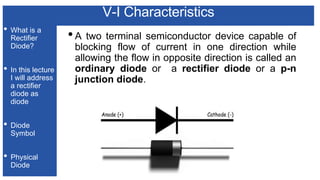
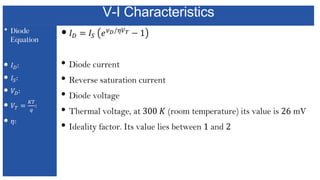
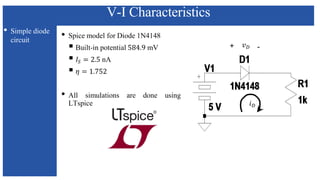
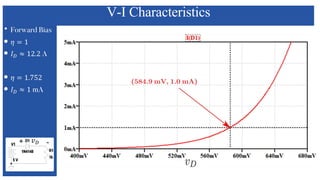
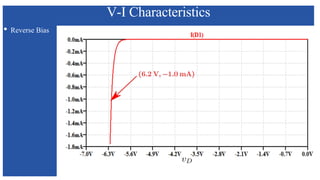
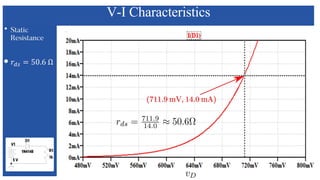
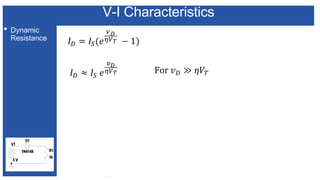
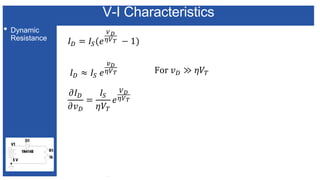
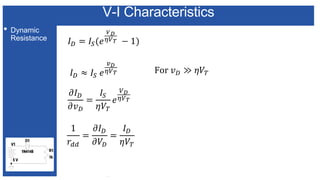
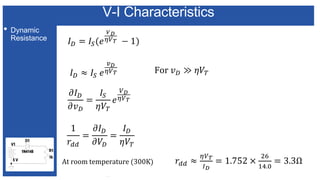
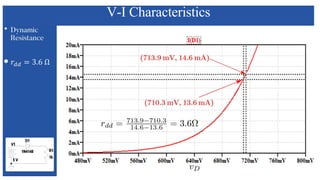
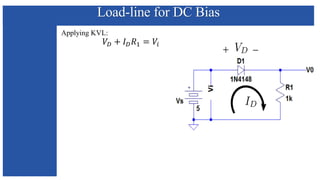
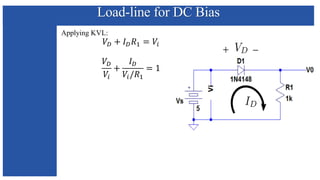
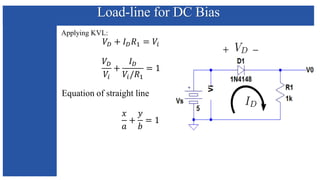
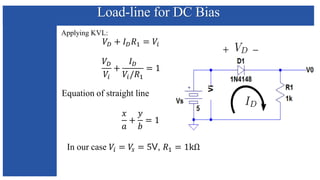
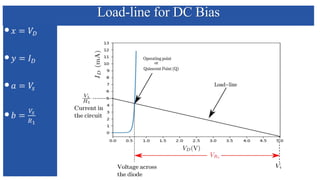
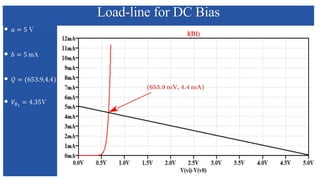
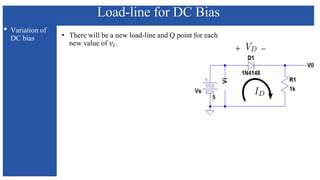
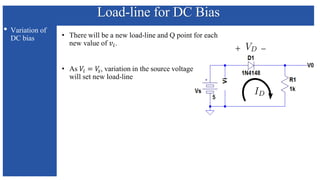
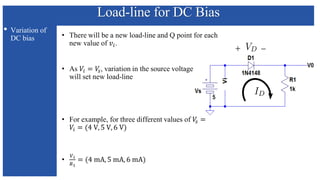
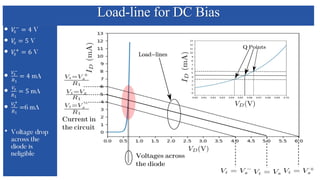
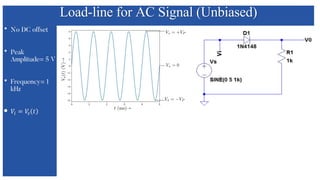
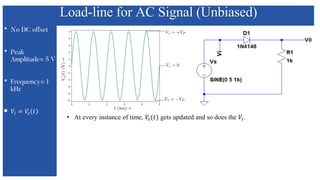
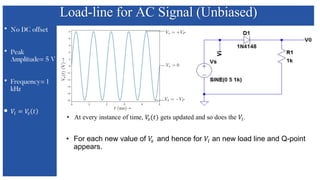
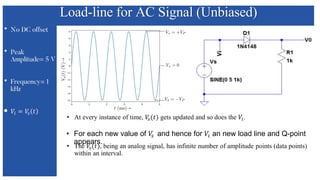
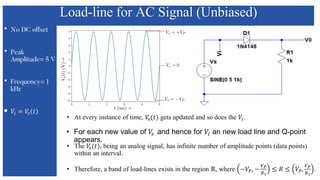
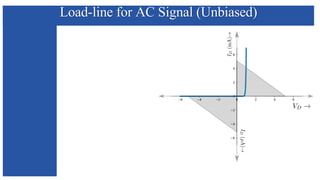
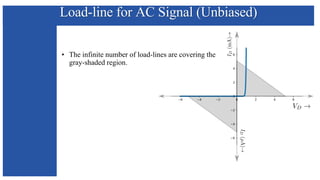
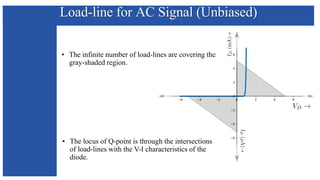
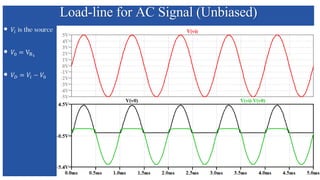
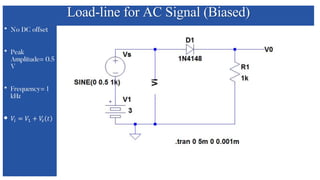
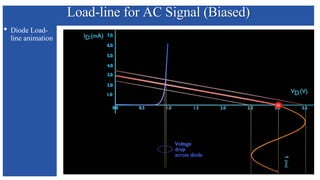
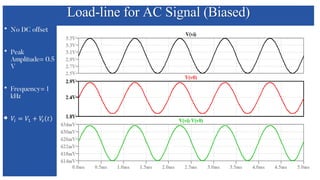
The document discusses the characteristics and functioning of p-n junction diodes, emphasizing their V-I characteristics, load lines, and operating points. It details how forward and reverse bias affects current flow, the role of load lines in circuit behavior, and how variations in load resistance and applied voltage influence the Q-point. Additionally, it explains the concepts of dynamic resistance and the operating characteristics of different types of diodes.