This document describes a preformulation study of candesartan cilexetil for a buccal (effervescent) tablet formulation. Key findings include:
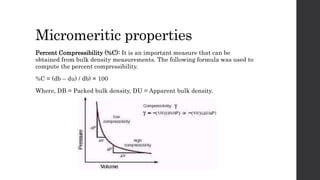
1) Candesartan cilexetil has good flow and compression properties making it suitable for direct compression tabletting.
2) An HPLC method was developed and validated for drug quantification with an R2 value of 1.0 indicating good linearity.
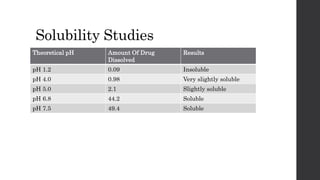
3) The drug was found to be non-hygroscopic and have pH-dependent solubility, which are important considerations for formulation development.
4) Compatibility studies using FTIR and DSC found no interactions between the drug and excipients.