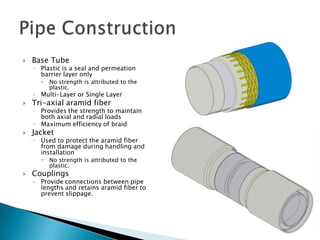
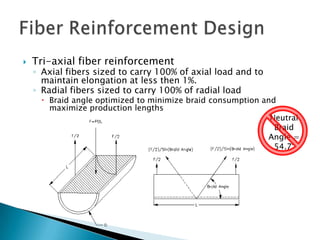
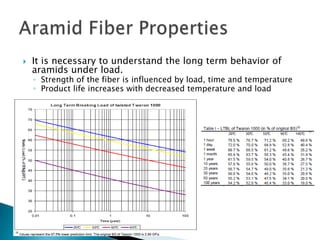
The document discusses the design of an aramid fiber reinforced pipe. It is designed to have a minimum 20 year lifespan operating at maximum allowable operating pressure (MAOP) and withstand hydrostatic testing up to 1.25x MAOP for 8 hours up to 3 times without degrading the 20 year design life. The pipe strength comes solely from the aramid fiber reinforcement, while the plastic layers provide a barrier but no strength. Various design considerations, such as fiber selection and long-term strength behavior, are discussed.