The document outlines key concepts and questions from Chapter 14 on company analysis and stock valuation. It discusses differentiating company analysis from stock valuation, growth companies versus growth stocks, valuation approaches and techniques for Walgreens, estimating inputs for valuation models, and techniques for estimating company sales, margins, and earnings. It also addresses factors for estimating earnings multipliers, competitive strategies, relative valuation ratios, present value of cash flow models, and value-added measures like EVA, MVA, and franchise value.






































![Required Rate of Return Estimate
• Nominal risk-free interest rate
• Risk premium
• Market-based risk estimated from the firm’s
characteristic line using regression
E(RFR)]
)
E(R
[
E(RFR)
R market
stock
stock
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pp14-230414120726-816fe843/85/PP14-ppt-39-320.jpg)
















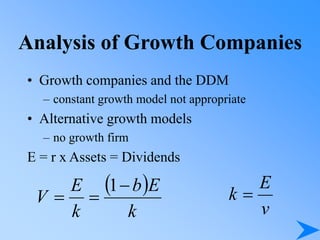
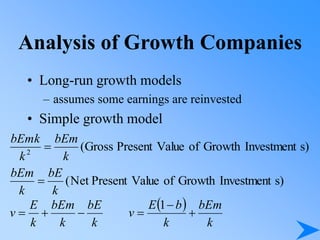
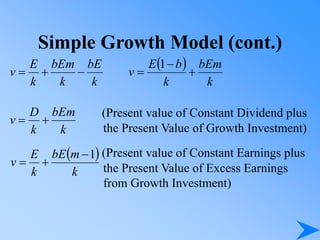






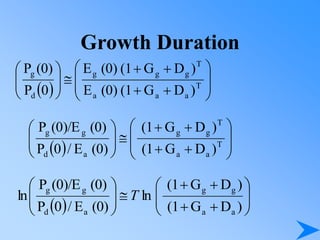
![Growth Duration
E’(t) = E (0) (1+G)t
N(t) = N(0)(1+D)t
E’(t) = E’(t) N(t) = E (0) [(1+G)t (1+D)]t
t
D)
G
(1
(0)
E
E(t)
T
a
a
a
T
g
g
g
d
g
)
D
G
(1
(0)
E
)
D
G
(1
(0)
E
0
P
(0)
P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pp14-230414120726-816fe843/85/PP14-ppt-67-320.jpg)