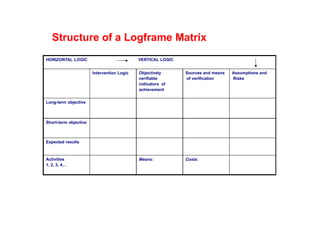
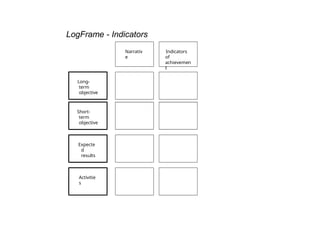
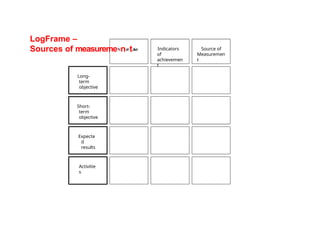
The document outlines the structure and purpose of a logframe matrix used in project management to design, implement, and monitor projects. It details various components such as long-term and short-term objectives, activities, expected results, and indicators of achievement, emphasizing the importance of clarity and accountability. Additionally, it describes the role of assumptions and risks that can impact project success, alongside guidelines for writing objectives and activities.