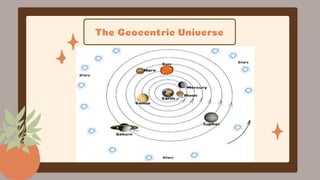
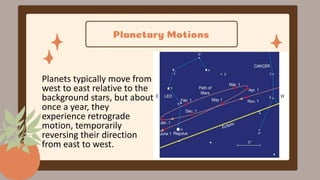
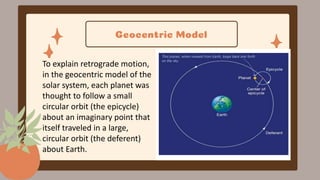
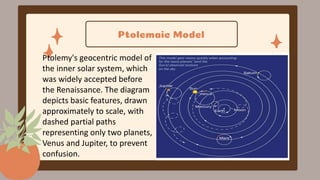
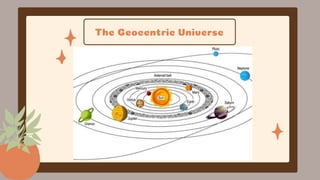
This document discusses the Copernican Revolution in astronomy. It explains that early models placed Earth at the center of the universe, but they could not explain observations of planetary motion. Copernicus proposed that the Sun, not Earth, is at the center of the solar system. Galileo then used a telescope to observe features of the moon, sunspots, and Jupiter's moons that supported Copernicus' model. Kepler analyzed detailed observations by Tycho Brahe to develop his three laws of planetary motion, establishing that planets move in ellipses with the Sun at one focus. Galileo and Kepler's work revolutionized astronomy by displacing Earth from the center and establishing the foundations of modern science.