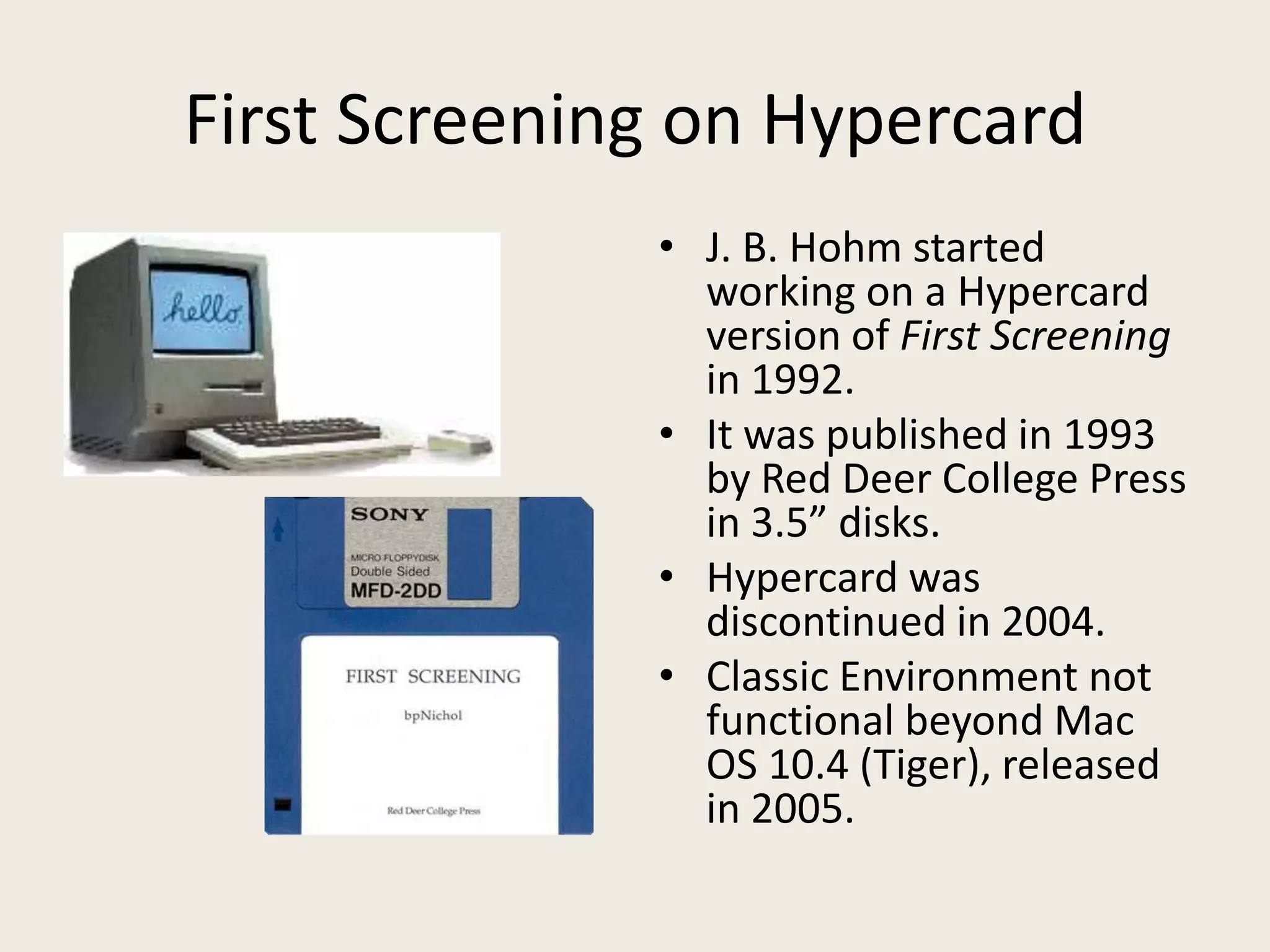
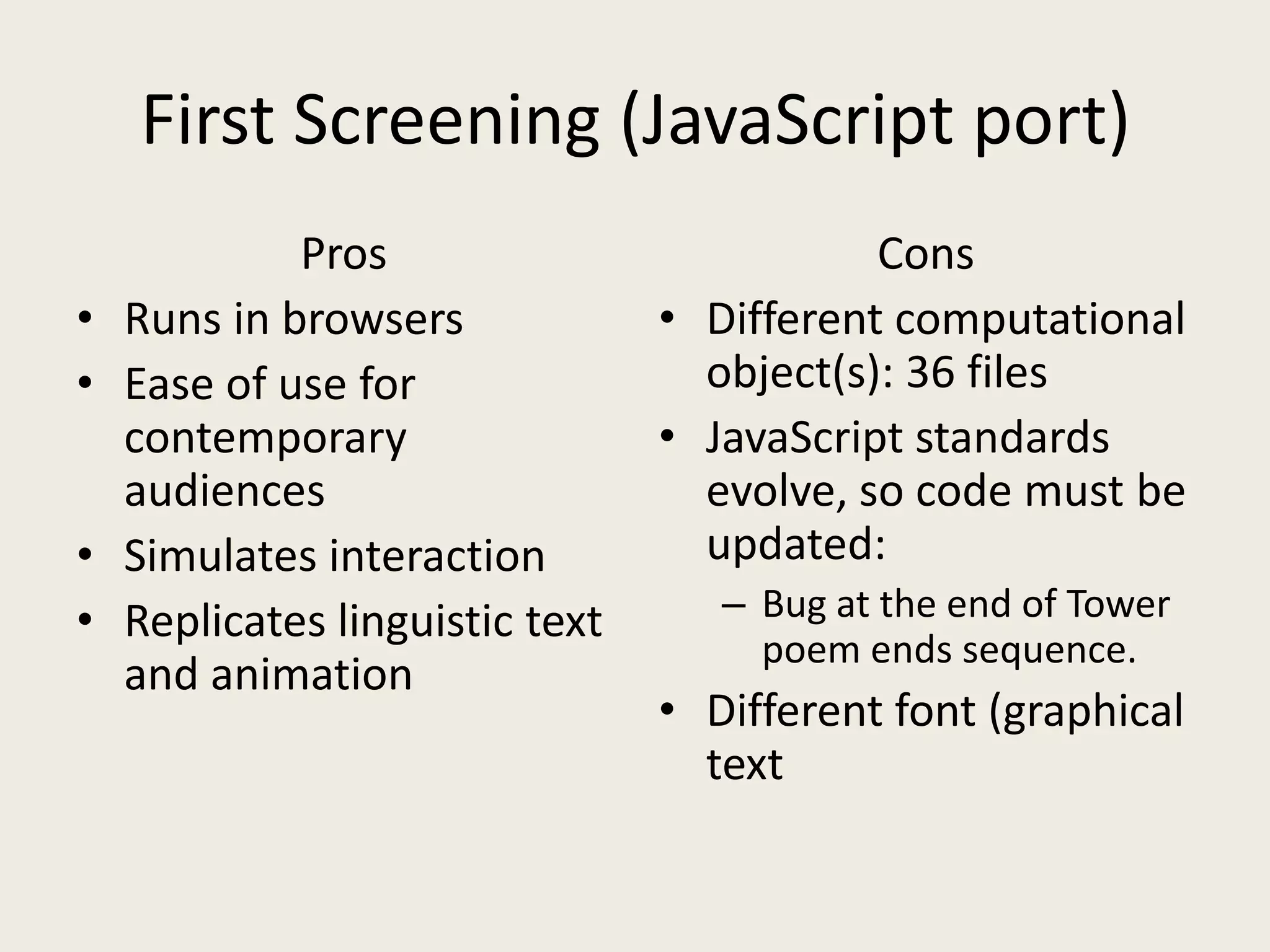
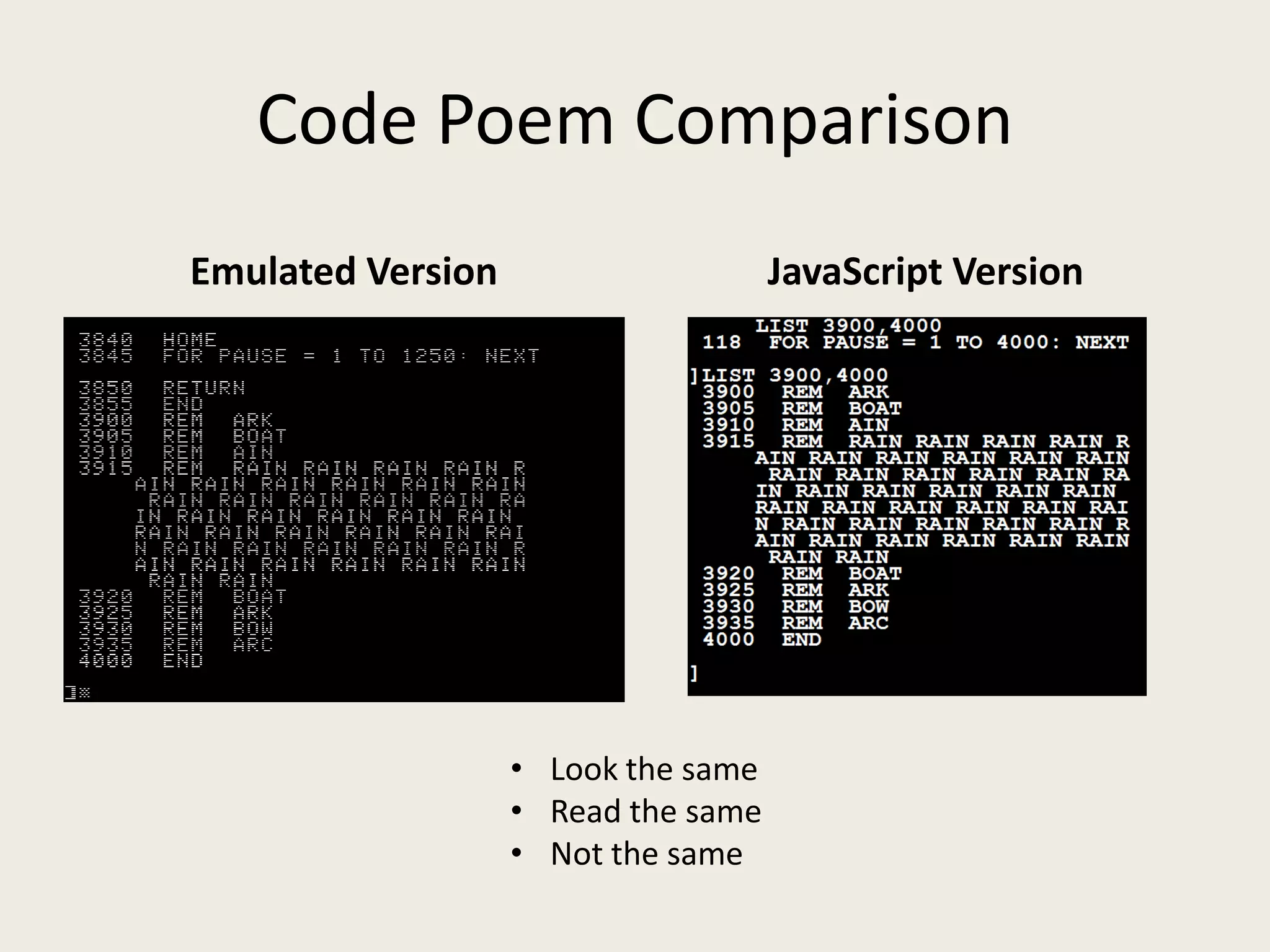
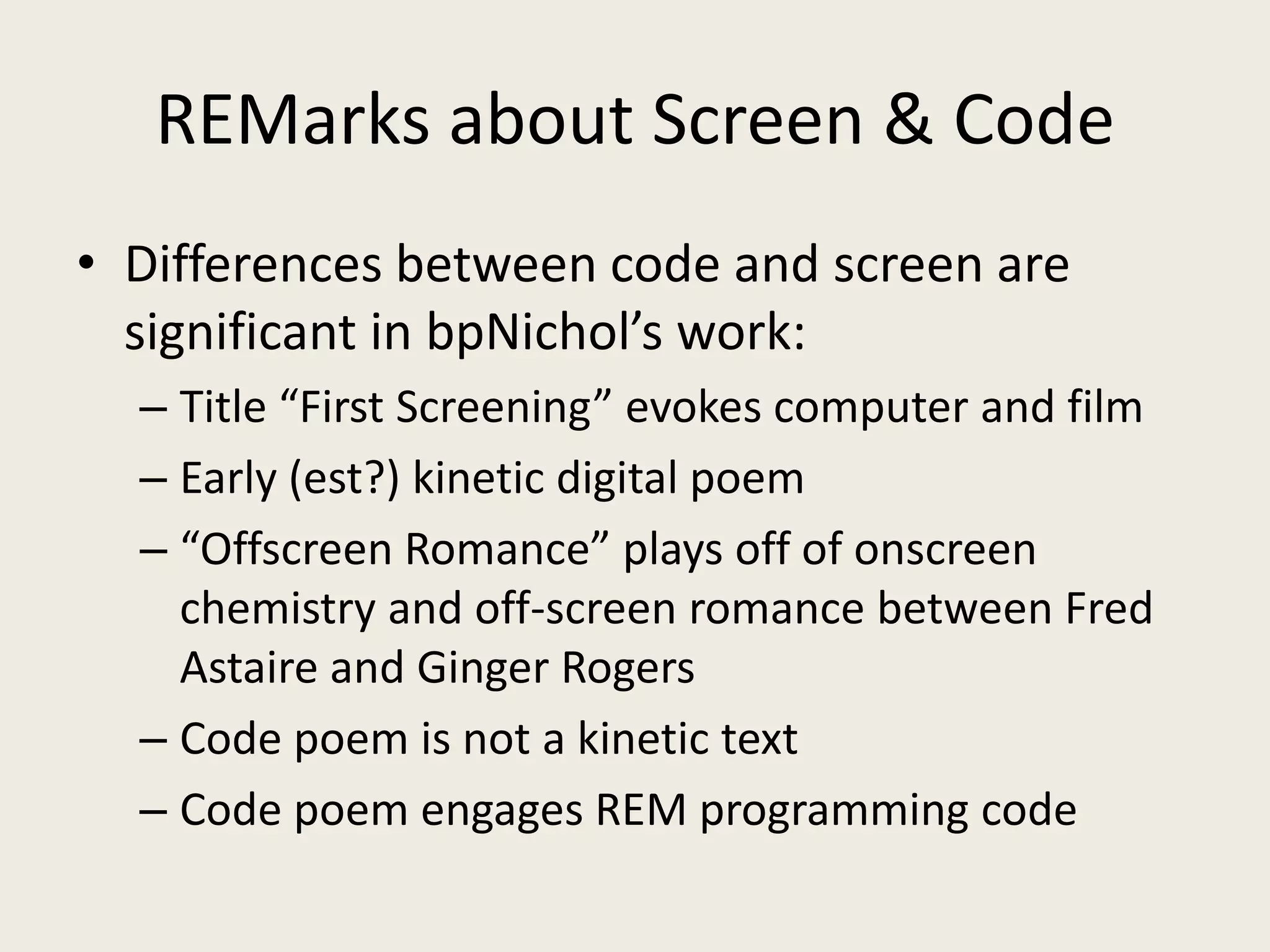
The document discusses digital preservation methods for electronic literature using the case of 'First Screening' by bpNichol, focusing on techniques like emulation, porting, and documentation. It highlights the challenges of translating e-literature to new formats while preserving linguistic text, graphical text, and interactivity. Recommendations include producing multiple versions, documenting decisions, and considering the original programming environment for effective preservation.