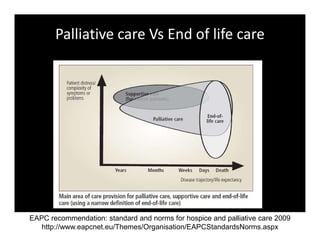
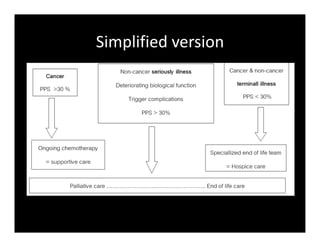
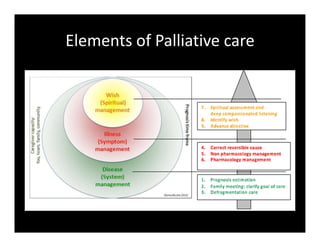
1. Palliative care focuses on relieving suffering through a holistic approach addressing the patient's physical, psychological, and spiritual needs using a 3S framework of system, symptom, and spiritual care.
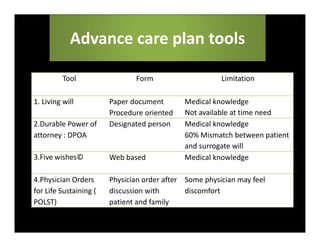
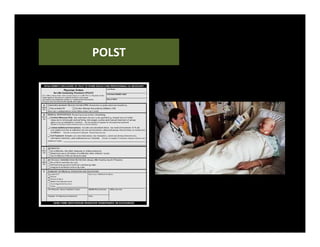
2. Advance care planning documents a patient's values and preferences for end-of-life care through a "wish" or goal of care and a living will or procedures they do/do not consent to, optionally designating a healthcare proxy.
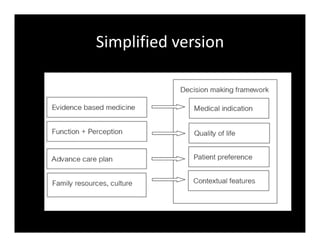
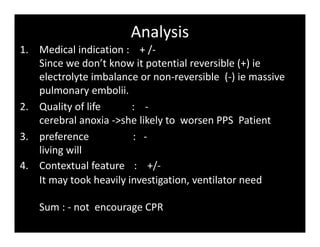
3. Medical ethical dilemmas are addressed through a 4 box model considering medical indication, quality of life, patient preference, and contextual factors to guide decision making in palliative care.