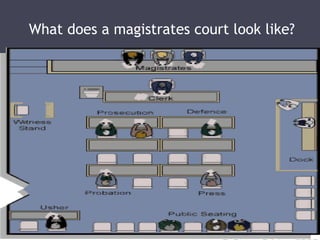
The document discusses criminal and civil law, types of offenses, and reasons for punishment. It explains that criminal law involves offenses against society, like theft, assault, and murder. Civil law deals with private disputes over contracts, money, and divorce. The document also lists different types of punishment and their aims, such as rehabilitation, deterrence, reparation, and protection of the public.