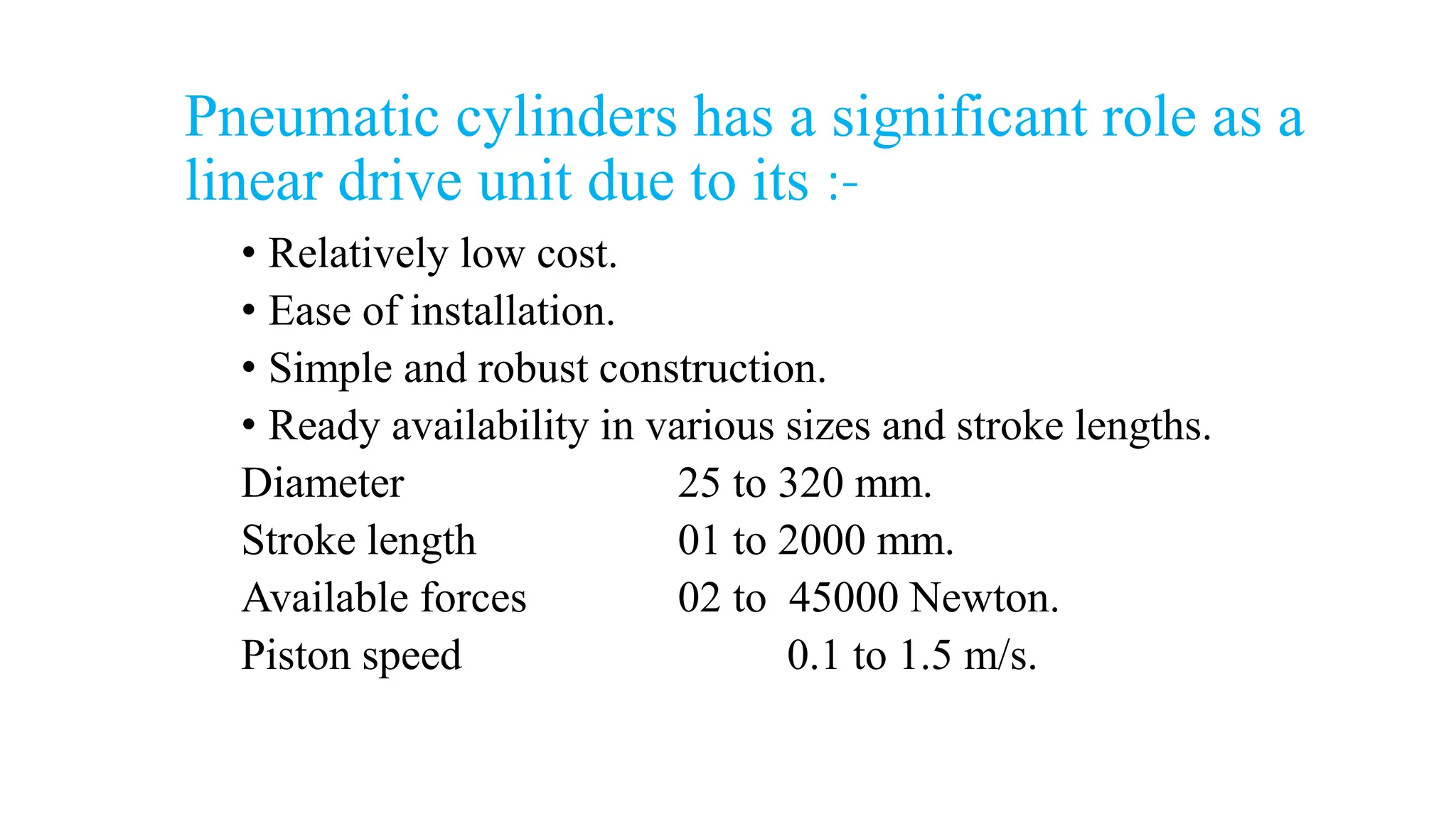
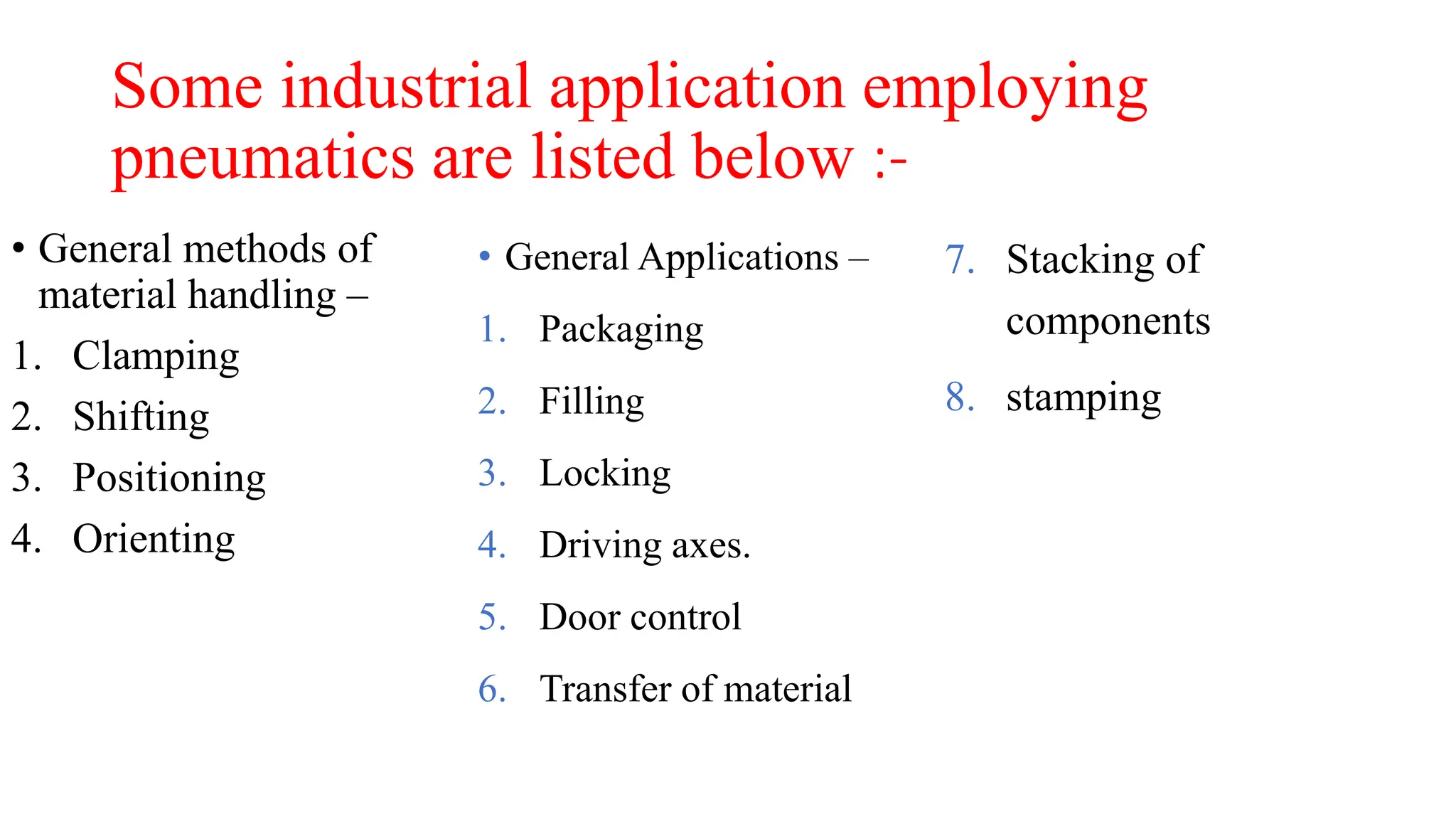
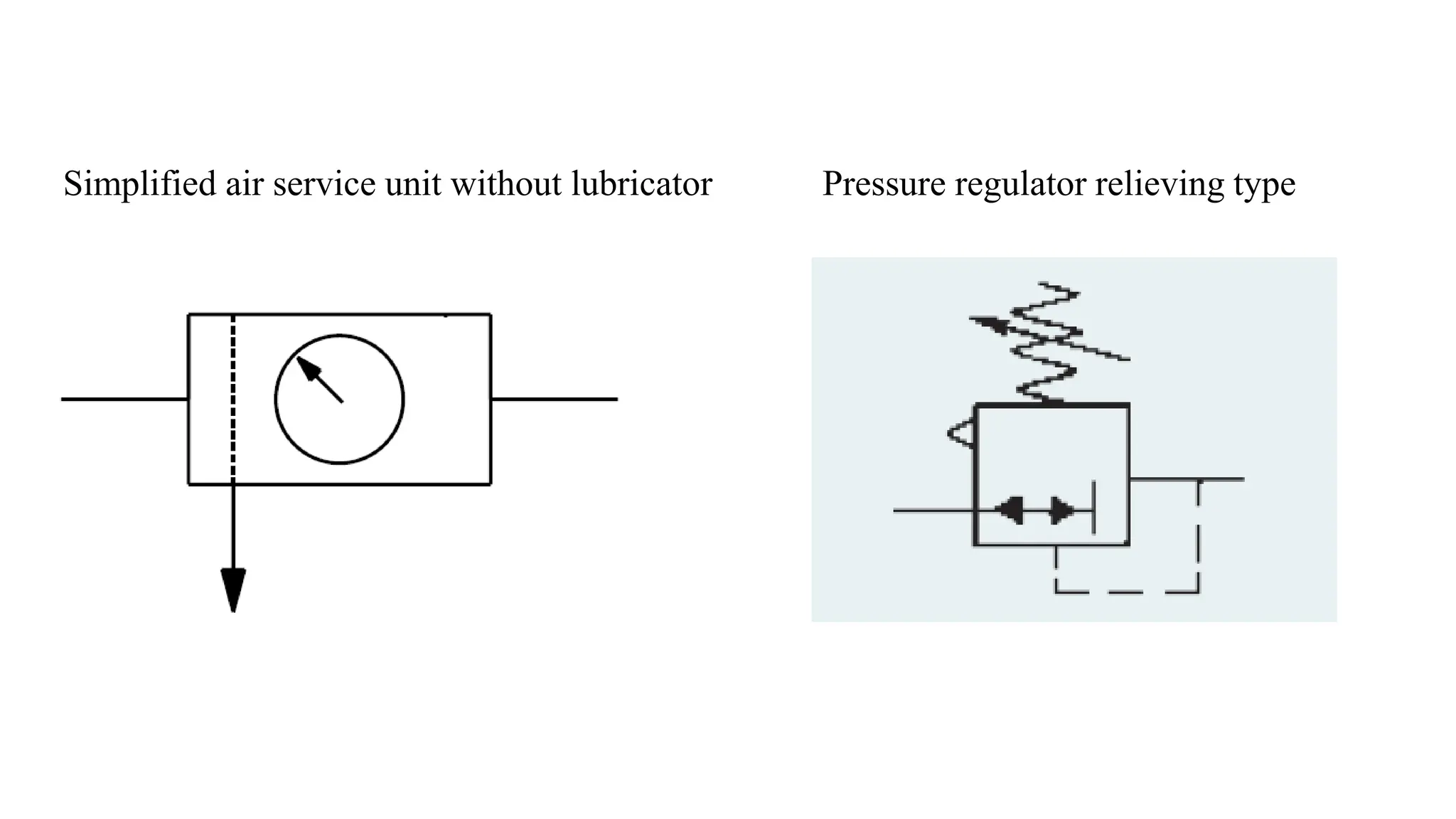
Pneumatics is the science dealing with the properties and behavior of compressed air, used to create motion and generate forces in various applications. Pneumatic systems, characterized by components such as cylinders, are cost-effective, easy to install, and widely used in industrial settings like material handling, packaging, and machinery operation. The advantages of using compressed air include its availability, safety, cleanliness, and the ability to transport and store energy effectively.