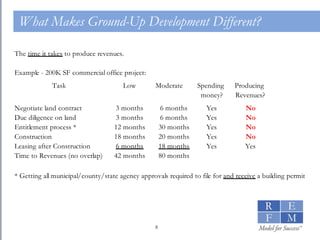
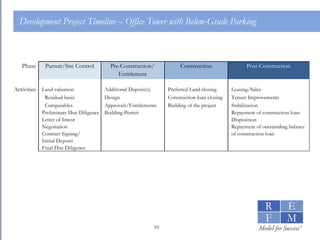
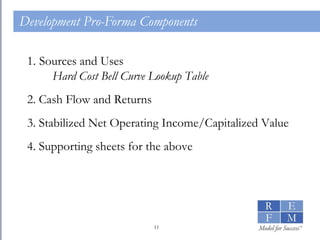
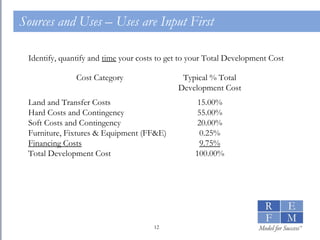
1. The document discusses the basics of real estate development modeling including goals of building confidence, enabling better analysis of investments, and increasing credibility. 2. It defines financial modeling as forecasting future financial outcomes based on current assumptions and provides "cardinal rules" for effective modeling like ensuring assumptions are reliable and annotating models. 3. It outlines key components of a development pro forma model including sources and uses, hard costs modeled as a bell curve, soft costs, furniture/fixtures/equipment, and financing costs.