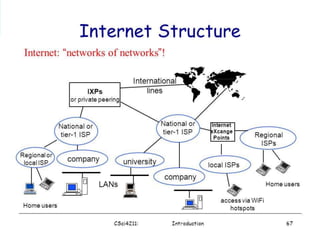
Mahesh Gadekar is presenting about the history and structure of the Internet. The document discusses how the Internet began as an experimental network started by ARPA in 1969 to create a decentralized network. It then covers the development of the Internet throughout the 1980s and 1990s until it became publicly available. The key features of the Internet discussed include the world wide web, email, file transfer, and communication tools. Both the advantages like access to information and disadvantages like security threats of the Internet are mentioned.