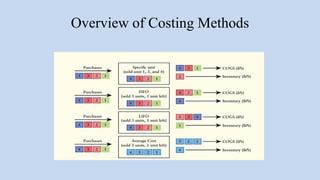
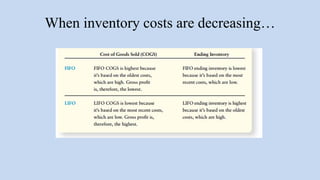
The document outlines key learning objectives related to inventory and merchandising operations, including inventory valuation, cost assumptions, and the impact of inventory errors on financial statements. It discusses various inventory costing methods such as FIFO, LIFO, and the average cost method, alongside their implications on cost of goods sold and gross profit. Additionally, it covers the evaluation of retail operations using inventory-related financial ratios and adheres to standards such as the lower of cost or net realizable value.