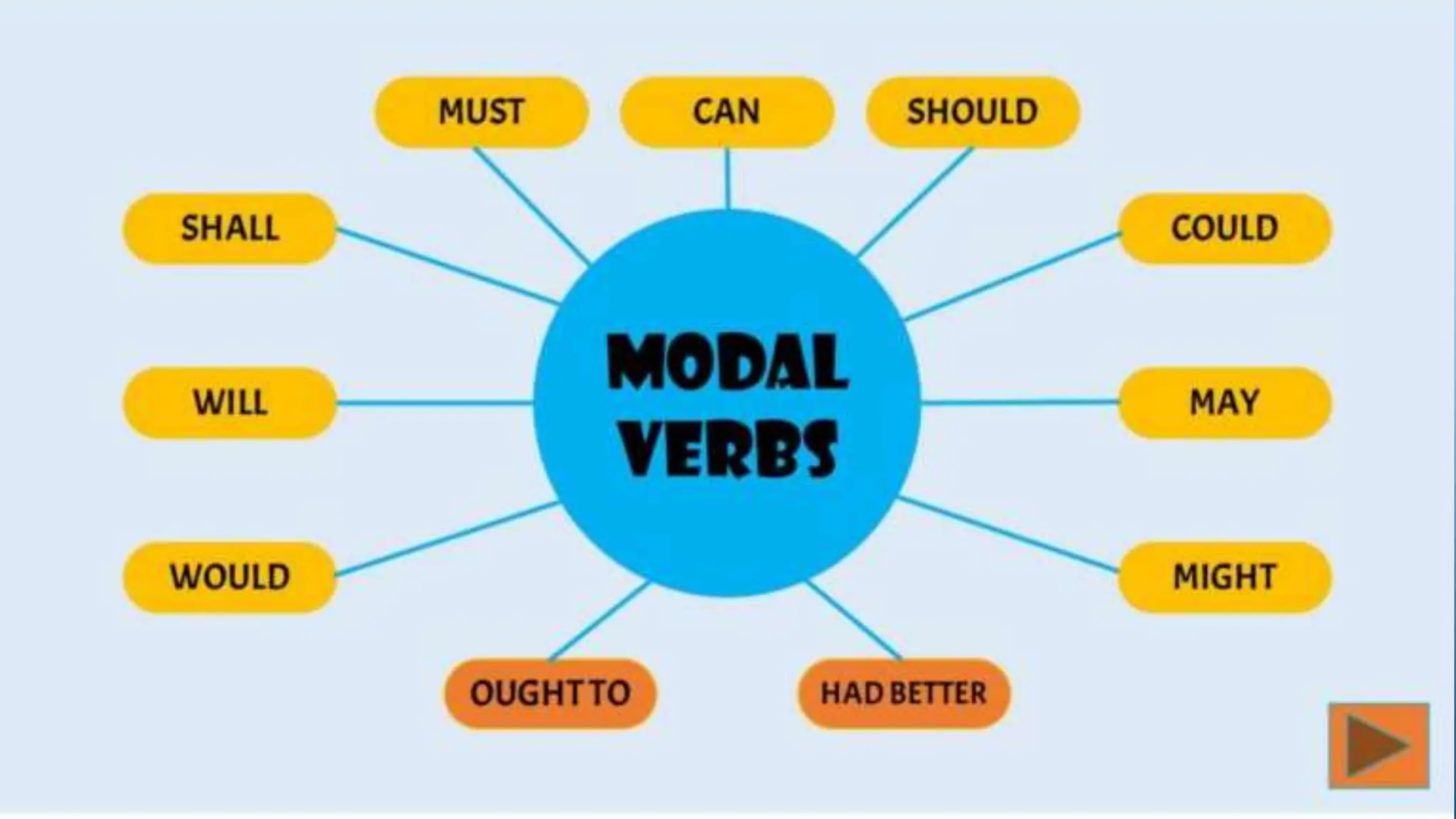
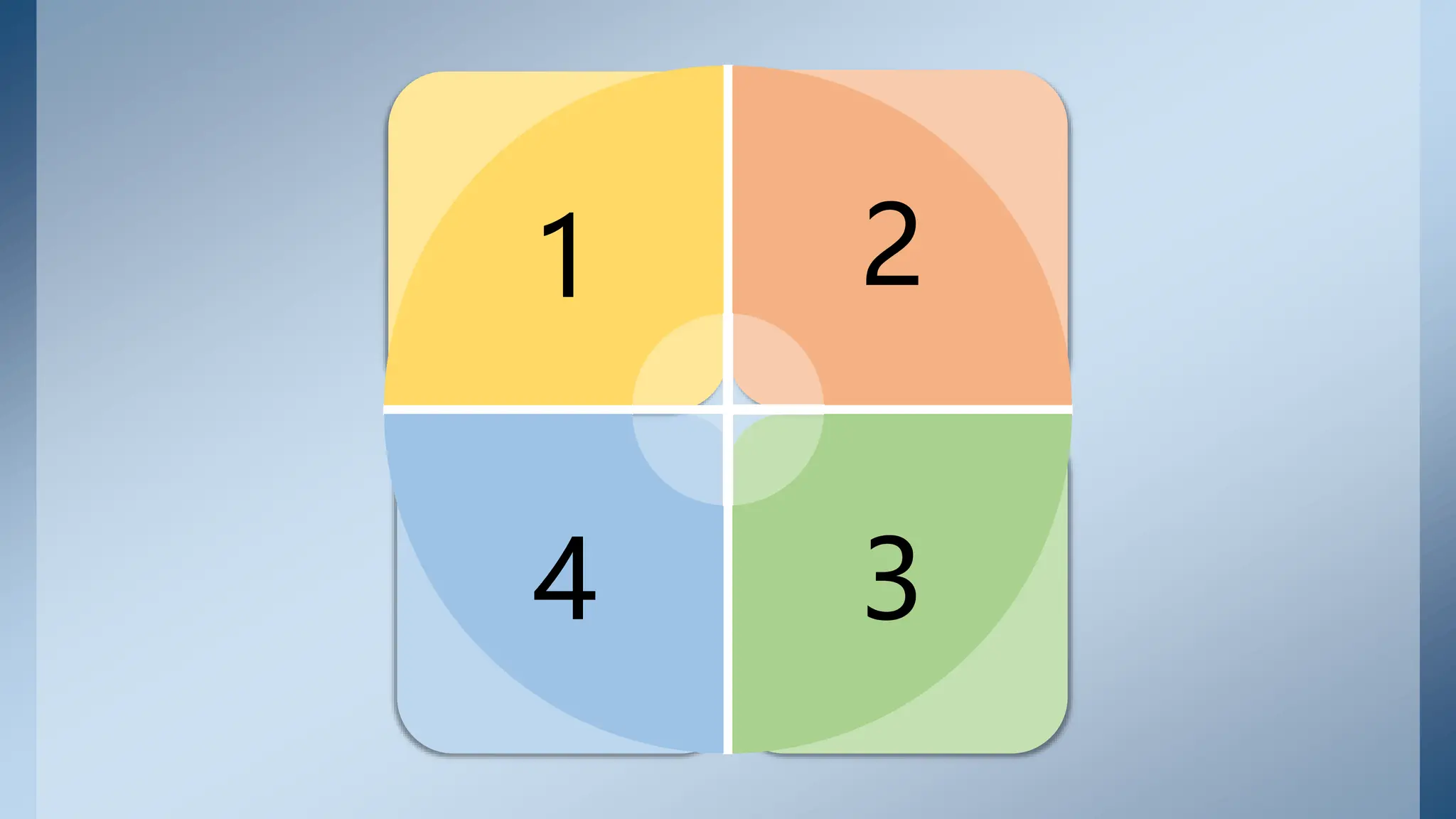
The document discusses the use of modal verbs to express permission, obligation, prohibition, and no obligation. It provides examples of modals used in each context:
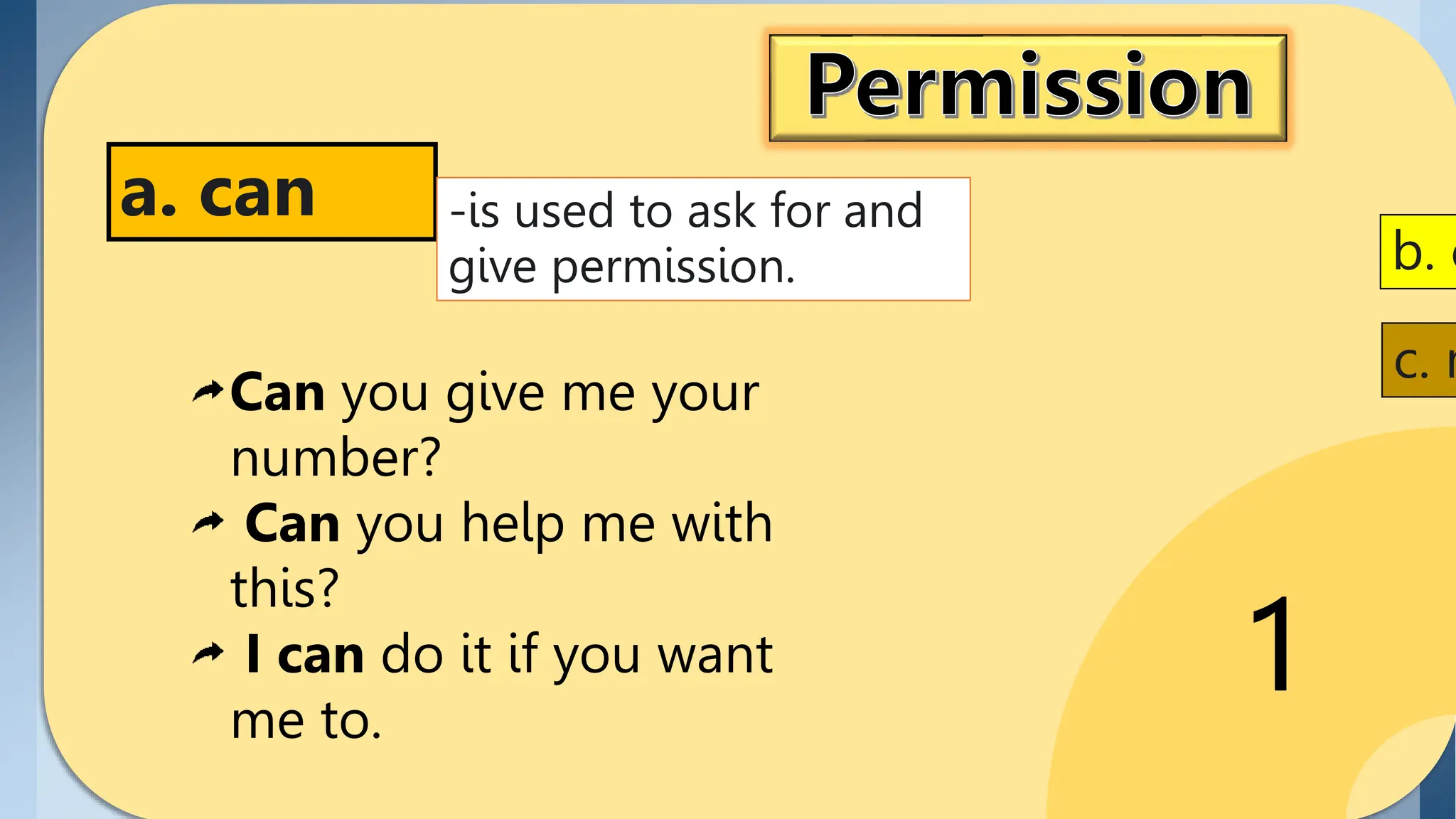
1. Permission is expressed using can, could, and may. Can is more casual while may is more formal.
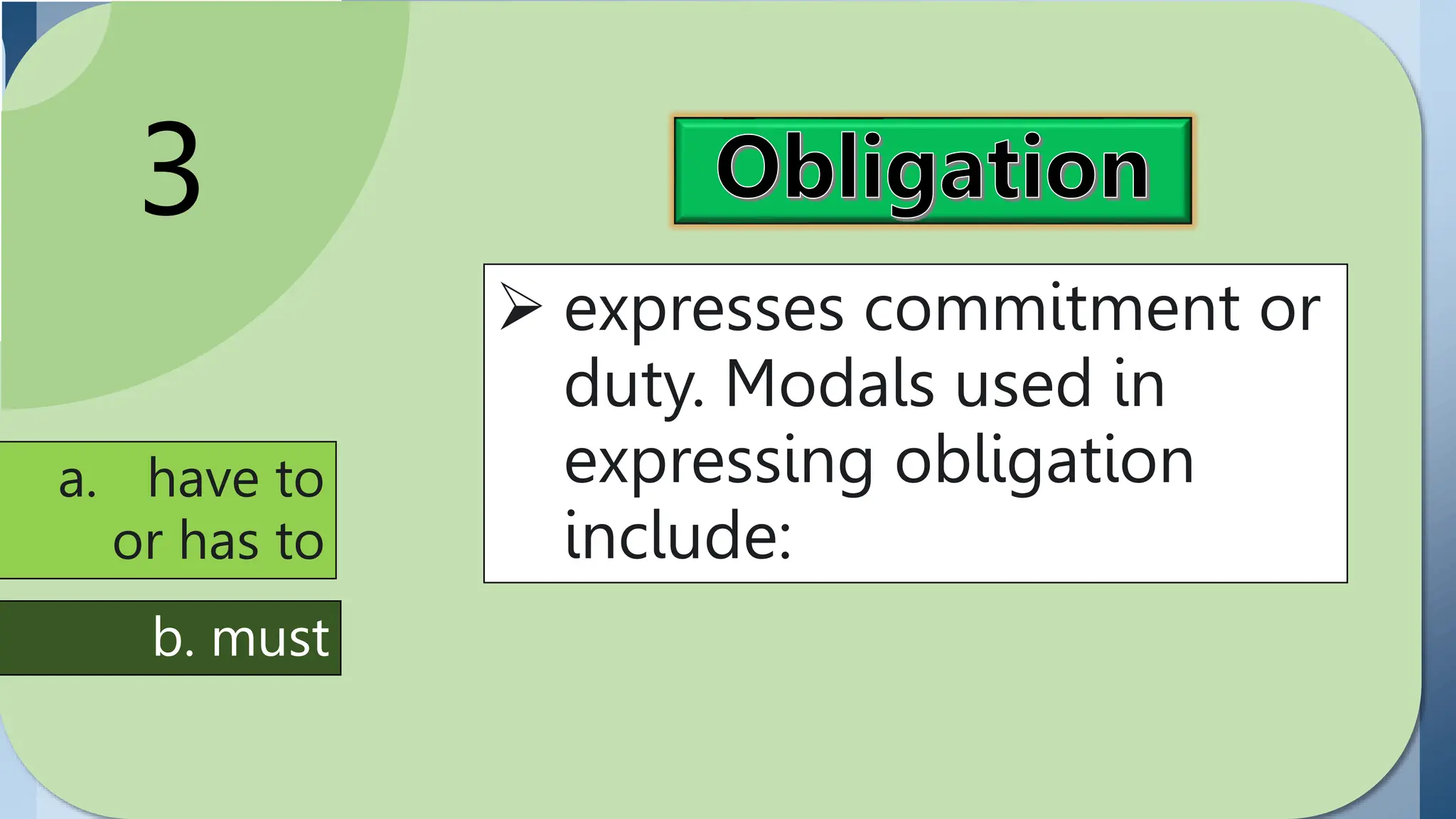
2. Obligation is expressed using have to/has to and must. Have to/has to refers to external obligations while must refers to internal or self-imposed obligations.
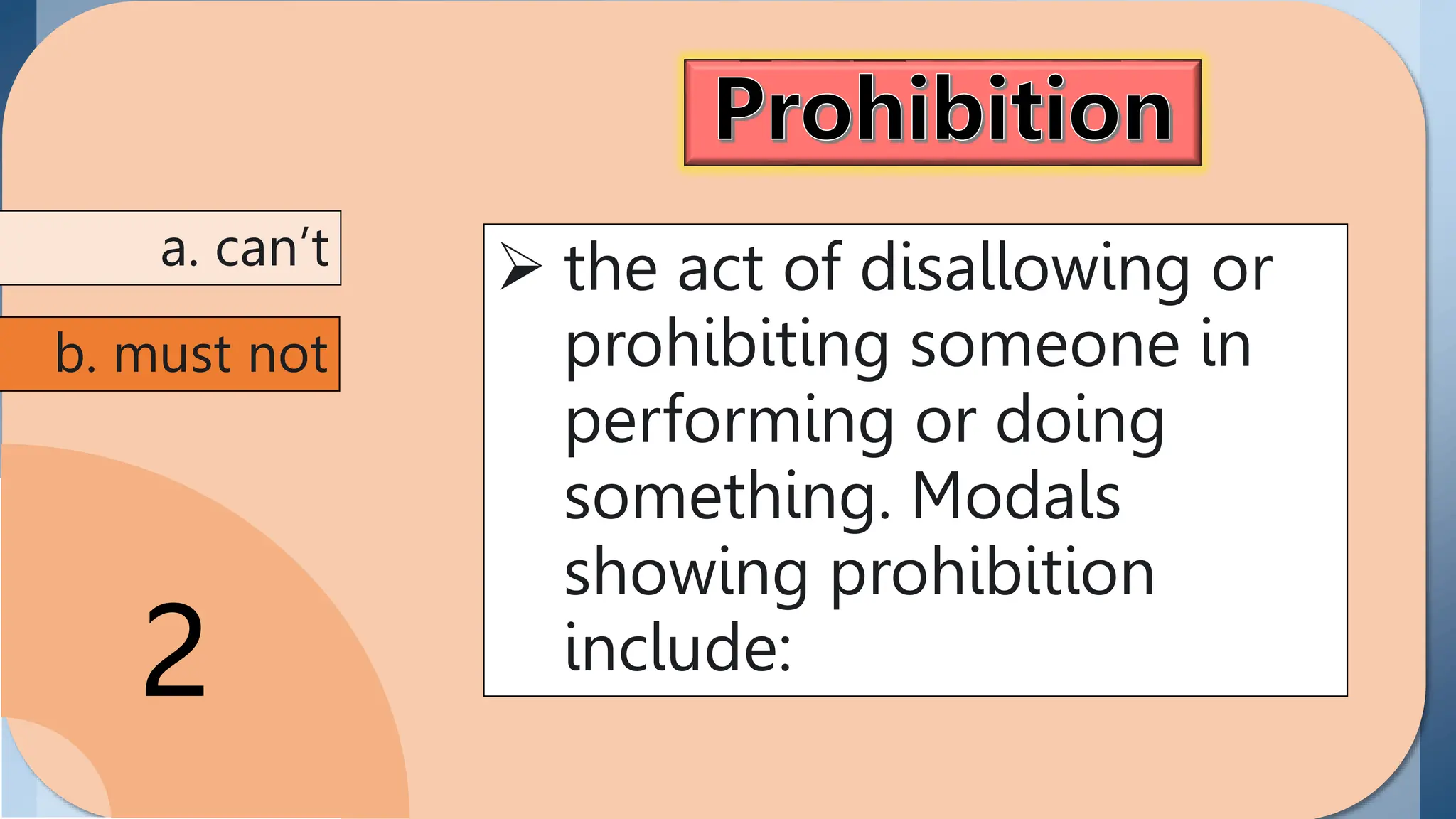
3. Prohibition is expressed using can't and must not/mustn't. Can't refers to rules not set by the speaker, while must not/mustn't refers to rules set by the speaker.
4. No obligation is expressed