- A pointer is a variable that stores the address of another variable. Pointers allow dynamic memory allocation and access to the value of the variable being pointed to using the indirection operator (*).
- Pointer variables are declared with a data type followed by an asterisk, such as int *ptr. They can be initialized by using the address-of operator (&) to store the address of another variable.
- Pointers can be used to access elements in an array by using pointer arithmetic. An array name itself is a constant pointer to the first element of the array.











![Pointer and Array
• When an array is declared, the compiler allocates
sufficient amount of memory to contain all the
elements of the array. Base address is the address of
the first element of an array.
Consider, int arr[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
• Assuming that the base address of arr is 2000 and each
integer requires two bytes, the five elements will be
stored as follows:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-pointers-220628152230-c9d72d58/85/PPS-POINTERS-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![Element arr[0] arr[1] arr[2] arr[3] arr[4]
Address 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008
• Here variable arr gives the base address, which is a
constant pointer pointing to the first element of the array.
• Hence arr contains the address of arr[0] i.e 2000. Therefore, arr
is equal to &arr[0].
• Now we can access every element of the array arr by
incrementing the pointer to move from one element to
another.
1 2 3 4 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-pointers-220628152230-c9d72d58/85/PPS-POINTERS-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![Pointer to Array
We can use a pointer to point to an array and then we can use that pointer to access the array
elements.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int *p = a; // Similar to int*p = &a[0]
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%dn", *p);
p++;
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-pointers-220628152230-c9d72d58/85/PPS-POINTERS-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![Output
1
2
3
4
5
Note: *(a+i) is same as a[i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-pointers-220628152230-c9d72d58/85/PPS-POINTERS-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![Array of Pointers
• Like an array of int,float, etc, we can also declare an array of
pointers.
Syntax: datatype *array_name[size];
Example:
int *arr_ptr[5];
Here arr_ptr is an array of 5 integer pointers. It means that this
array can hold the address of 5 integer variables.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-pointers-220628152230-c9d72d58/85/PPS-POINTERS-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![Example:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int *arr_ptr[3];
int a = 10, b = 20, c = 50, i;
arr_ptr[0] = &a;
arr_ptr[1] = &b;
arr_ptr[2] = &c;
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("Address = %dt Value = %dn", arr_ptr[i], *arr_ptr[i]);
}
• return 0;
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-pointers-220628152230-c9d72d58/85/PPS-POINTERS-pptx-17-320.jpg)















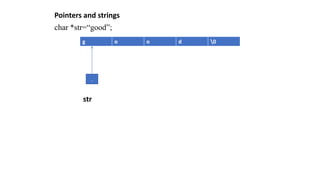
![Pointers and strings
• We know that strings are treated as character arrays
• They can be initialized as follows:
• char str[5] =“good”;
• The compiler will automatically inserts null character ‘0’ at the
end of the string
• C provides a method to create strings using pointer variables of
type char
• char *str=“good”;
• This will create a string and stores its address in the pointer
variable str and str points to the 1st character of the string
“good”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-pointers-220628152230-c9d72d58/85/PPS-POINTERS-pptx-33-320.jpg)
![Pointers and strings
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char str[]="Hello";
char *pstr;
pstr =str;
printf("n The string is:");
while(*pstr!='0')
{
printf("%c",*pstr);
pstr++;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps-pointers-220628152230-c9d72d58/85/PPS-POINTERS-pptx-35-320.jpg)



