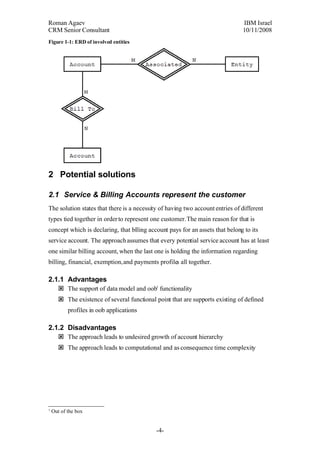
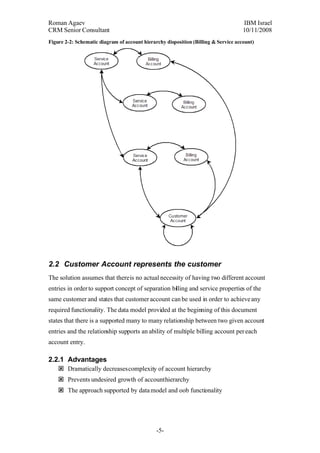
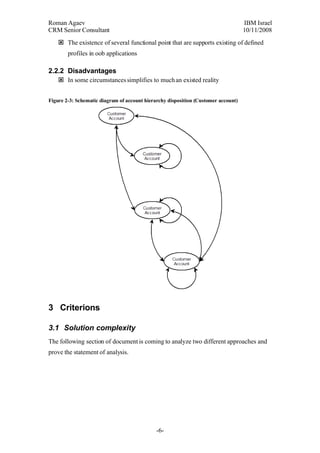
This document proposes two approaches to account structure: 1) having separate service and billing accounts represent a customer, and 2) having a single customer account represent a customer. The single customer account approach decreases complexity and prevents unnecessary account growth while still supporting necessary functionality. However, it may oversimplify some real-world scenarios. The best solution may be a combined approach using customer accounts for private customers and separate service/billing accounts for corporate customers.