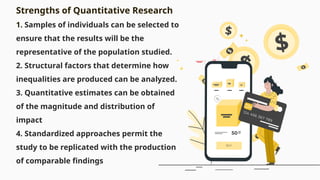
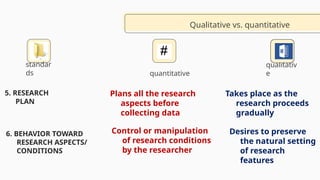
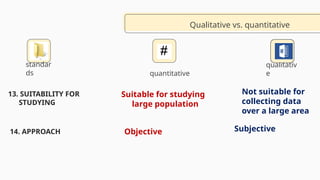
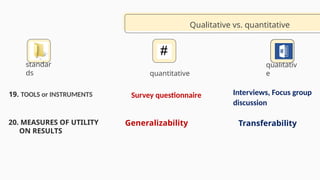
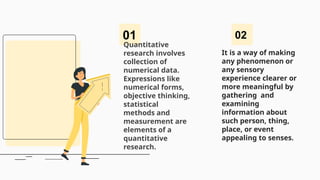
The document outlines the principles and characteristics of quantitative research, highlighting its focus on numerical data, objective analysis, and the strength of relationships among variables. It contrasts quantitative research with qualitative research, emphasizing the structured and replicable nature of quantitative studies while discussing strengths such as representativeness and the ability to analyze inequalities. Additionally, it provides examples of measurements and factors to consider in academic performance studies.


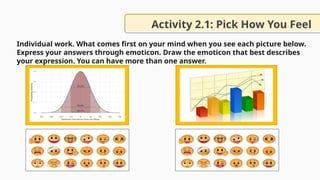

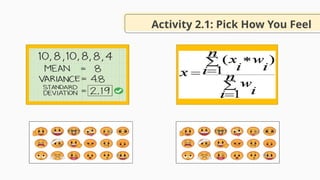
![Behavior]
1. Determining the respondents’ academic grades and arrived at
96, 97, 78, and 60.
2. Determining the respondents’ level of agreement to factors
that correlate with academic performance.
3. Determining respondents’ stress levels from 1-10 and arrived
at 5, 6, 7 and 8
4. Computing for the strength of relationship between the family
stress with academic performance where you arrived at .7328
interpreted as strong relationship of variables.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-pracres2-240813142408-15814e43/85/Practical-Research-2-Week-2-for-Prelims-pptx-9-320.jpg)