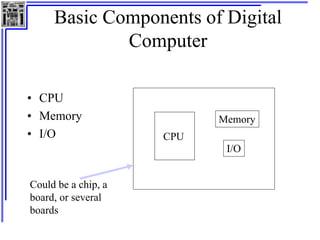
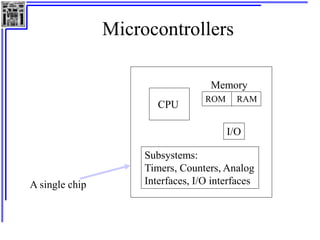
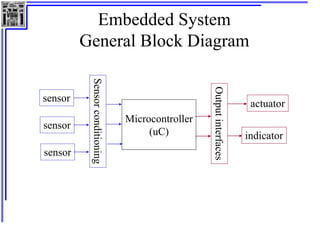
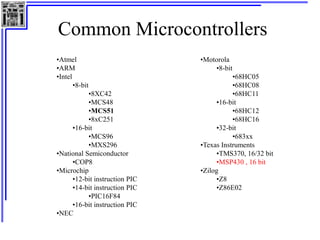
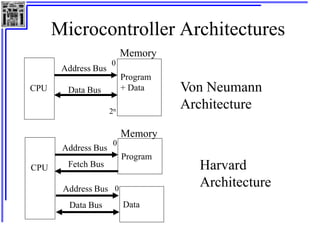
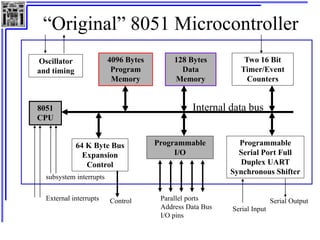
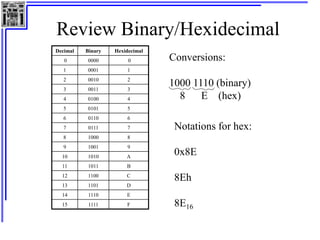
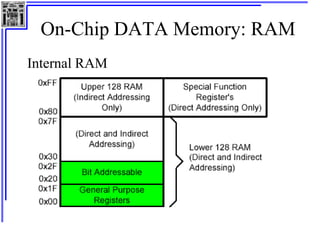
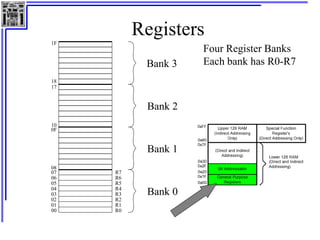
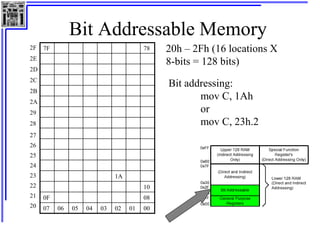
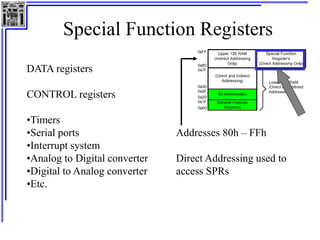
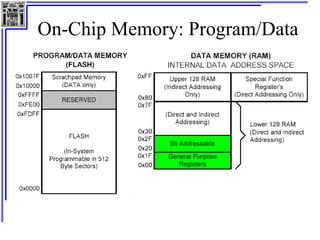
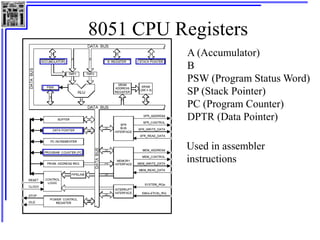
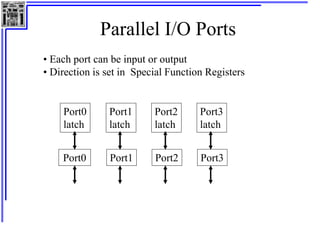
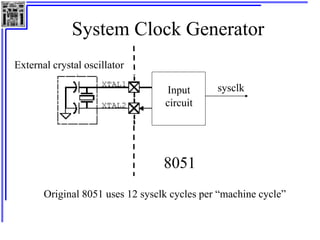
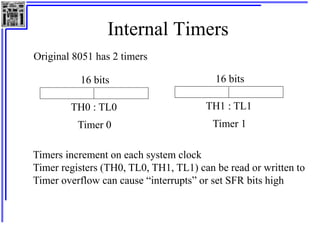
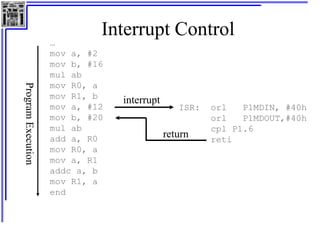
This document provides an overview of microcontrollers and the MSP430 family. It discusses the basic components of digital computers and microcontrollers. Microcontrollers integrate a CPU, memory, and input/output ports on a single chip. Embedded systems use microcontrollers to provide real-time control through sensors and actuators. Common microcontrollers include those from Texas Instruments, Atmel, Intel and others. The MSP430 is a 16-bit microcontroller from TI. Specific features of the 8051 microcontroller family such as memory organization, registers, I/O ports, timers and interrupt control are described.