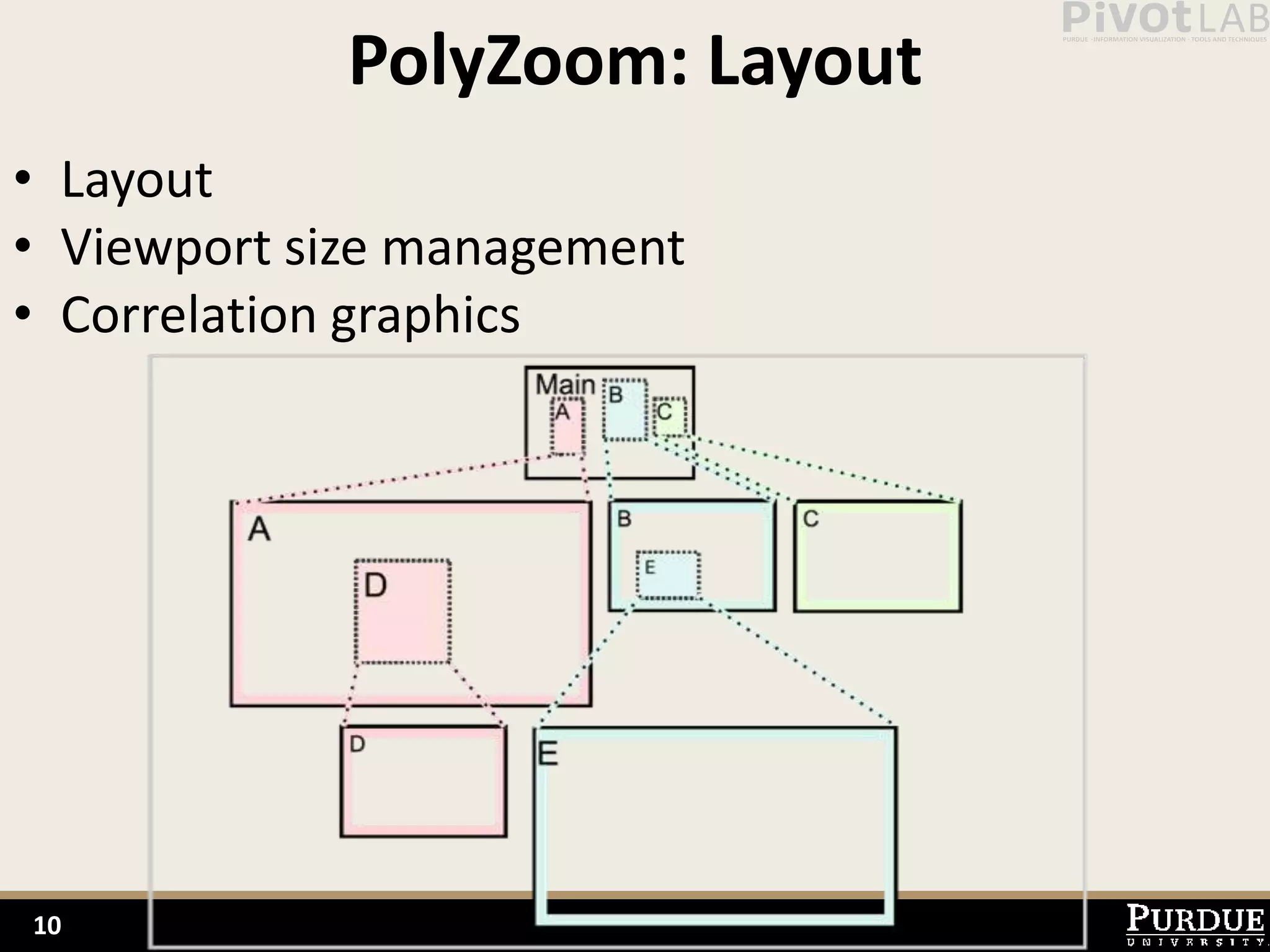
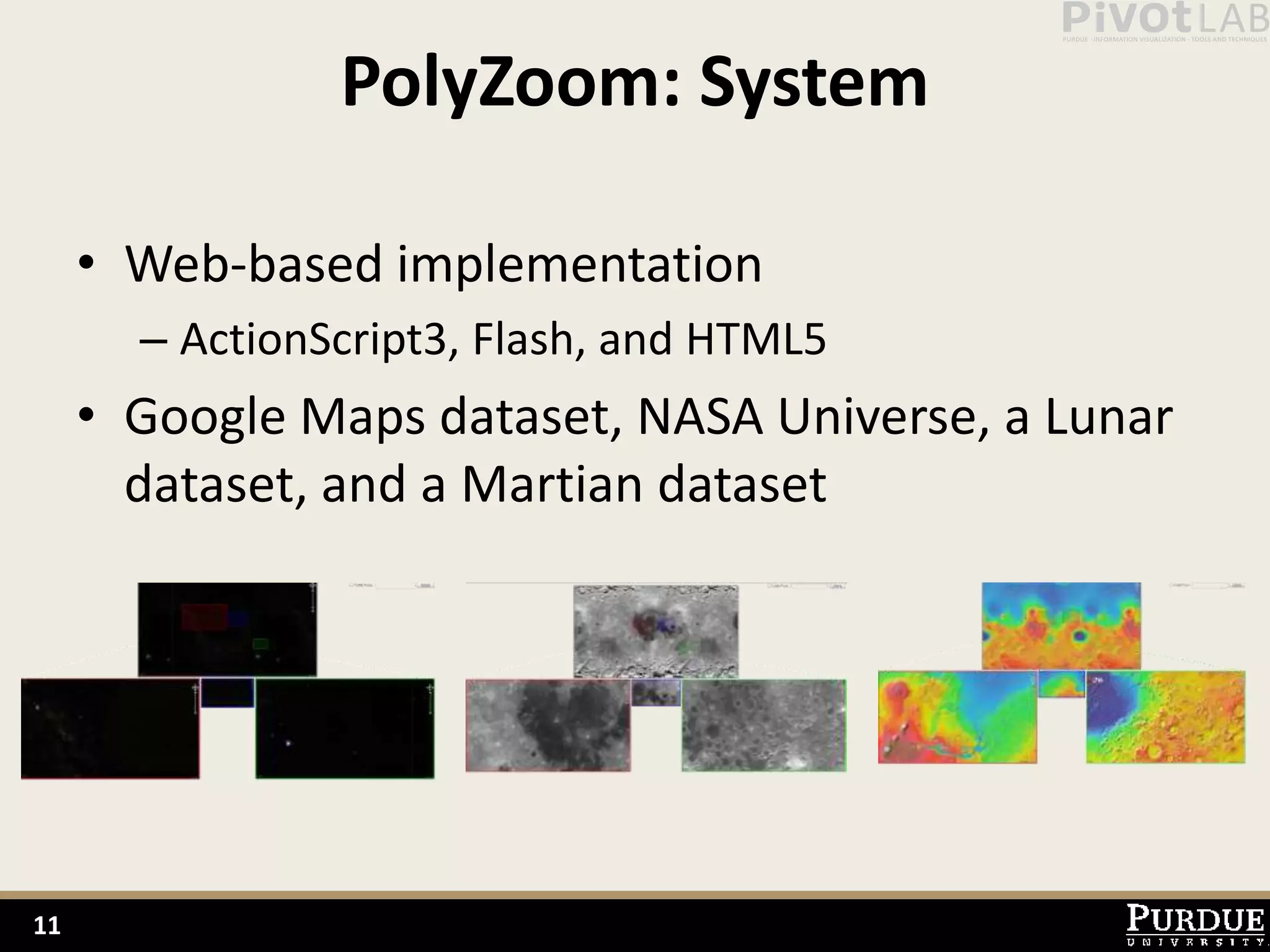
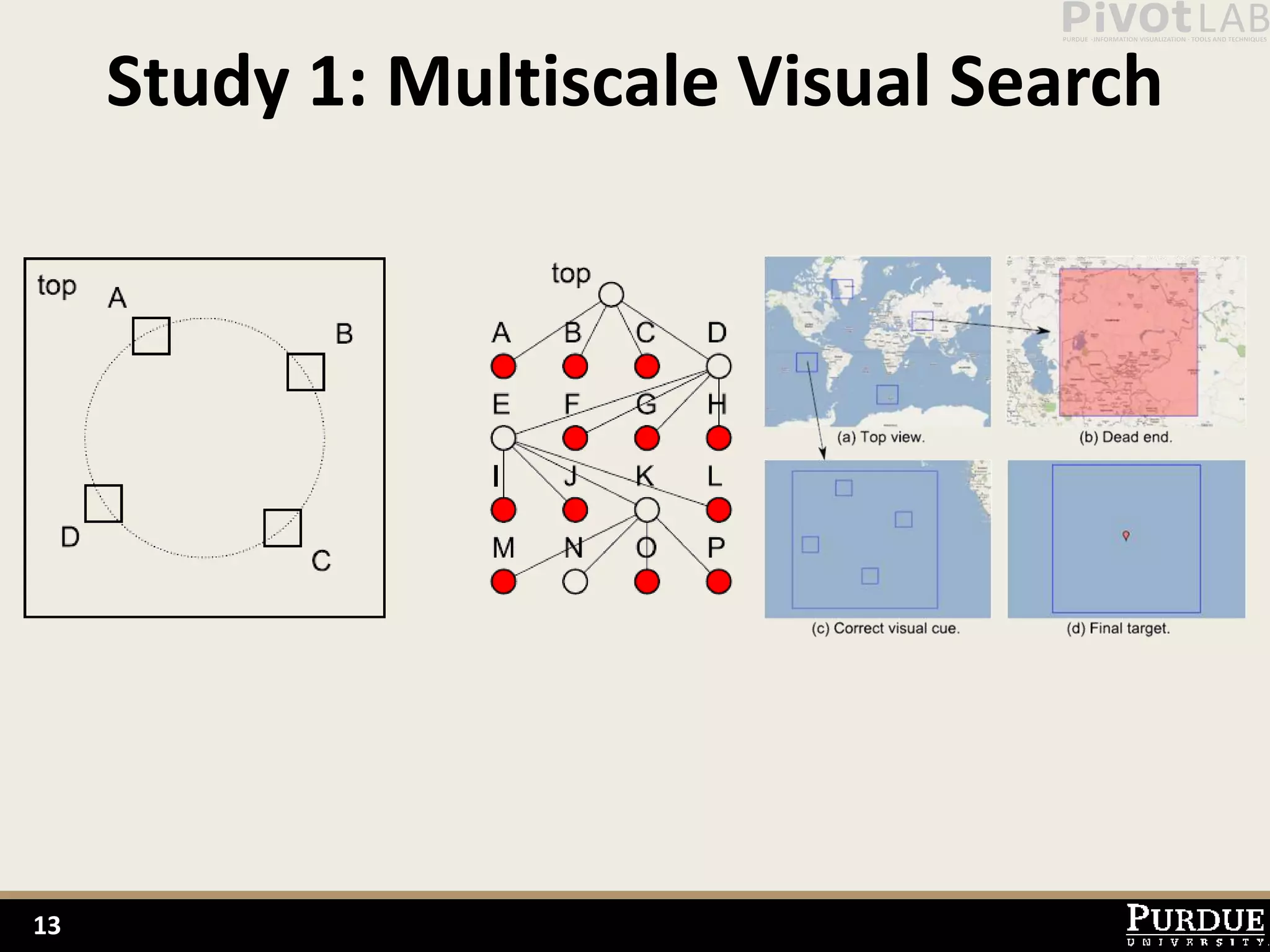
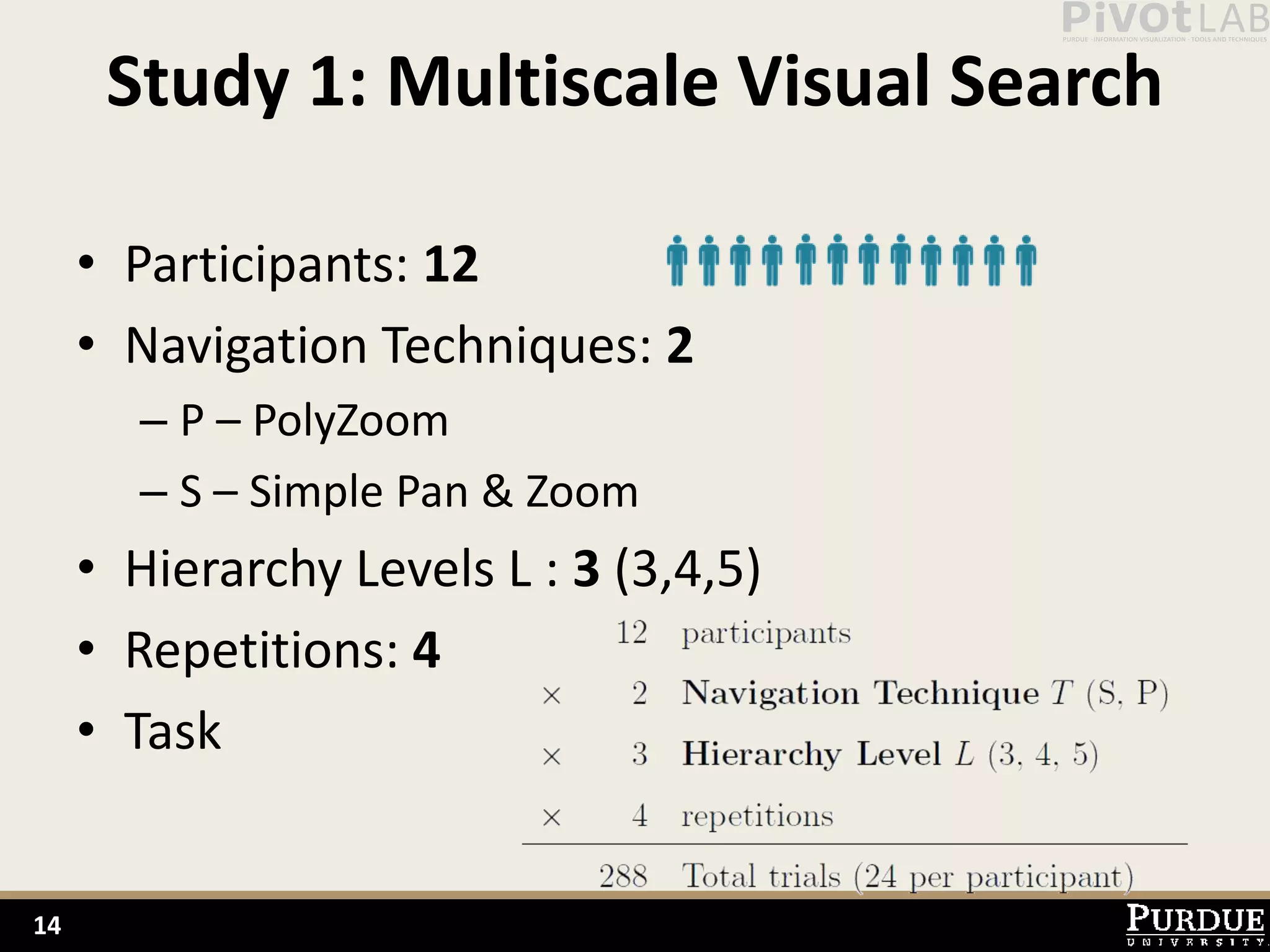
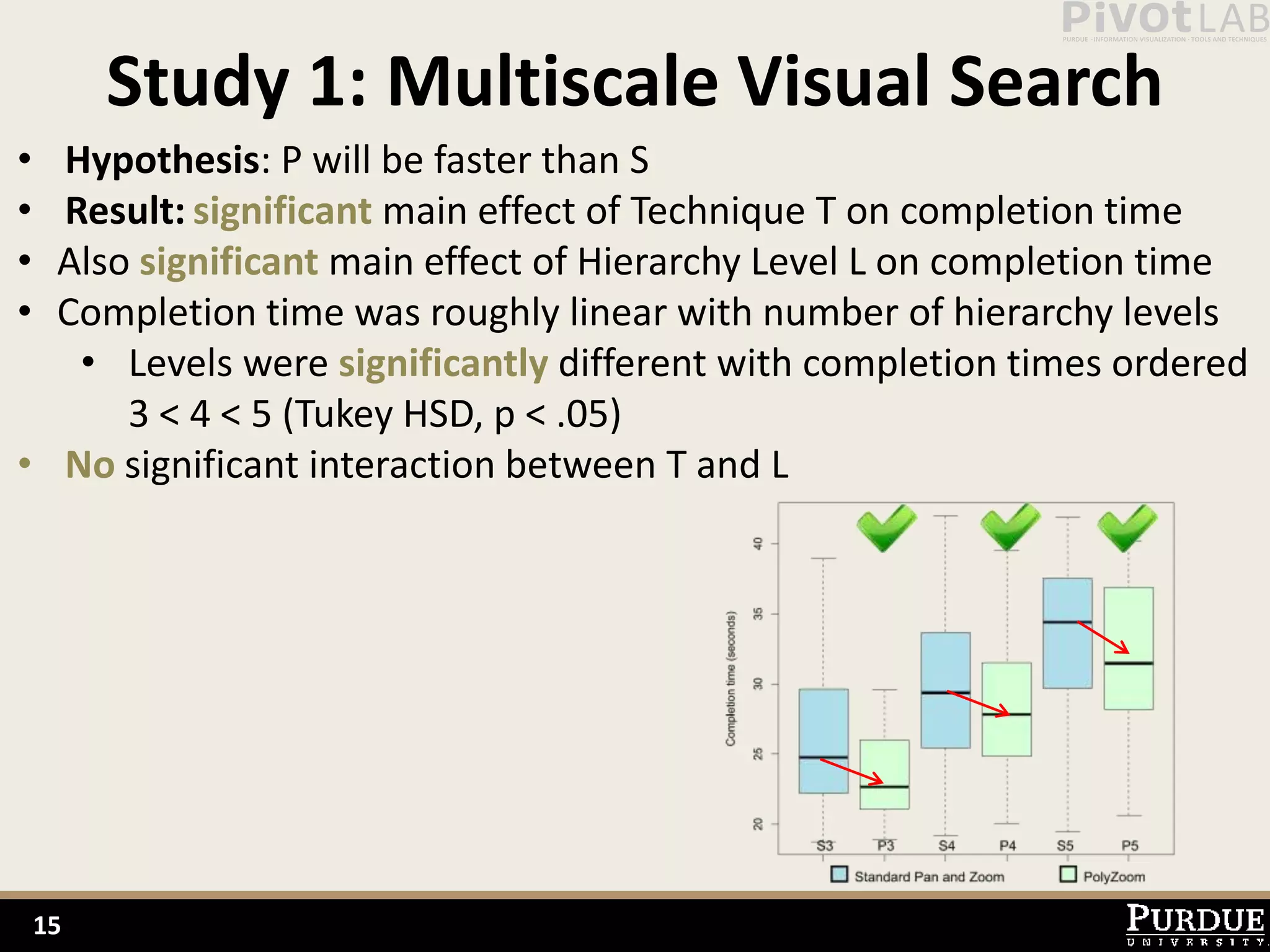
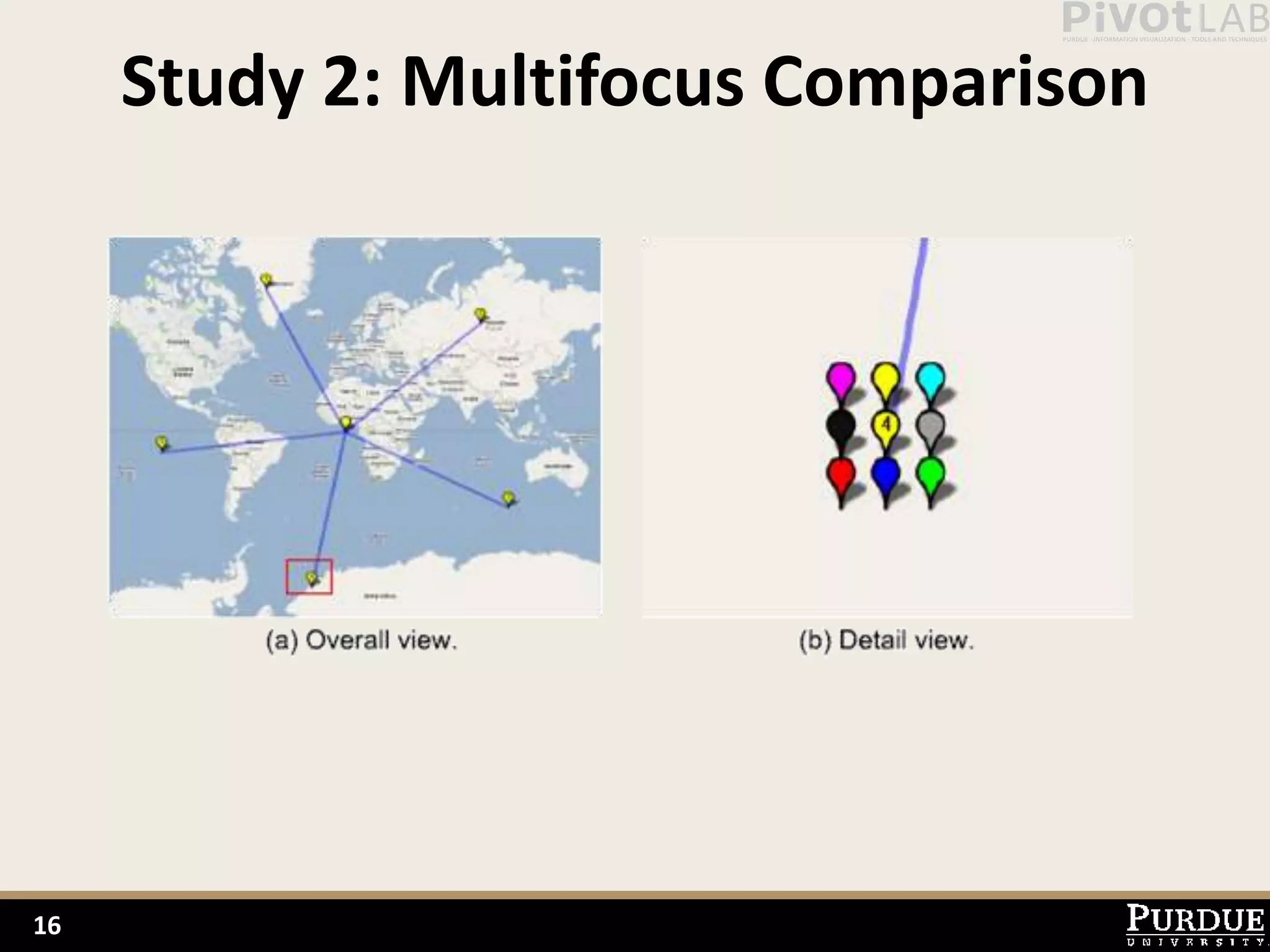
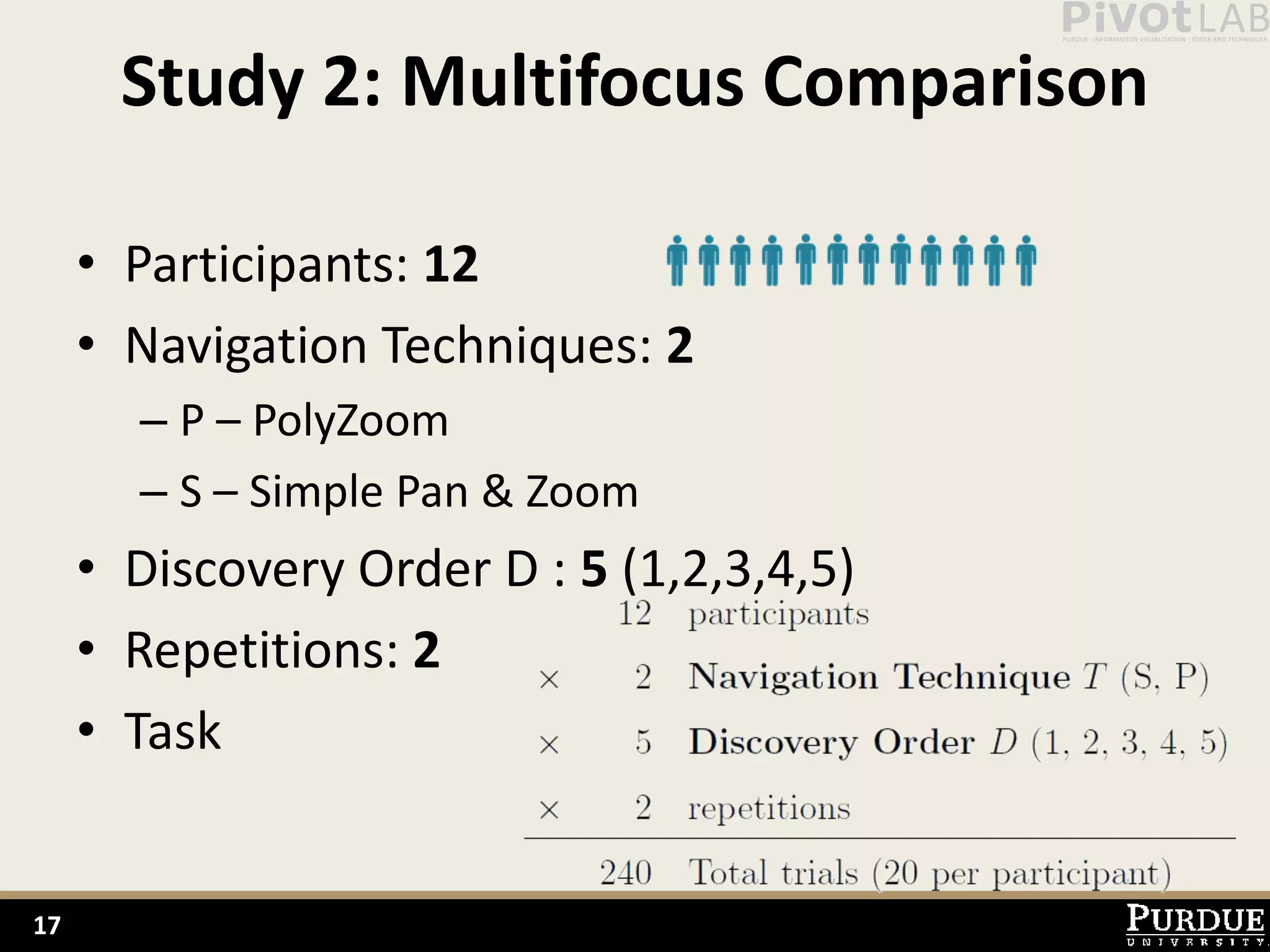
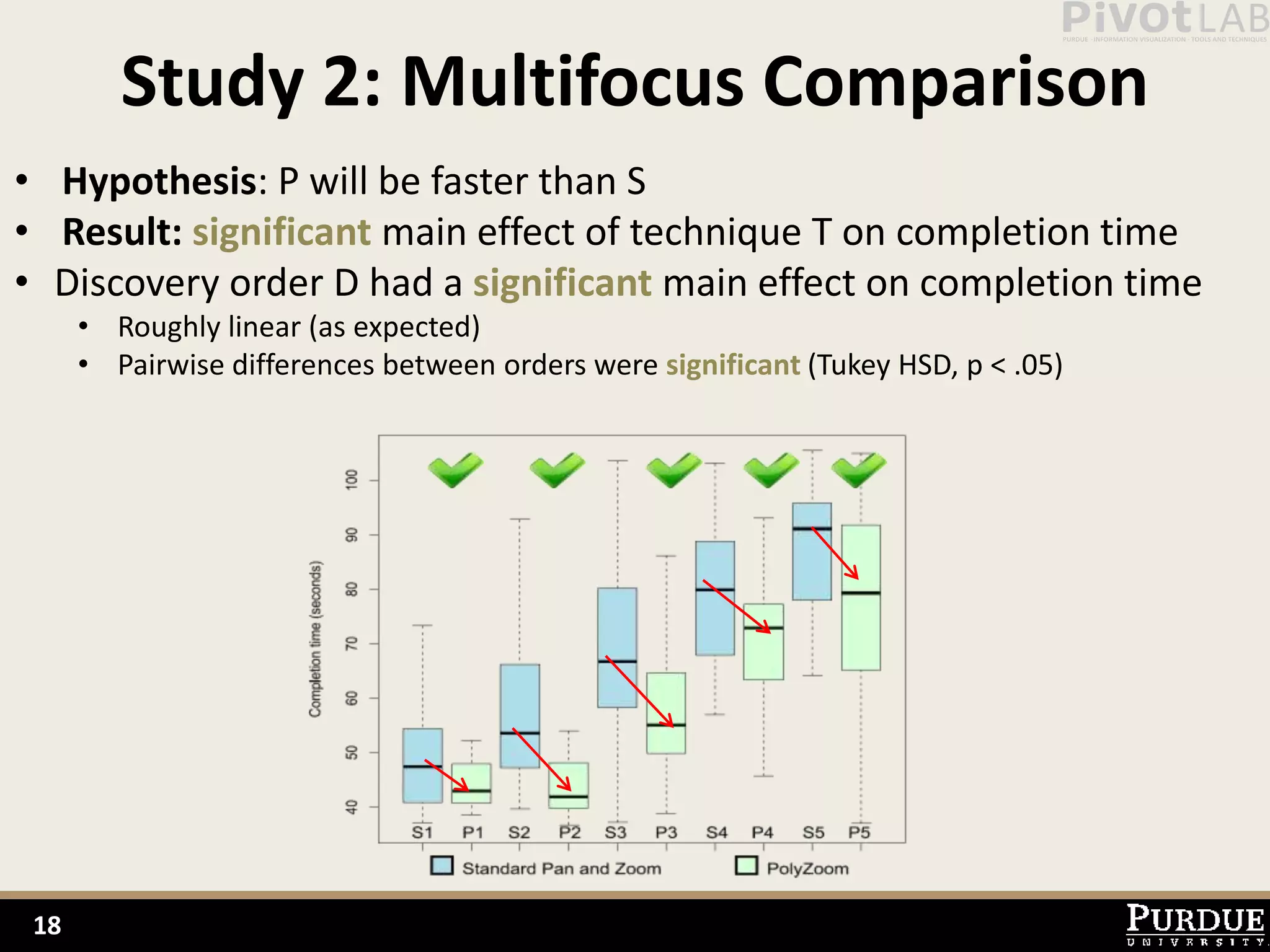
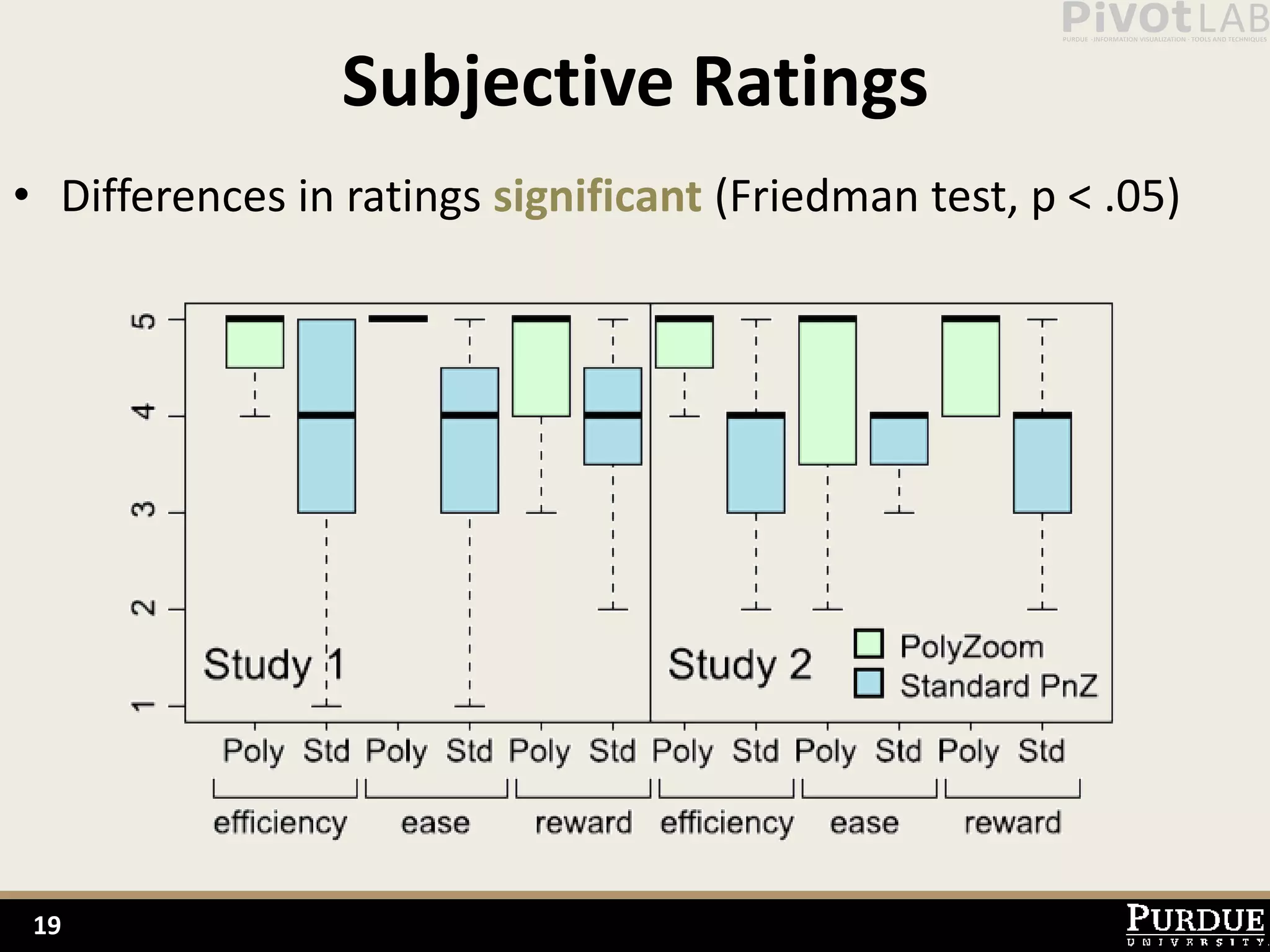
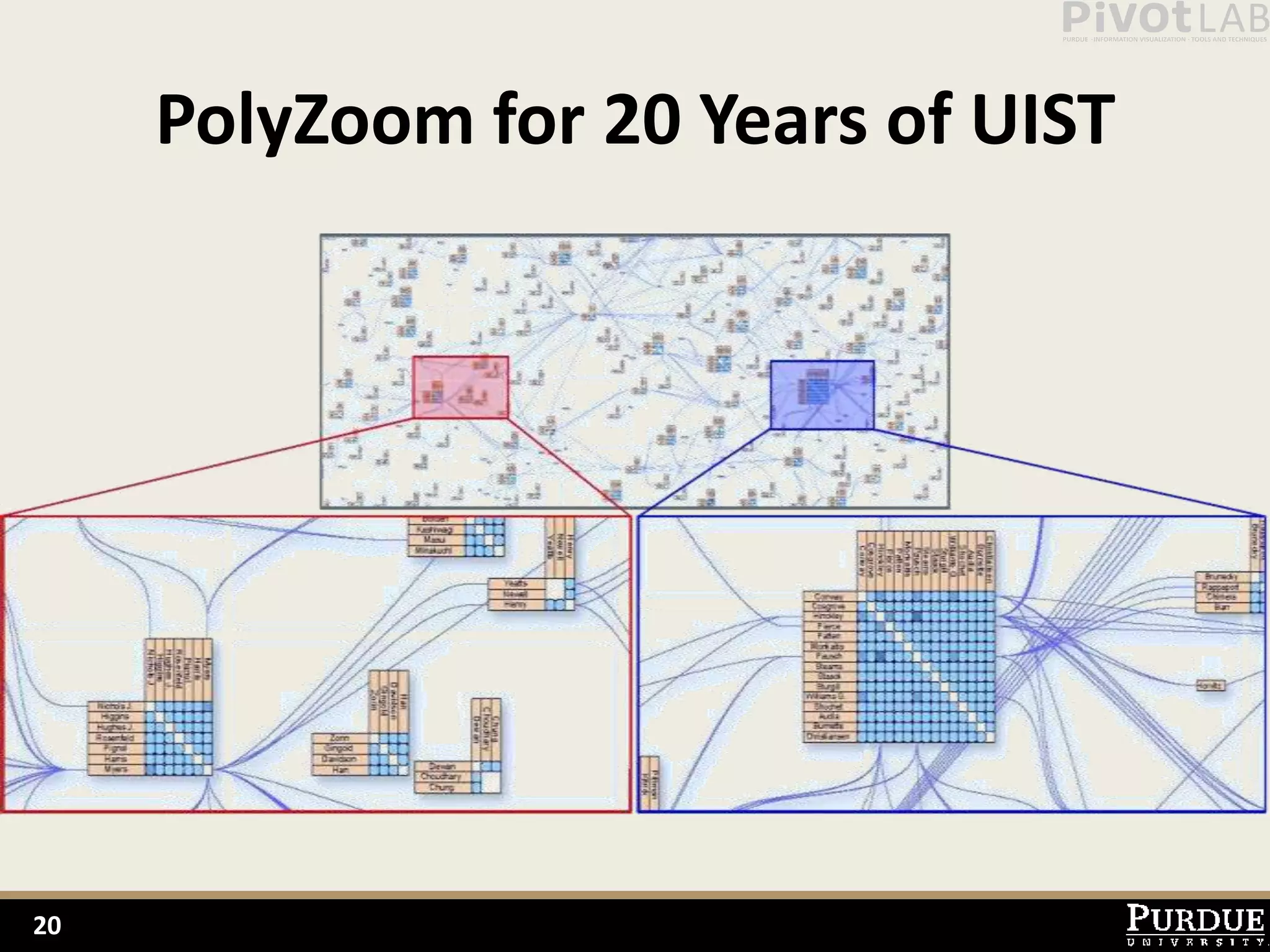
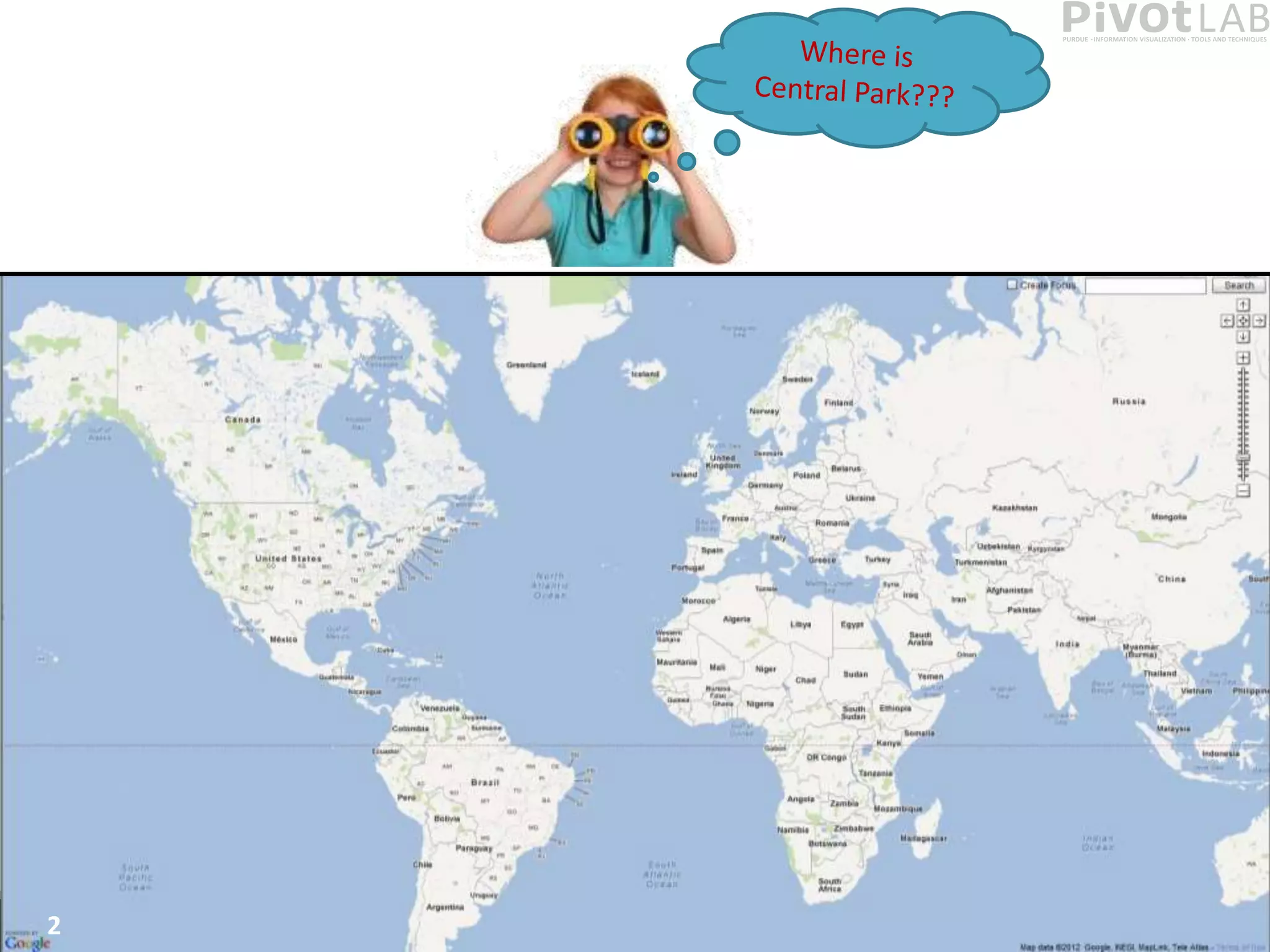
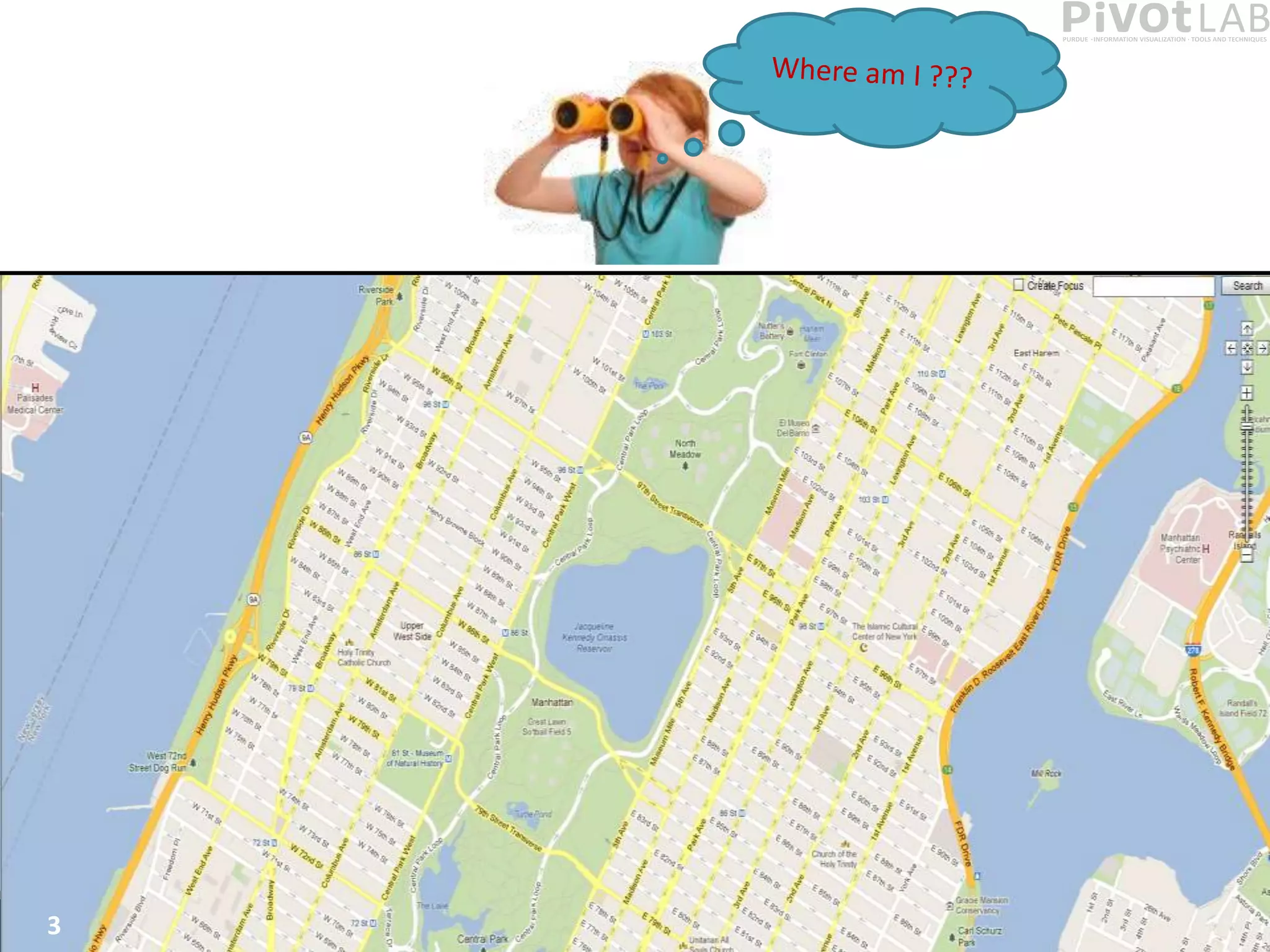
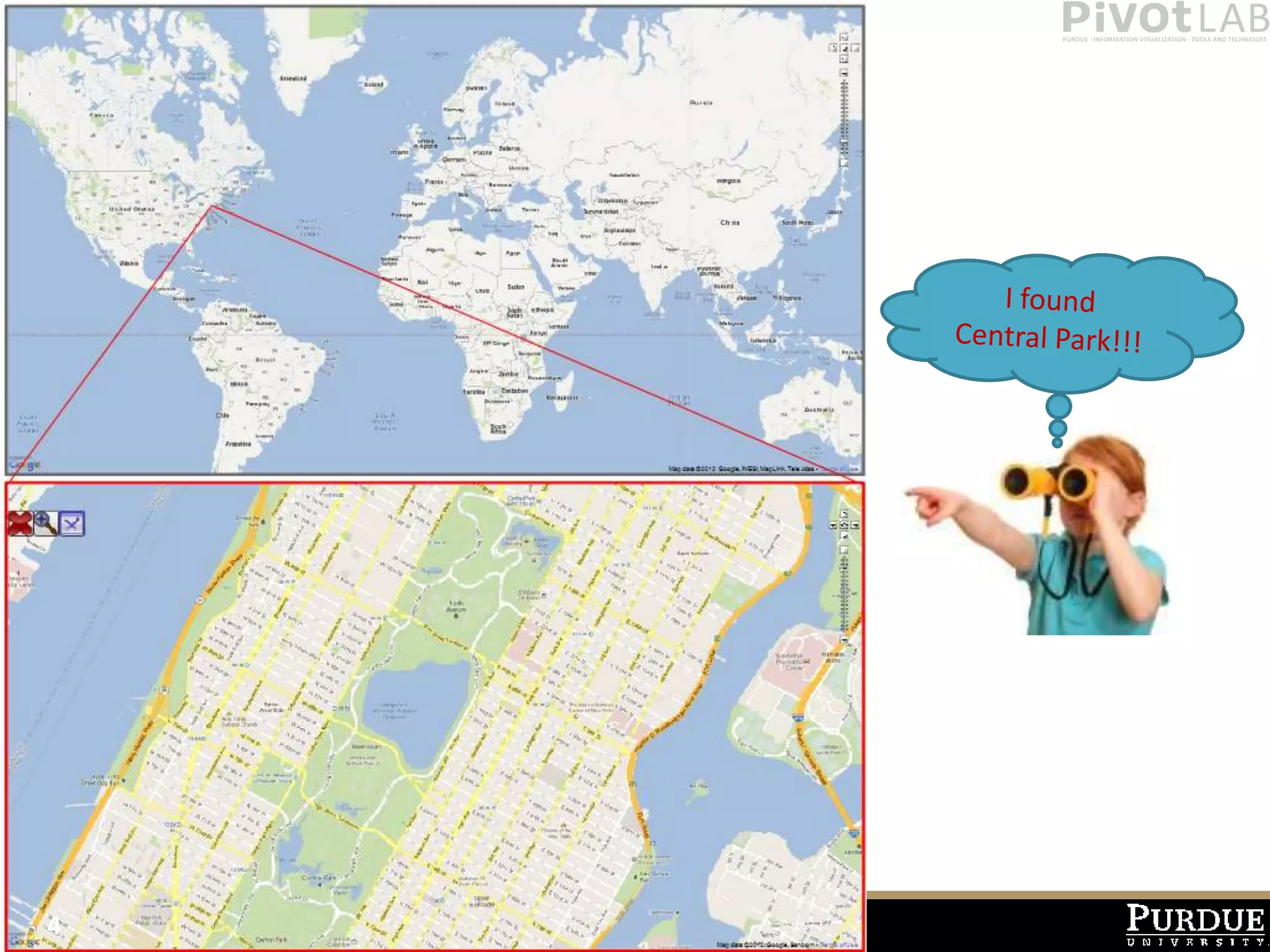
The document presents Polyzoom, a multiscale and multifocus navigation technique for 2D visual spaces, aimed to improve user interaction in large datasets like Google Maps. Two user studies demonstrate that Polyzoom significantly outperforms traditional pan and zoom techniques in terms of completion time for both multiscale visual searches and multifocus comparisons. The design goals of Polyzoom include maintaining multiscale and multifocus awareness without distortion or overlap.


![PolyZoom
• PolyZoom is a multiscale multifocus technique for navigating in 2D
visual spaces
– Allows users to iteratively build a hierarchy of focus regions
– Allows maintaining awareness of multiple scales of the visual space
• [Video]
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polyzoom-web-120507145426-phpapp01/75/PolyZoom-Multiscale-and-Multifocus-Exploration-in-2D-Visual-Spaces-7-2048.jpg)