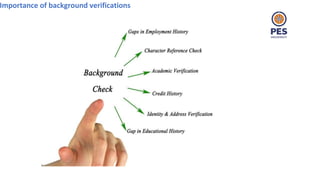
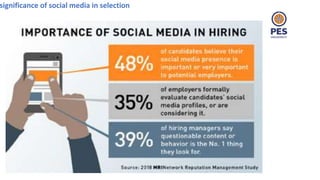
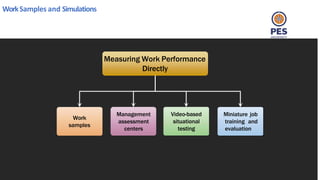
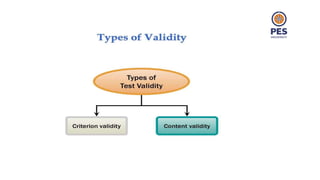
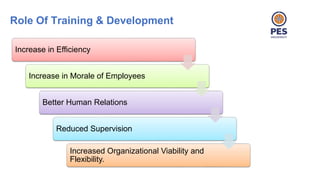
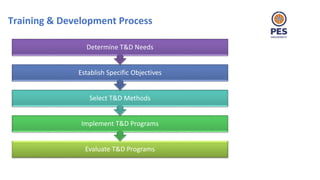
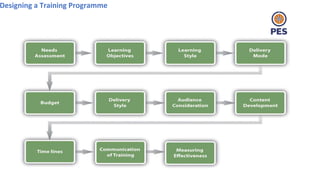
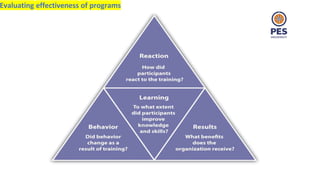
The document outlines principles of human resource management, focusing on recruitment, selection processes, training, and development. It emphasizes the significance of various methods for hiring and employee development, including work samples and simulations, alongside the importance of reliability and validity in selection tests. Additionally, it details training needs assessment, training methods, and the role of training in enhancing organizational efficiency and employee performance.