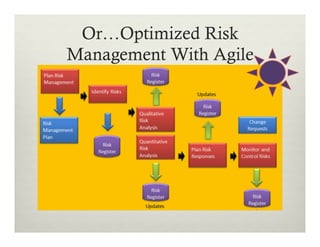
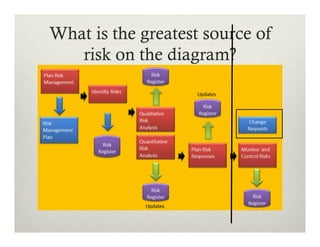
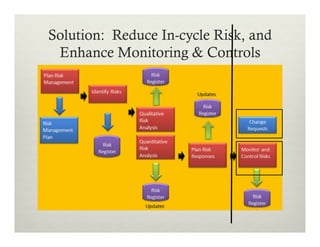
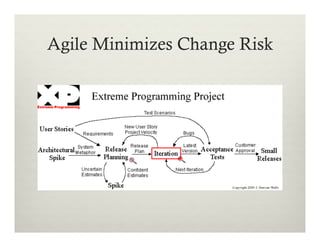
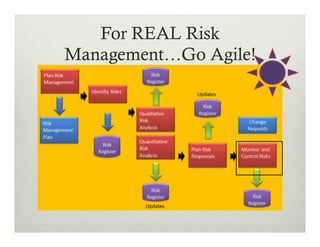
This document summarizes a presentation on using Agile practices to manage risks in software development projects. It discusses how core Agile practices like frequent collaboration, iterative delivery of working software, and addressing hard problems earlier can help reduce and control risks. It also explains how scaled Agile frameworks and practices like automated testing, continuous integration and delivery further enhance risk monitoring and management. The overall proposition is that Agile approaches are better than traditional methods for managing risks and improving control over project delivery outcomes.