.