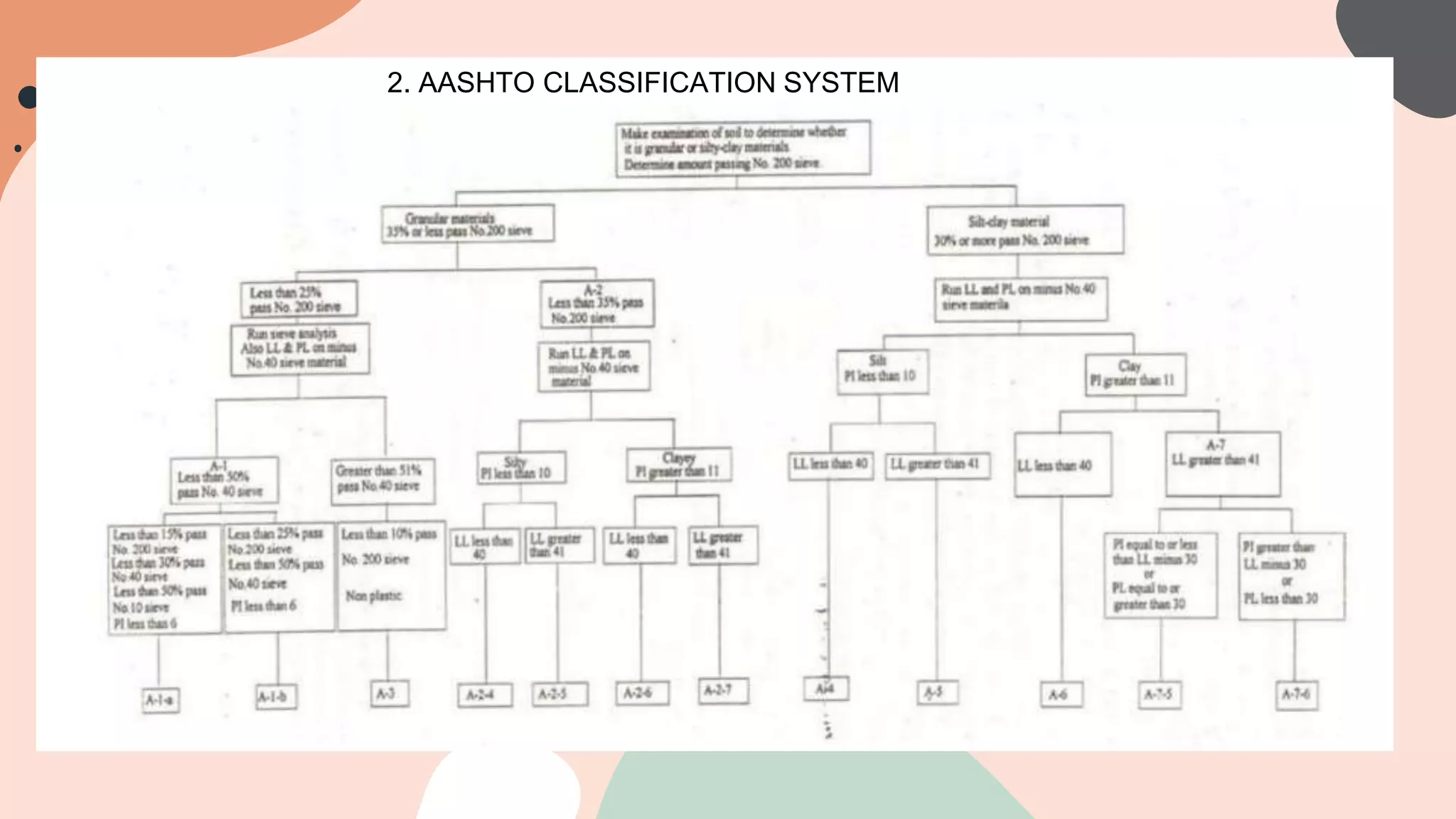
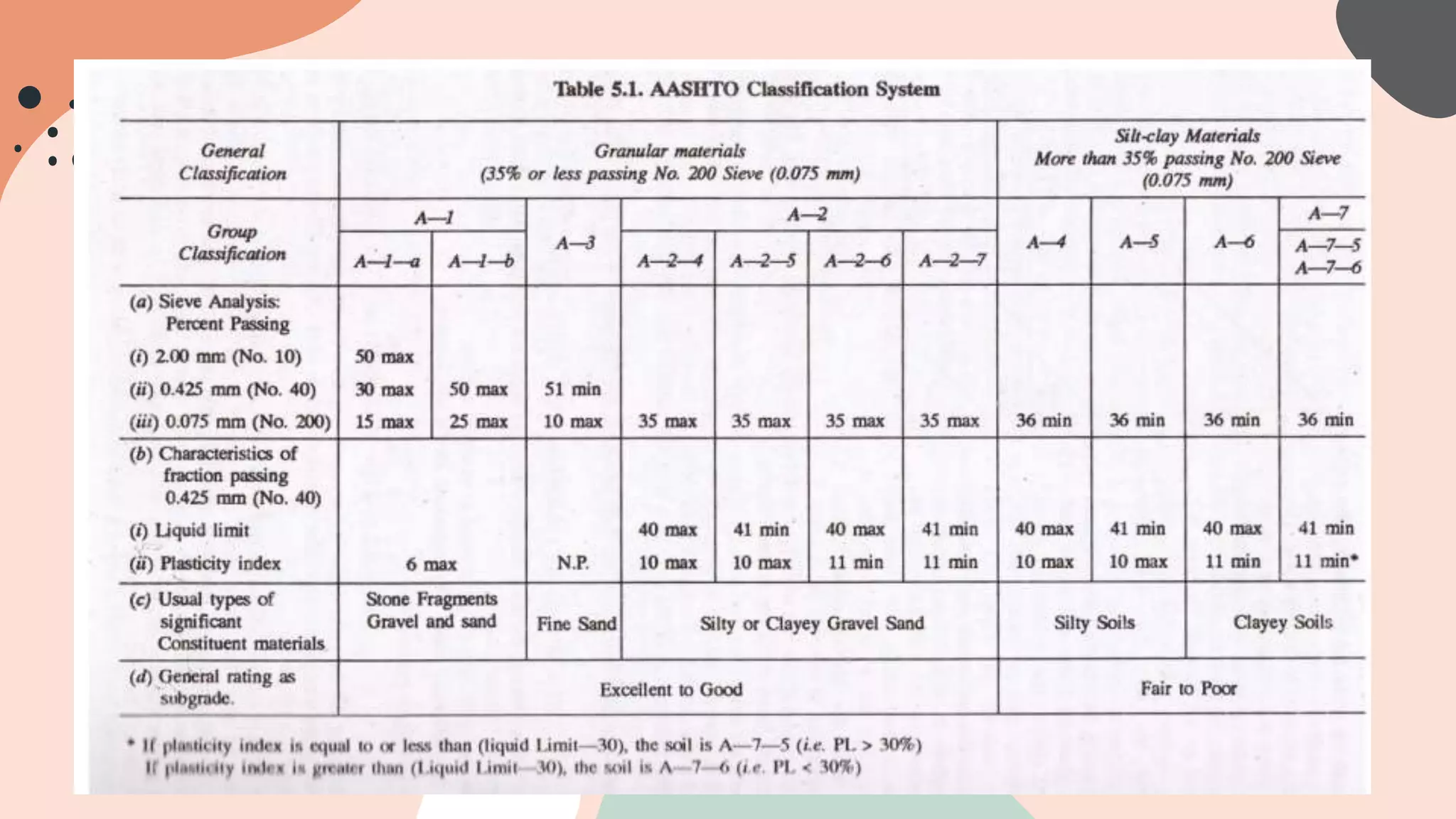
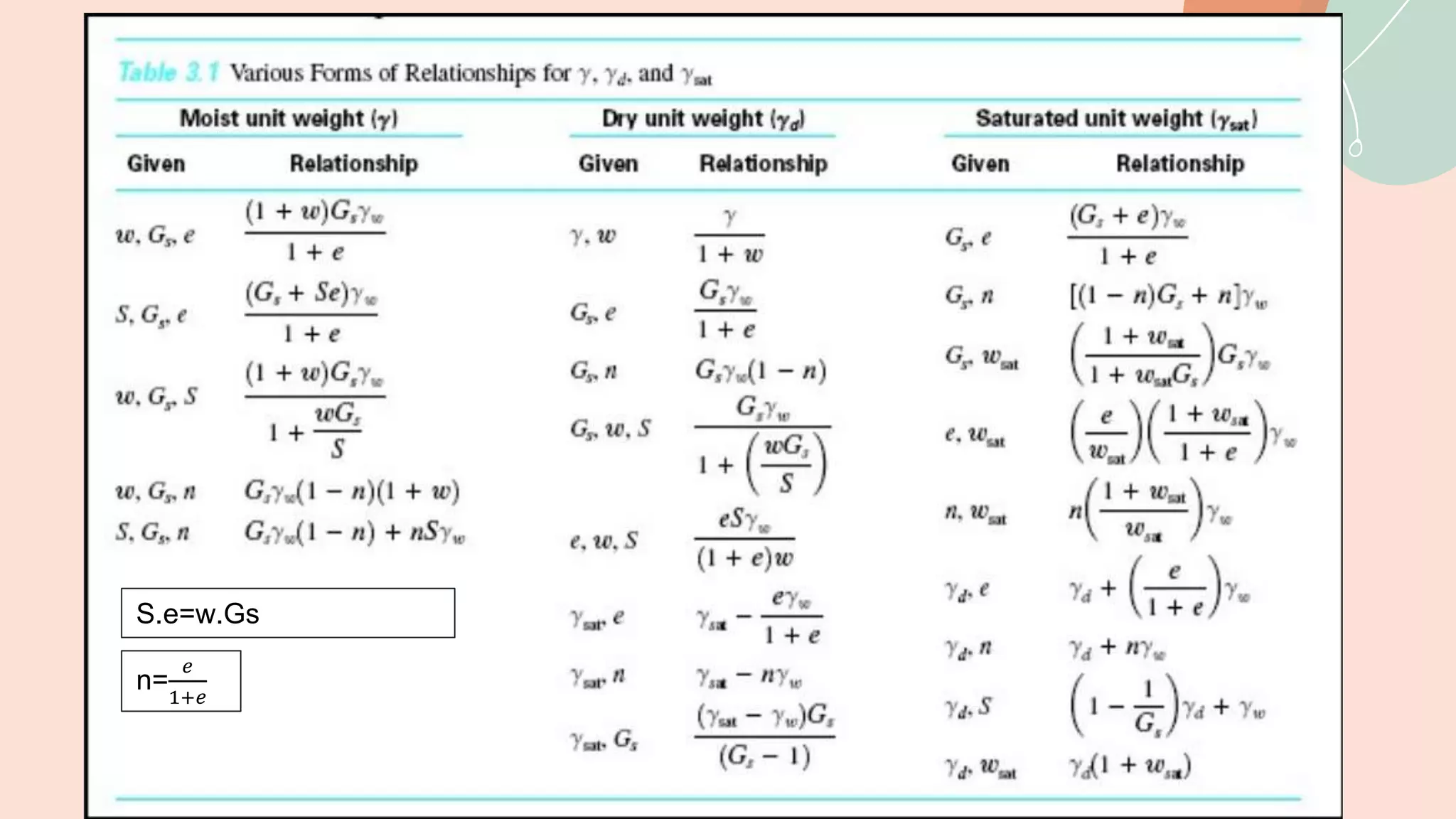
This document discusses different soil classification systems including the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) and the American Association of State Highways and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) system. It provides details on classifying soils based on particle size distribution, liquid limit, and plasticity index using these systems. The USCS uses the No. 200 sieve, liquid limit tests, and plasticity chart to classify soils as gravel, sand, silt, clay, or organic. It also defines key volumetric ratios and properties for soils such as void ratio, saturation, unit weight, and specific gravity.


![1.USCS
- ONLY NEED SIEVE ANALYSIS AND ATTERBERG LIMITS TO CLASSIFY SOIL.
- The coarse grained soils are those having more than 50% of soil being retained on the
No.200 sieve [0.075mm].
- Fine-grained soils are those that allow more than 50% to pass through the No.200
sieve.
% Gravel = % retained on No.4 sieve (4.75mm opening)
% Sand= % retained between No.200 sieve on No.4 sieve
% Fines= % passing No.200 sieve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-topic12-230317063105-e8dc6c25/75/PPT-SOIL-CLASSIFICATION-3-2048.jpg)