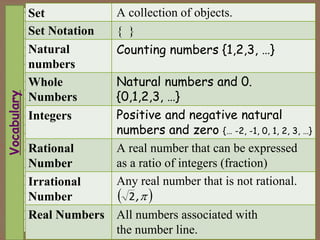
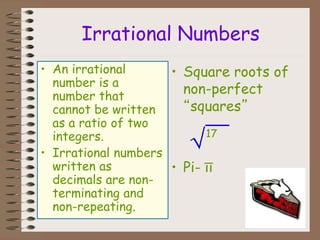
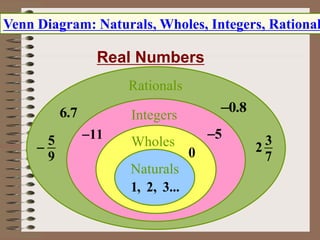
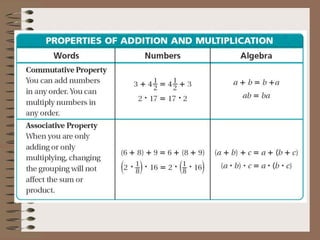
The document is a presentation focused on the operations of rational numbers, aimed at helping students apply the order of operations and their properties to solve problems. It defines key concepts including rational and irrational numbers, as well as their representations on the number line and in set notation. Additionally, it poses essential questions to guide students' understanding of these mathematical concepts.