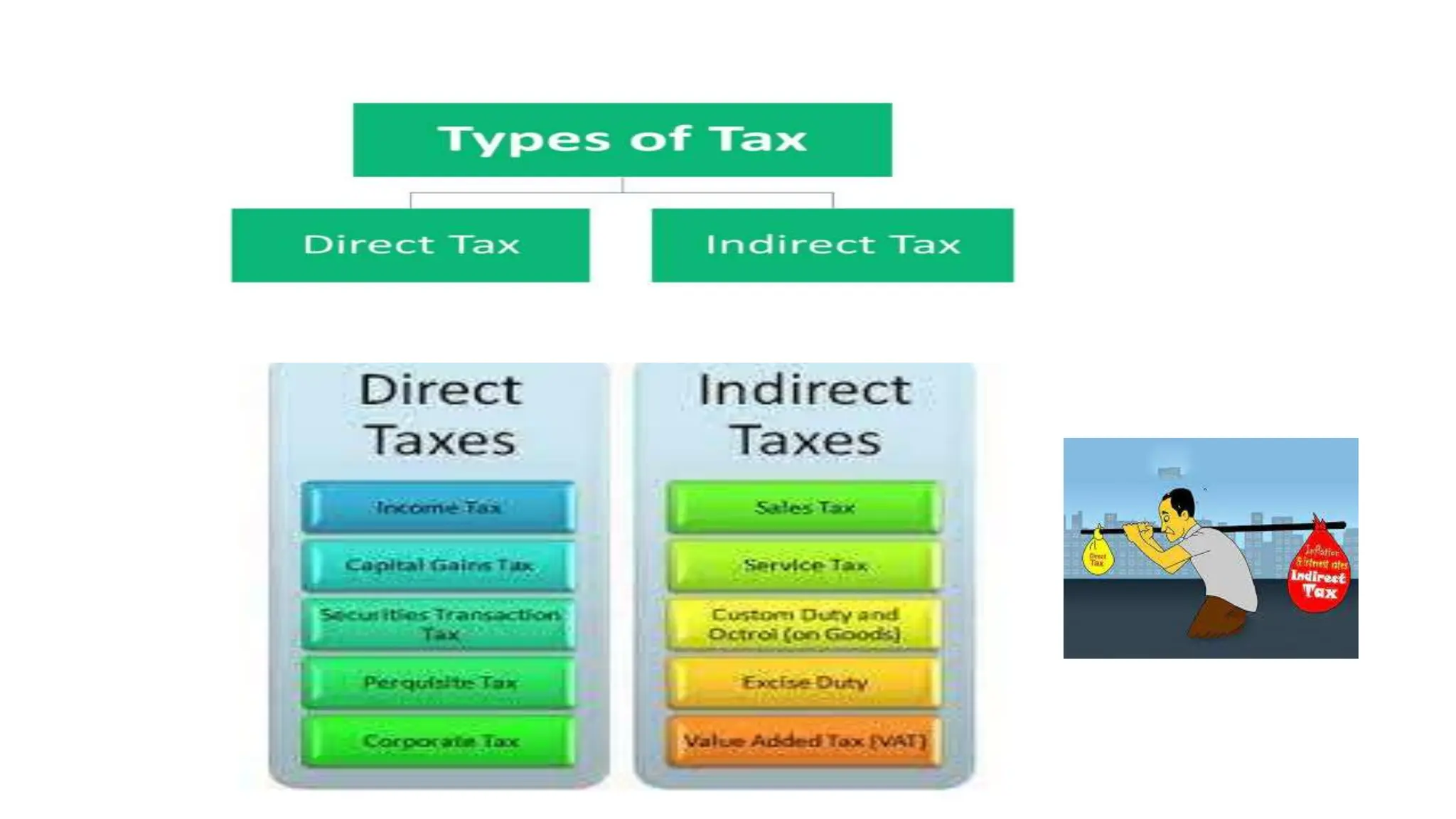
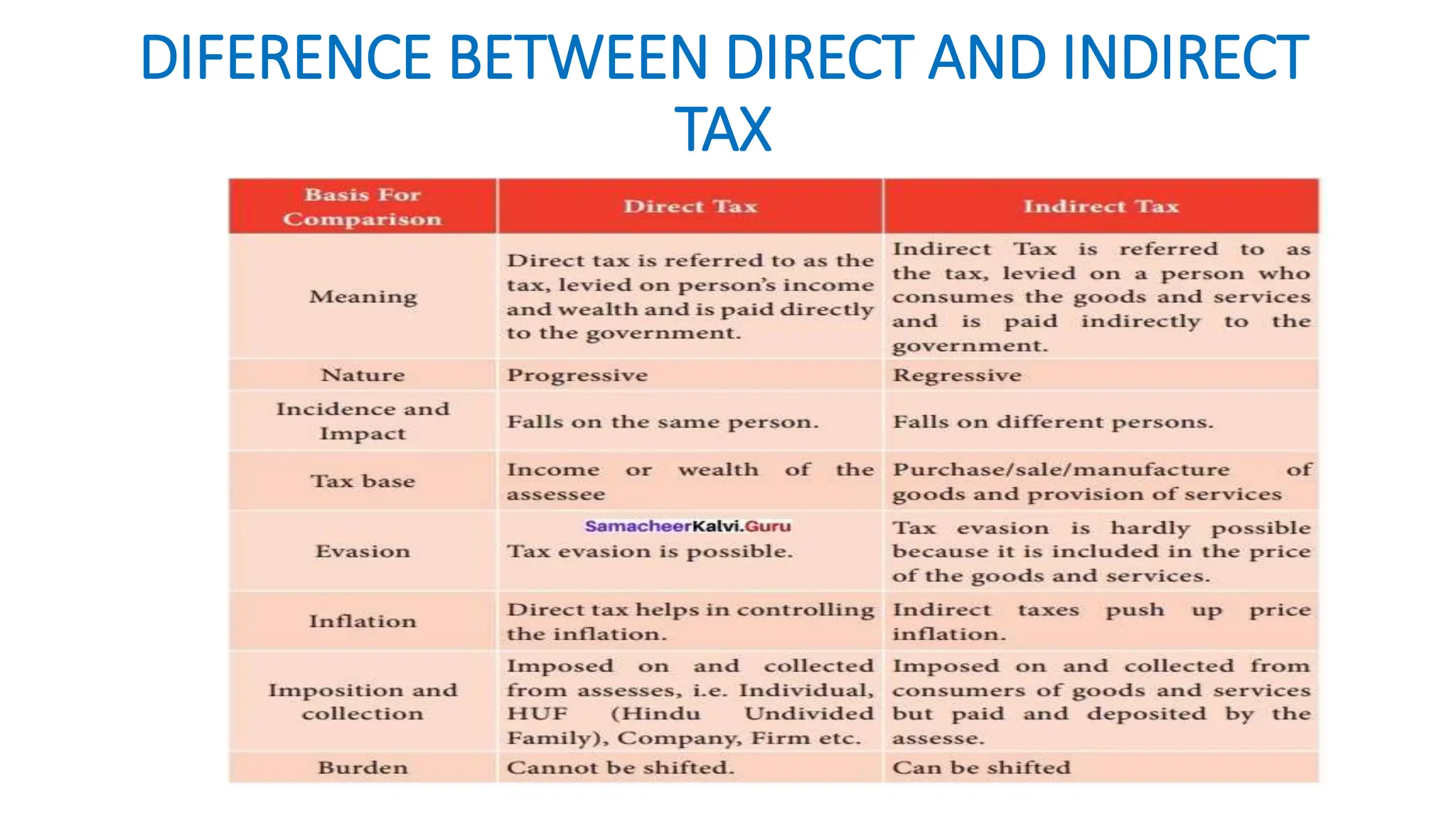
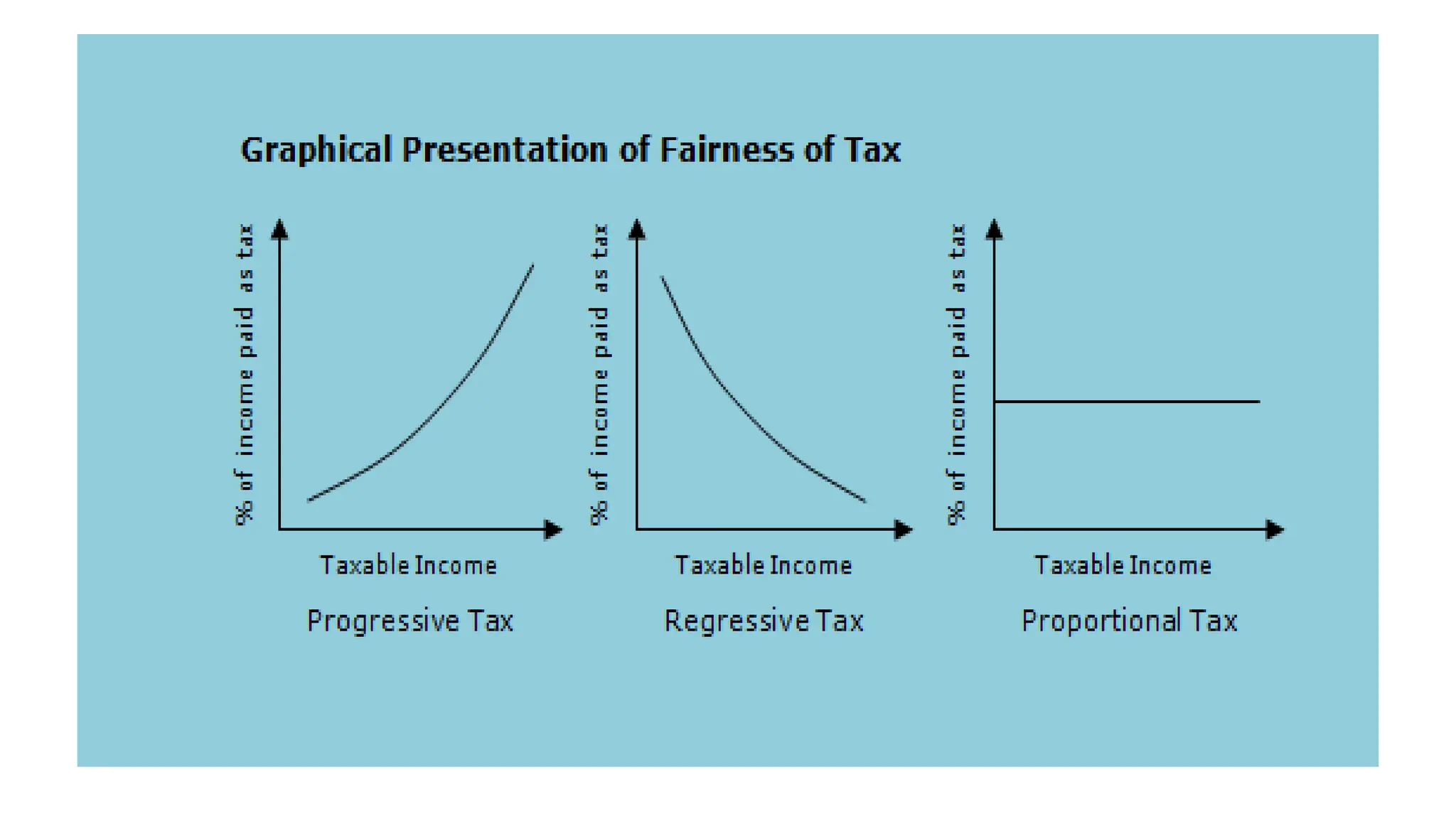
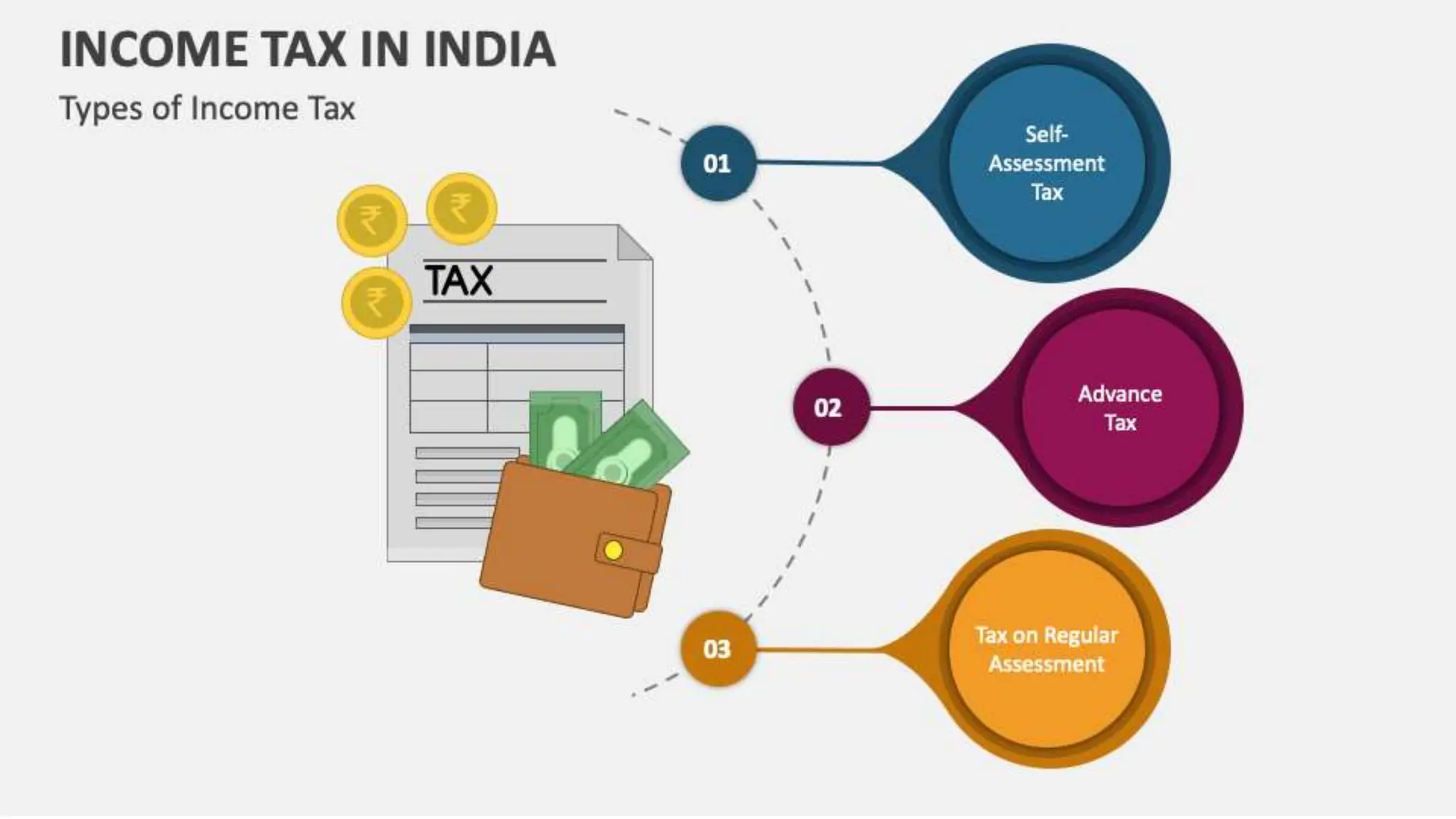
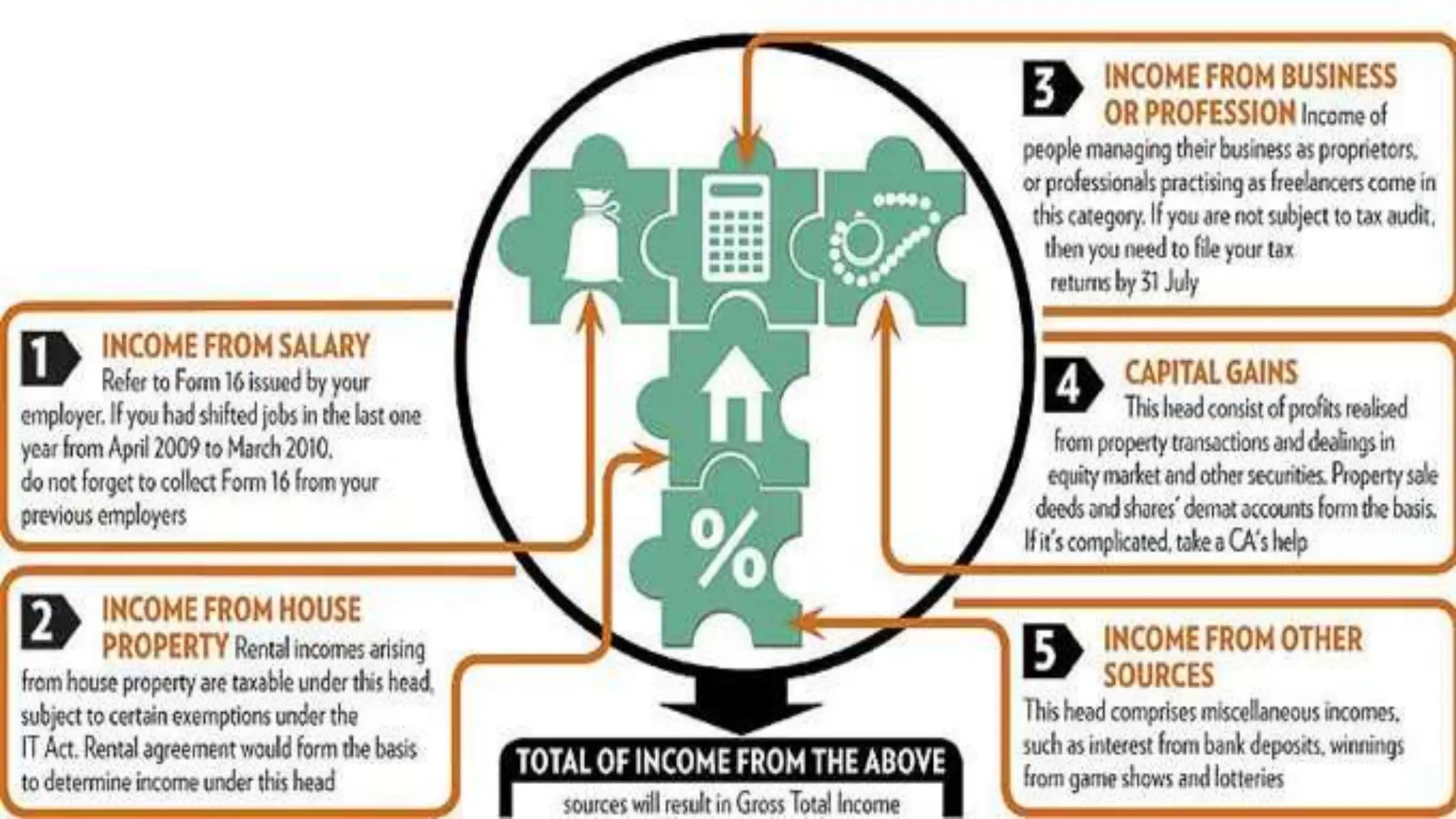
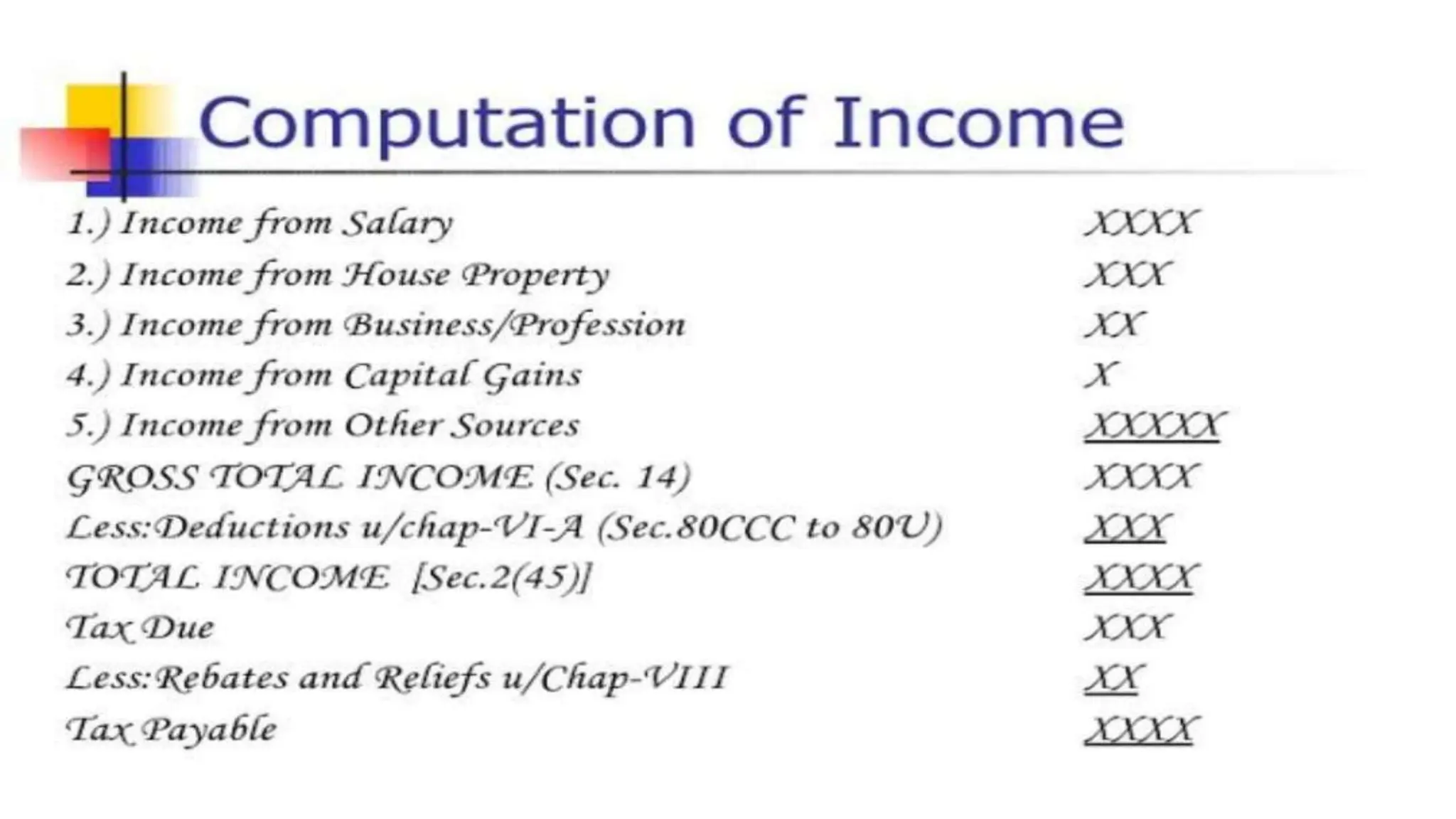
Income tax is a mandatory tax imposed by governments on income earned by individuals and businesses. It plays a vital role in funding public services and infrastructure. There are two main types of taxes - direct taxes like income tax that are directly paid by entities and indirect taxes included in the price of goods and services. In India, income tax slabs and rates are determined by the annual union budget and taxpayers must pay income tax according to the slab they fall under based on their income level. Income tax revenue is used by the government to finance activities, fund welfare programs, promote economic growth and development, and reduce income inequality in society.