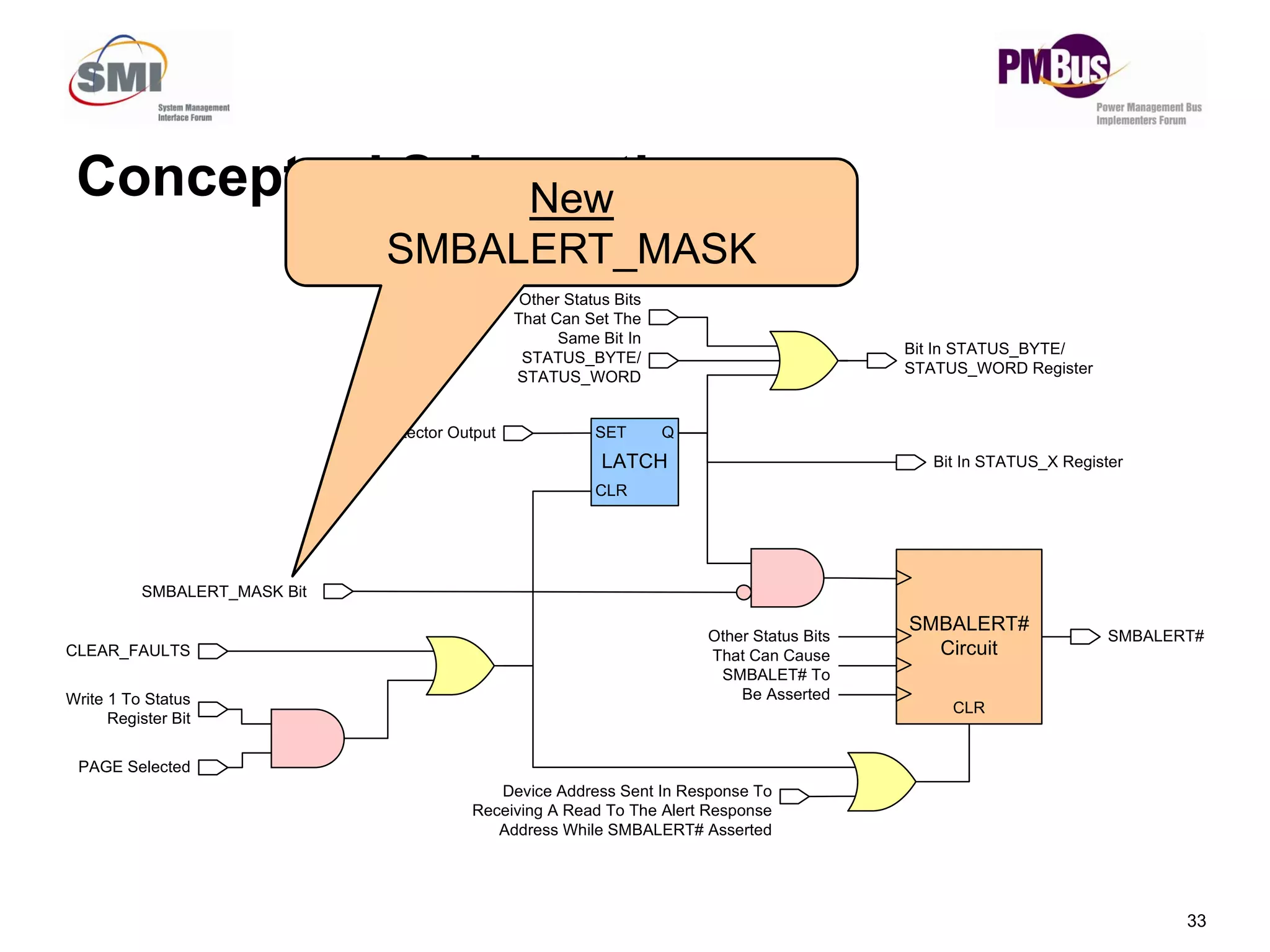
The document discusses updates to the PMBus specification and application profiles to better support servers and data centers. Key points include:
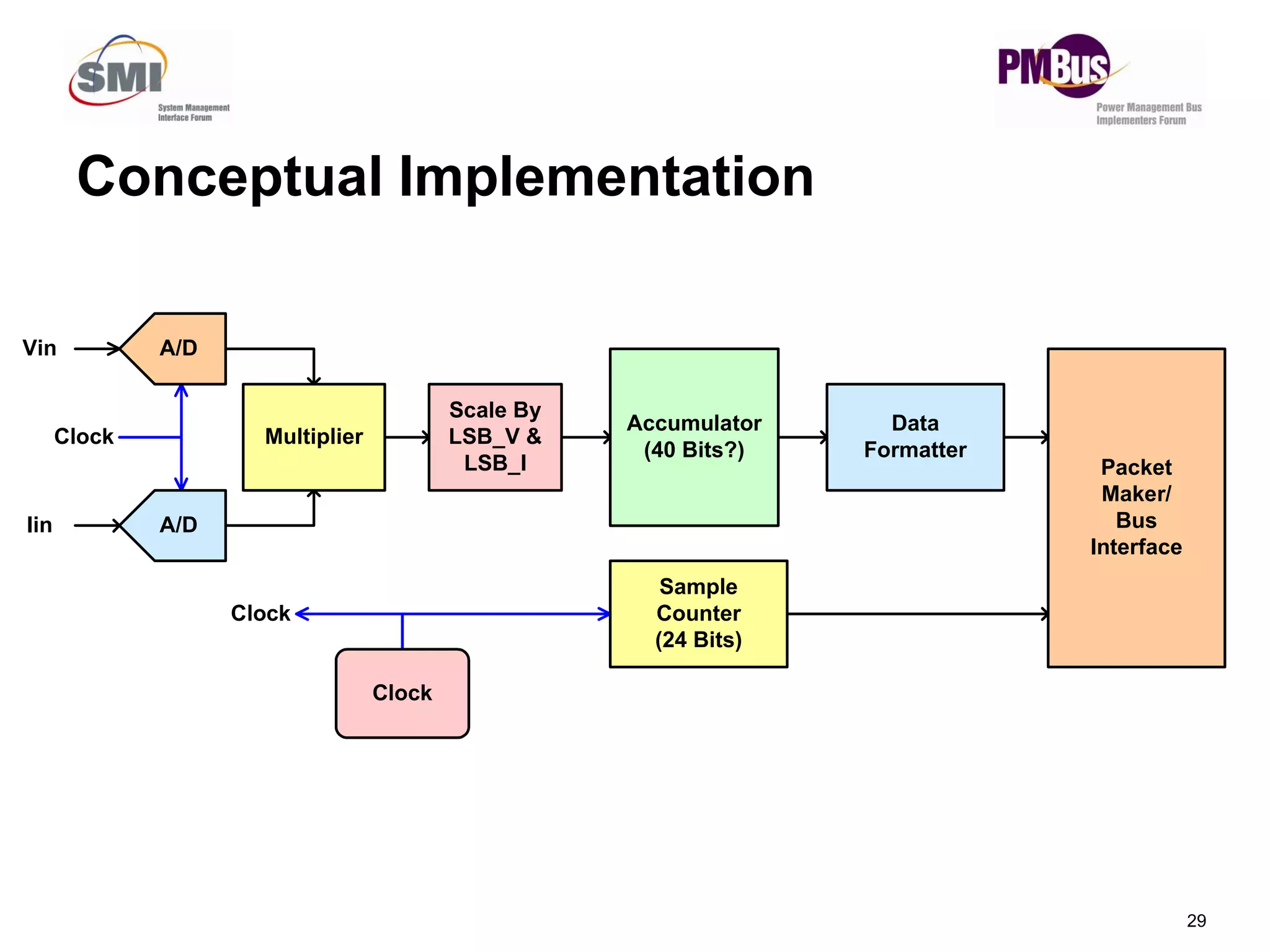
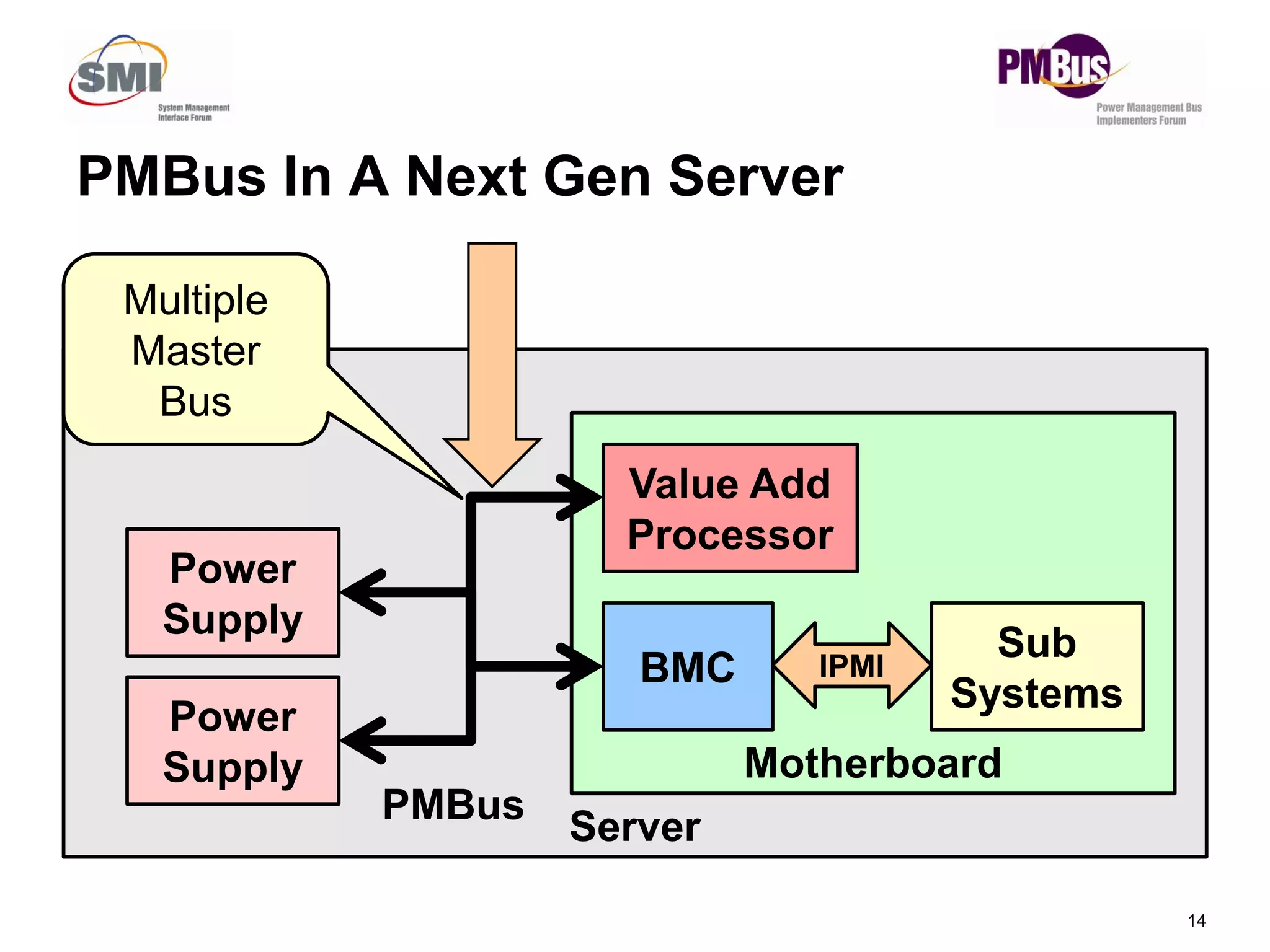
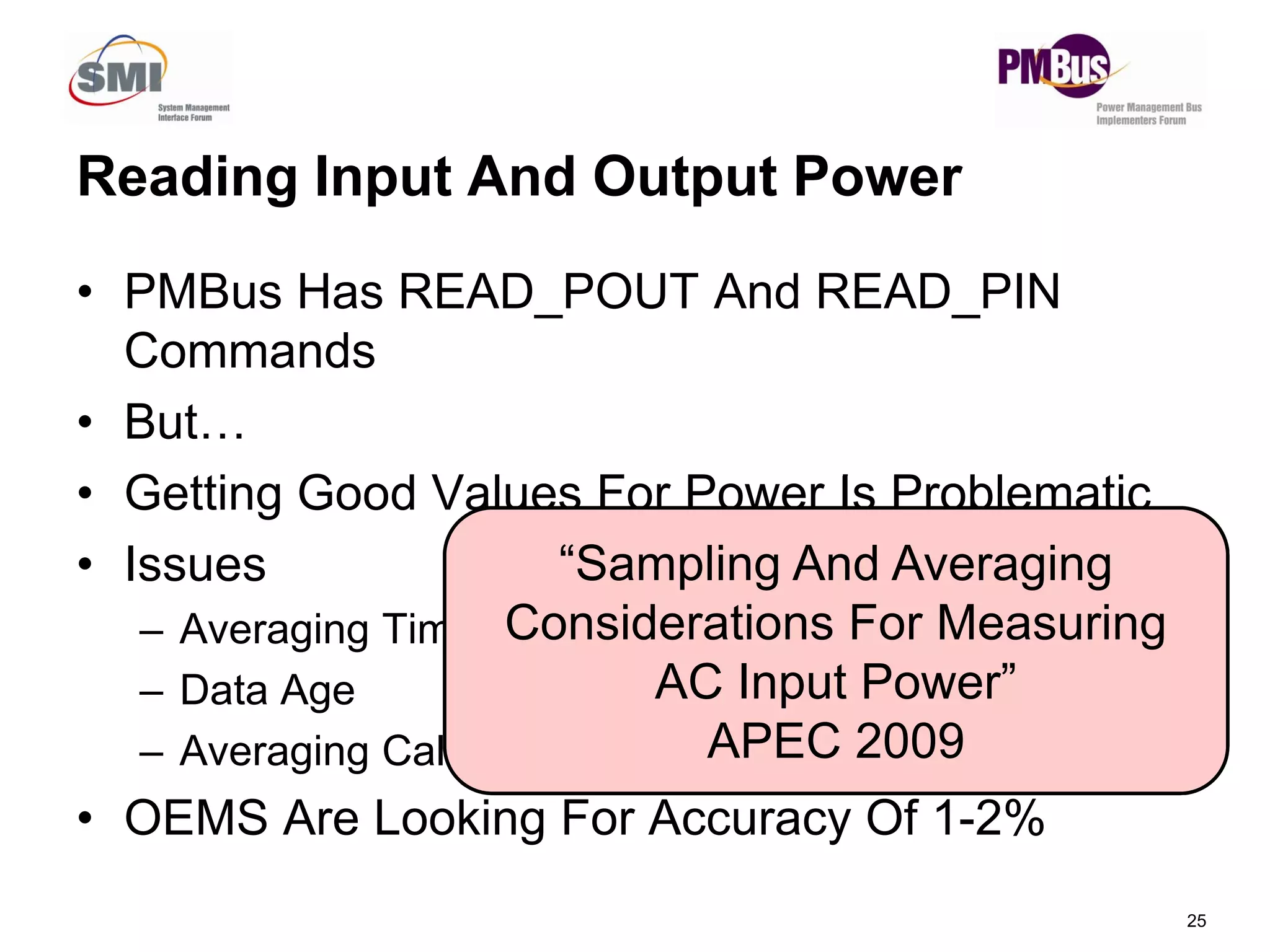
- New commands like PAGEPLUS and READ_EIN/READ_EOUT to improve reading power in multi-master systems.
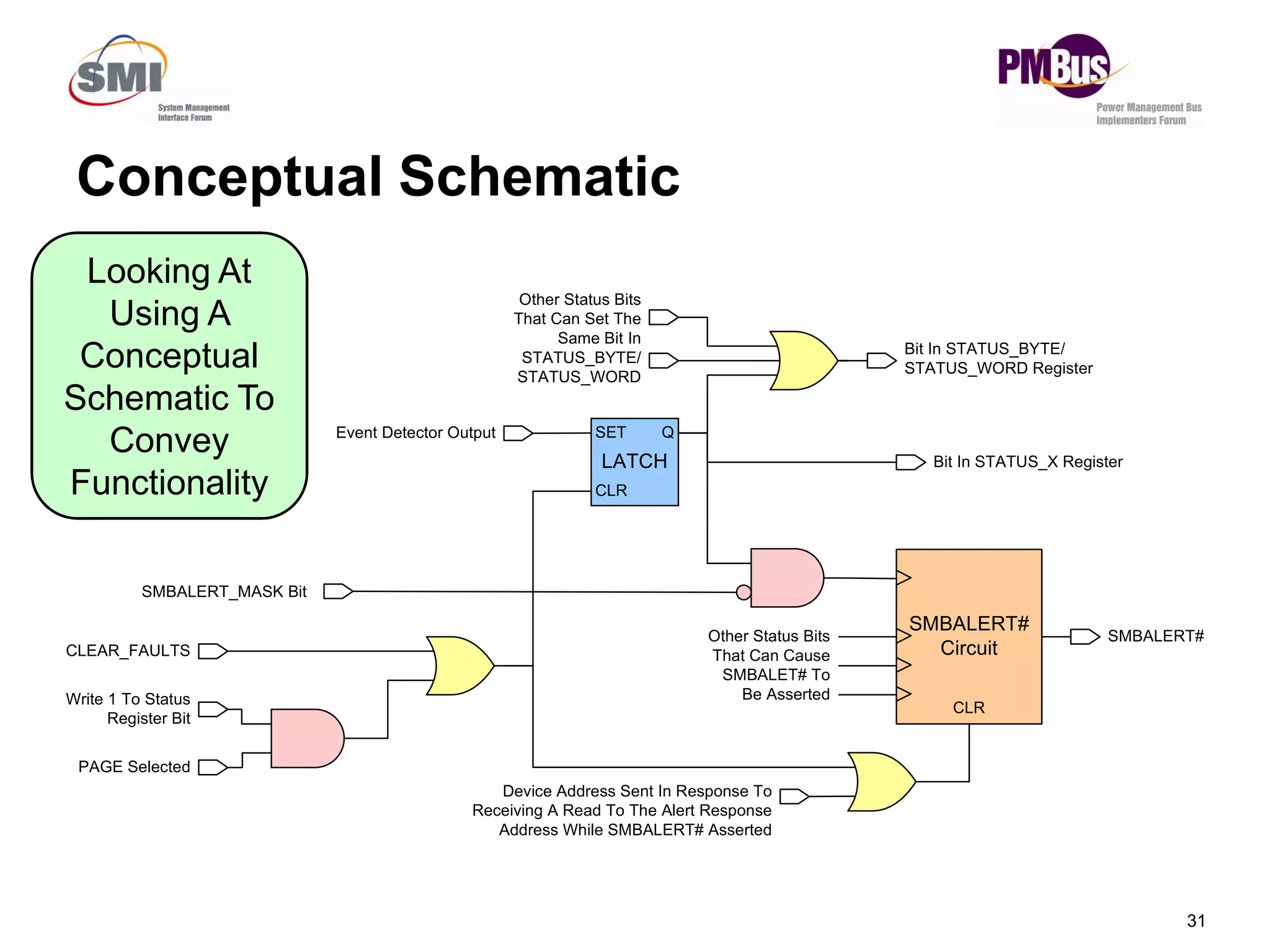
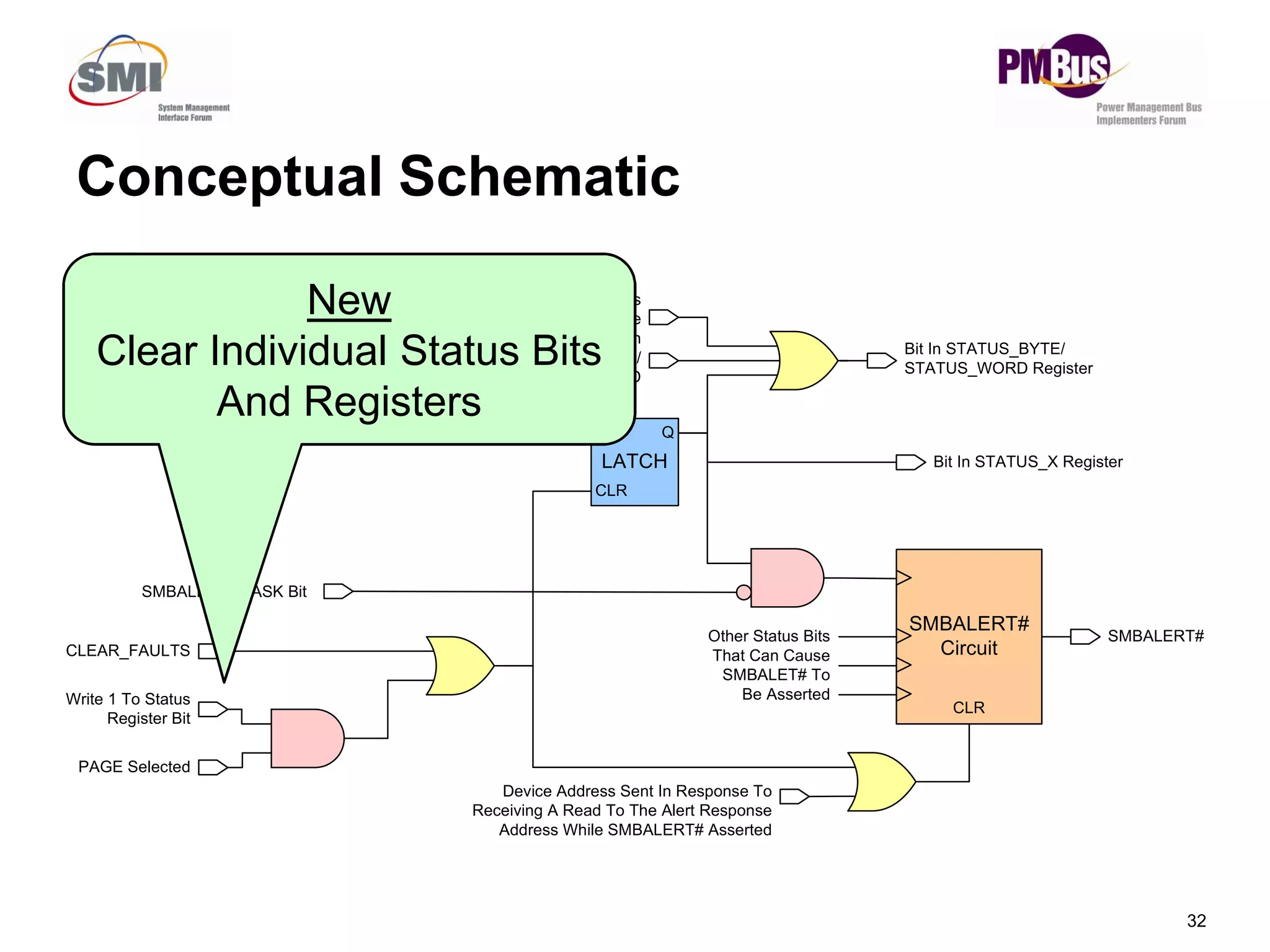
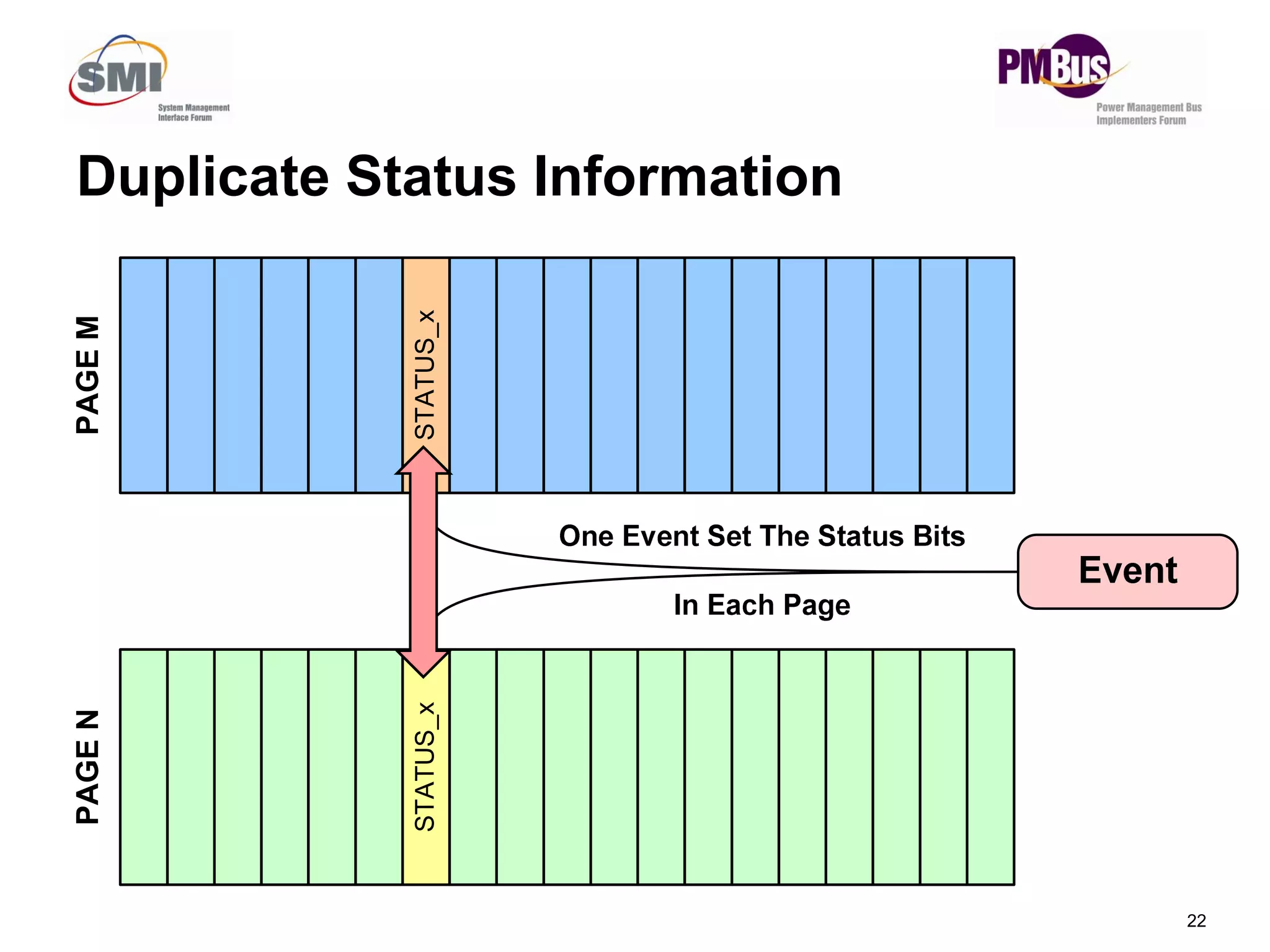
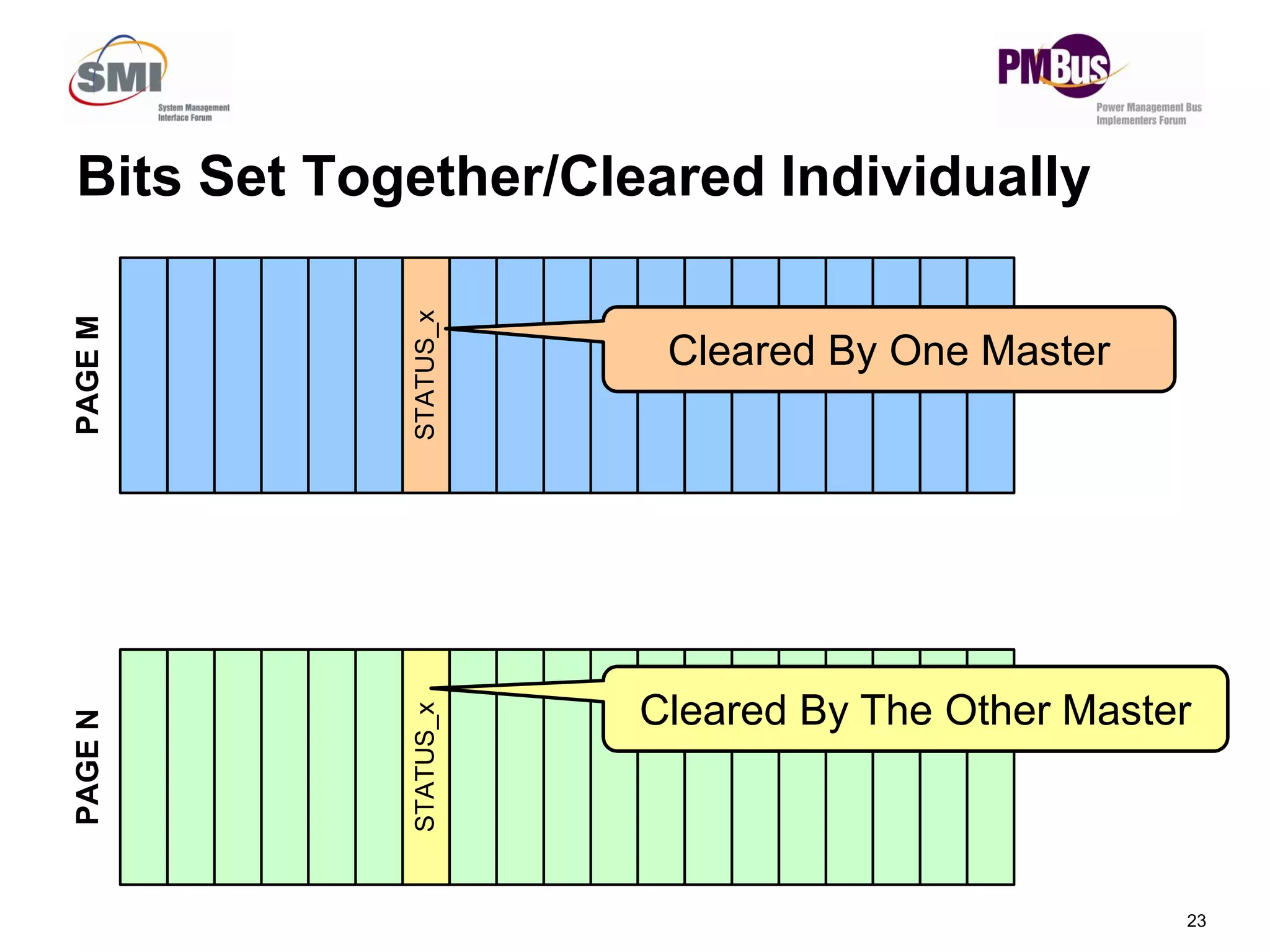
- Clarifying status bits and SMBALERT# signaling to reduce conflicts between masters.
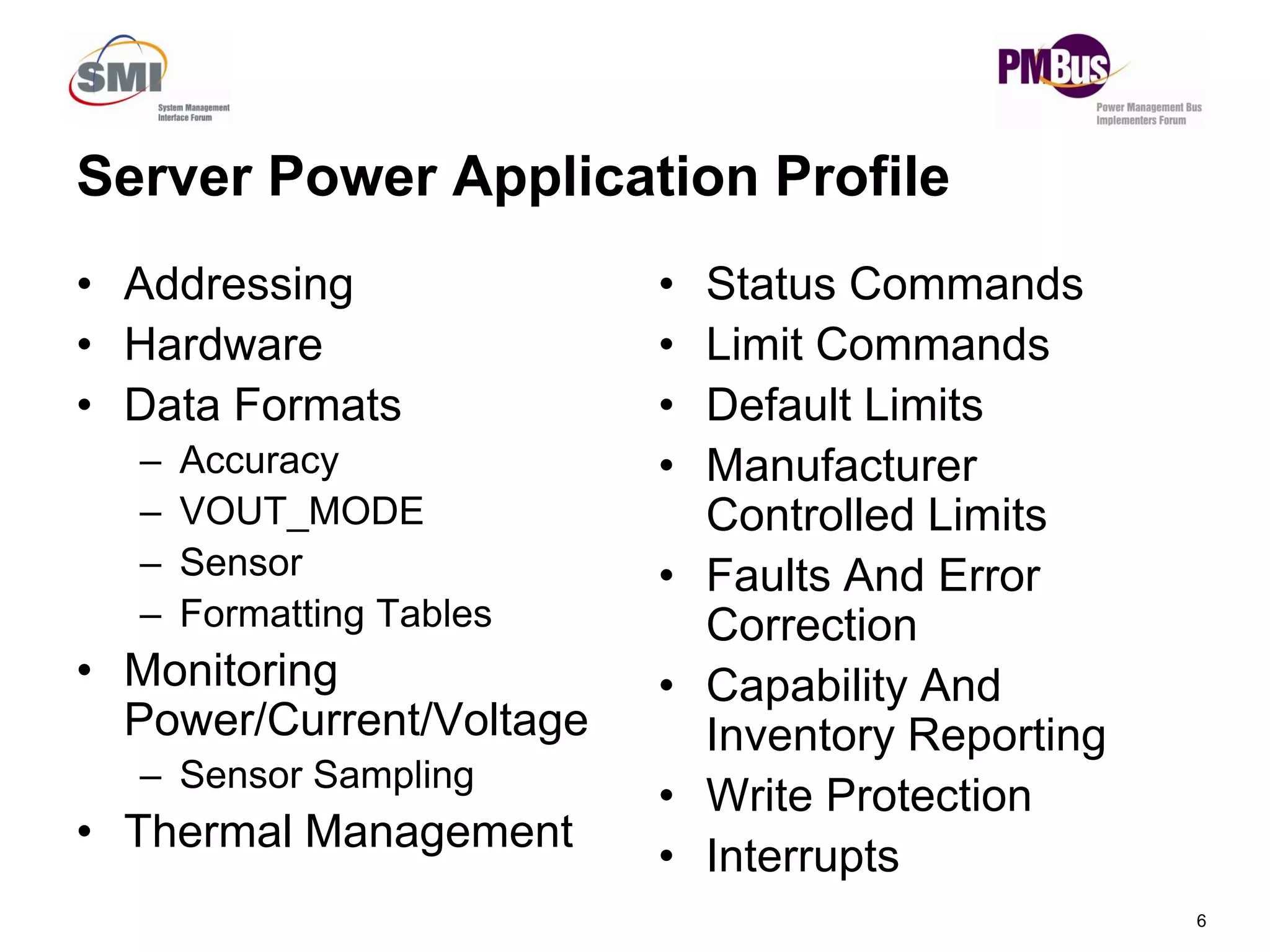
- The server power application profile will specify requirements like monitoring power consumption.
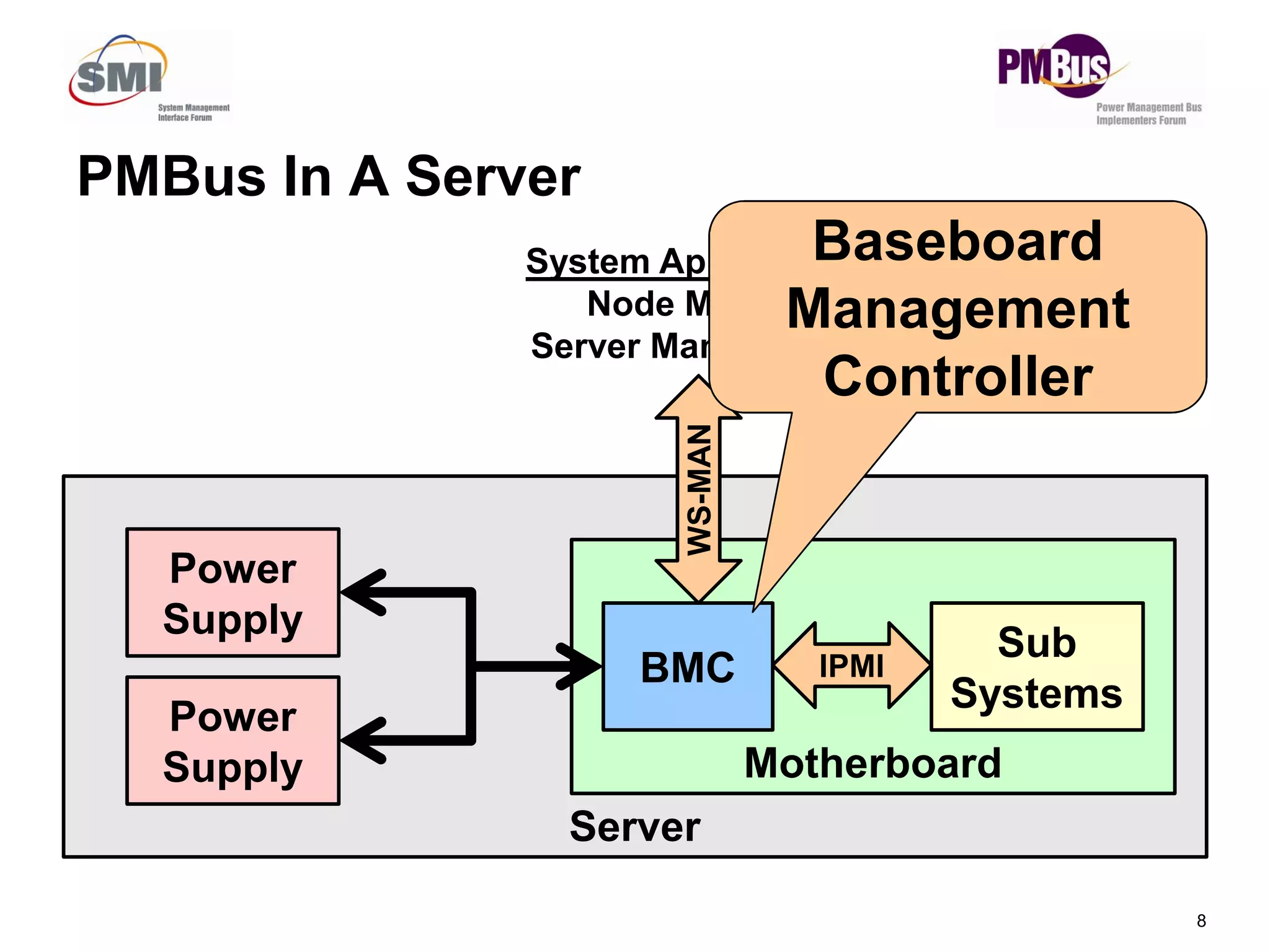
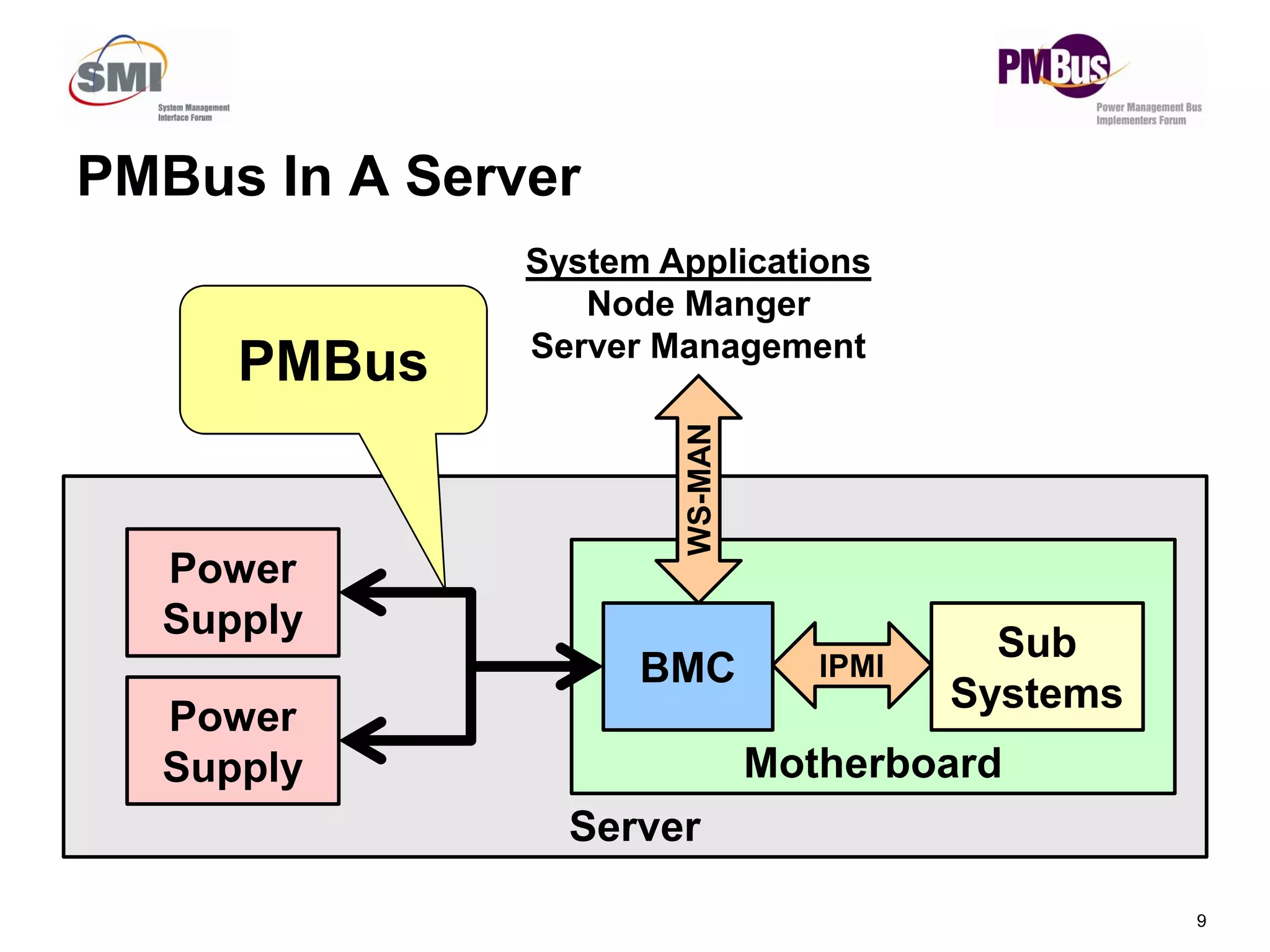
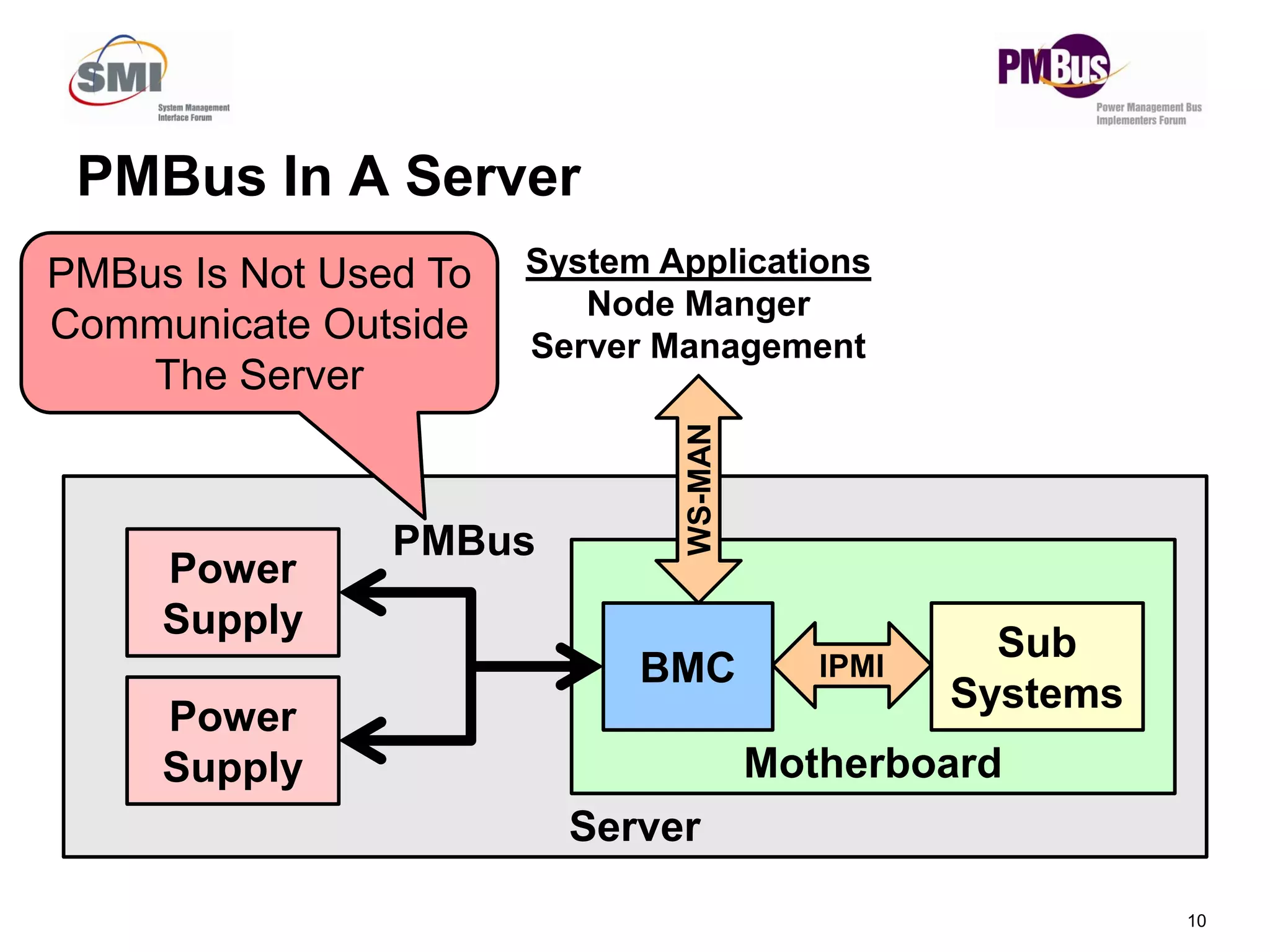
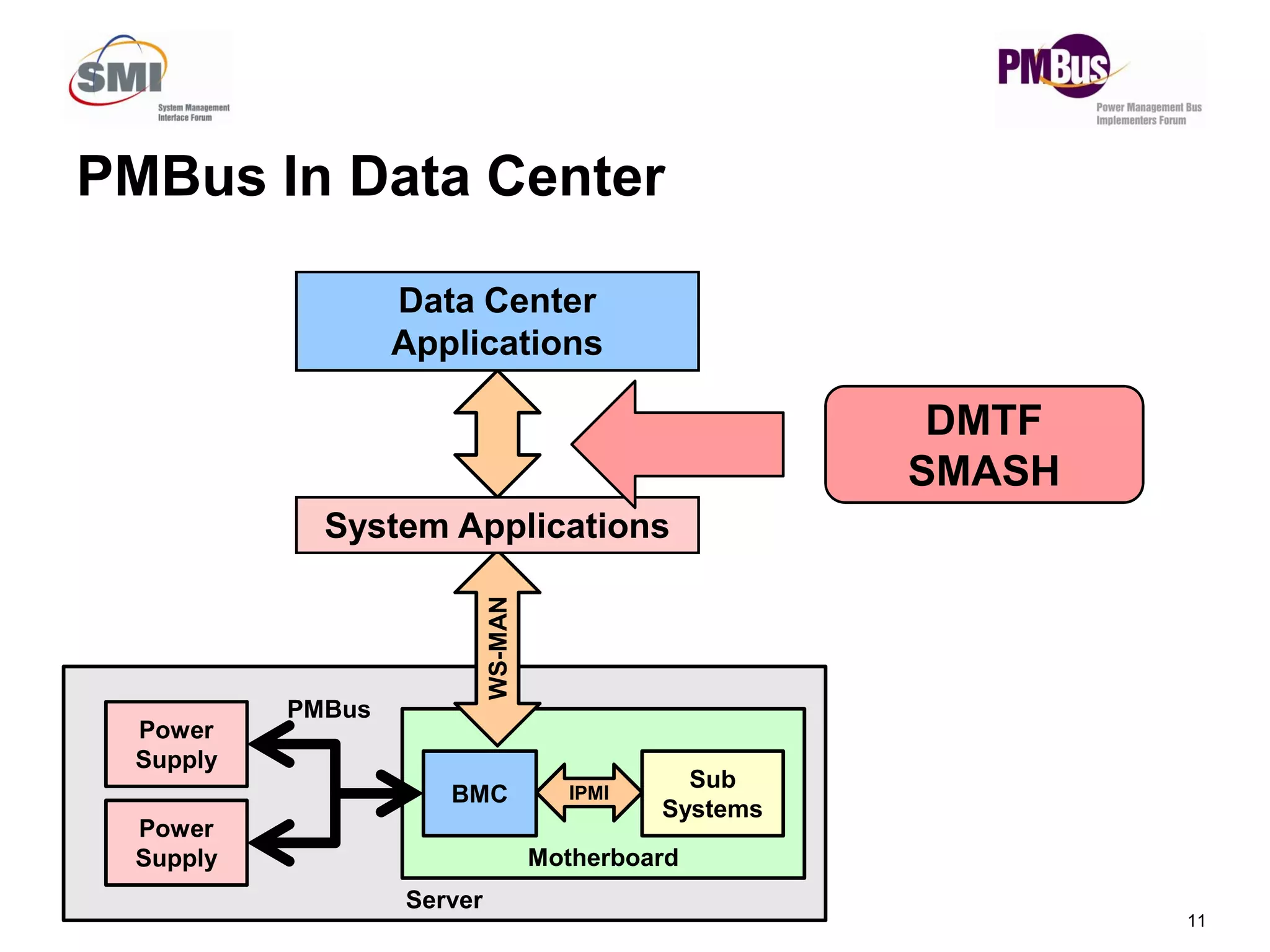
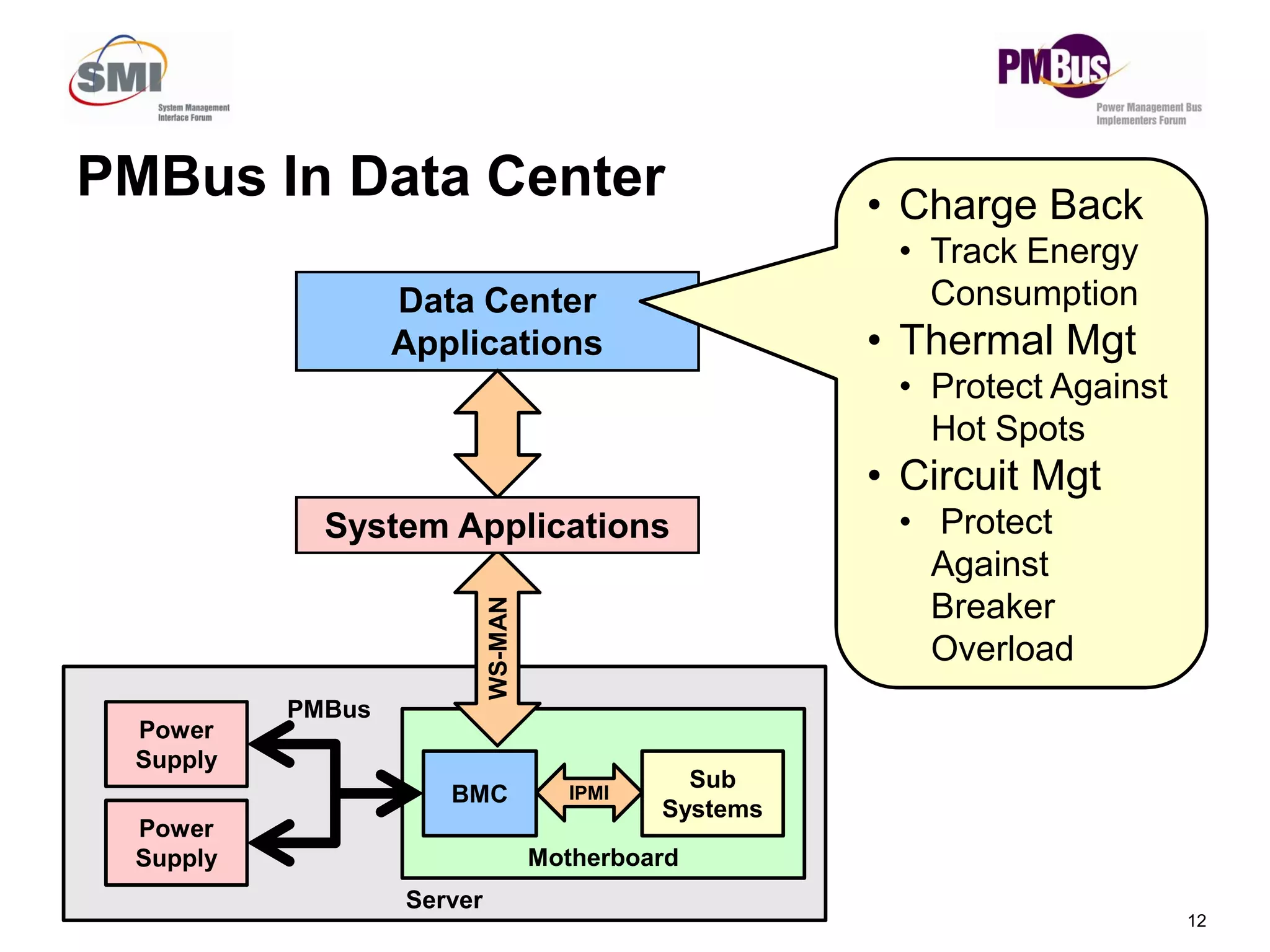
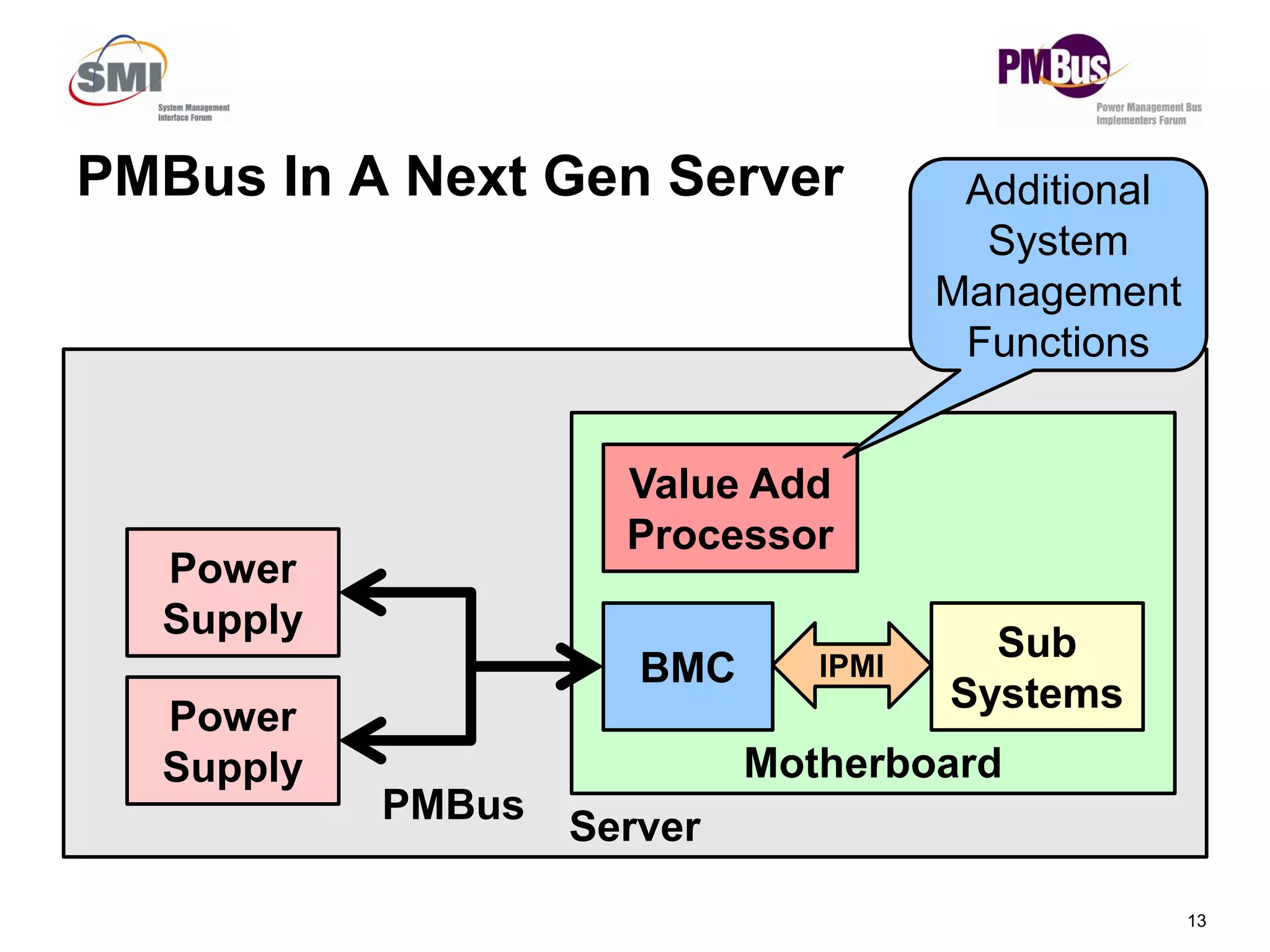
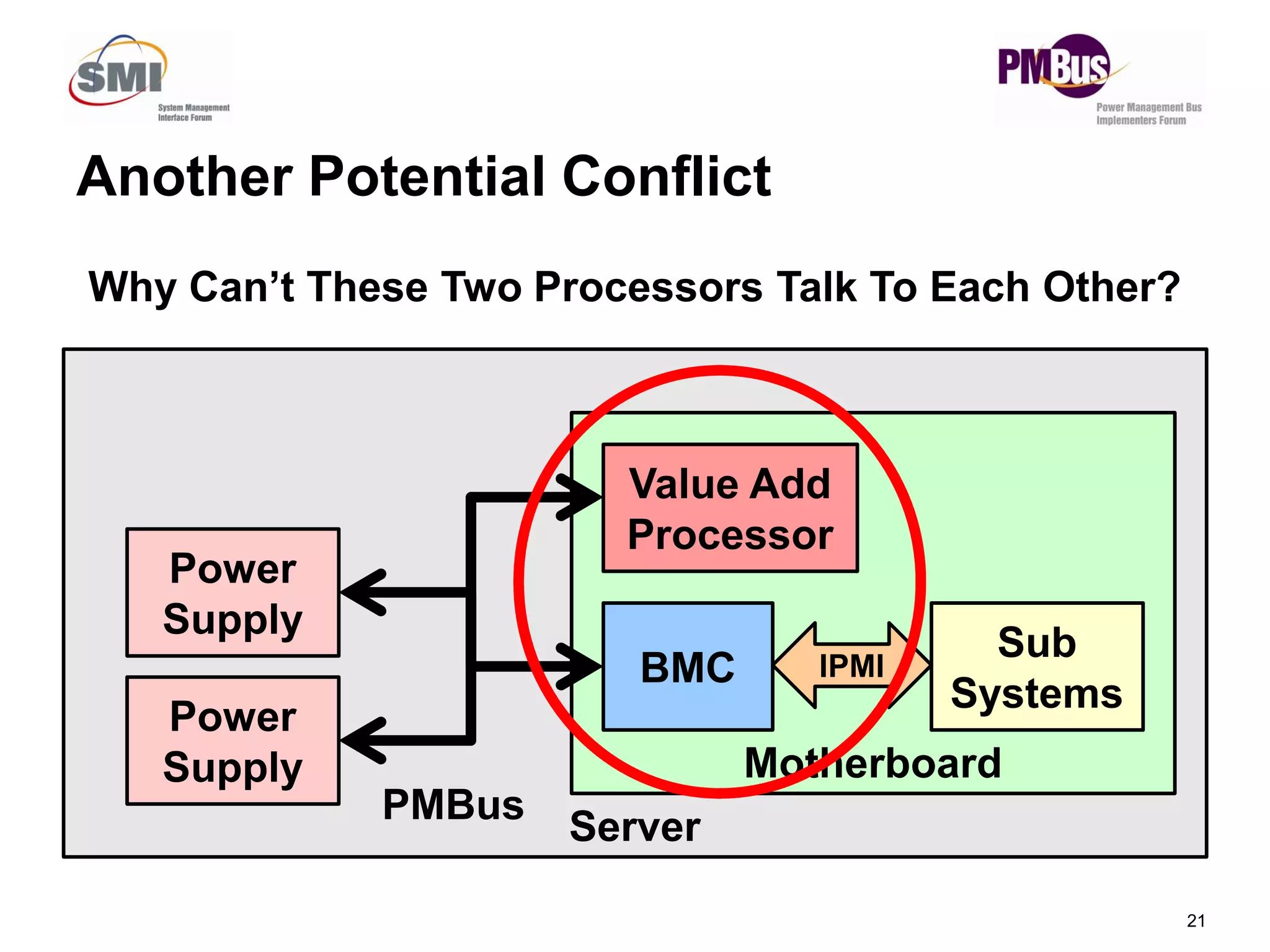
- PMBus is currently used inside servers but not for external communication. Data centers could use it for applications like power tracking and thermal management between servers.




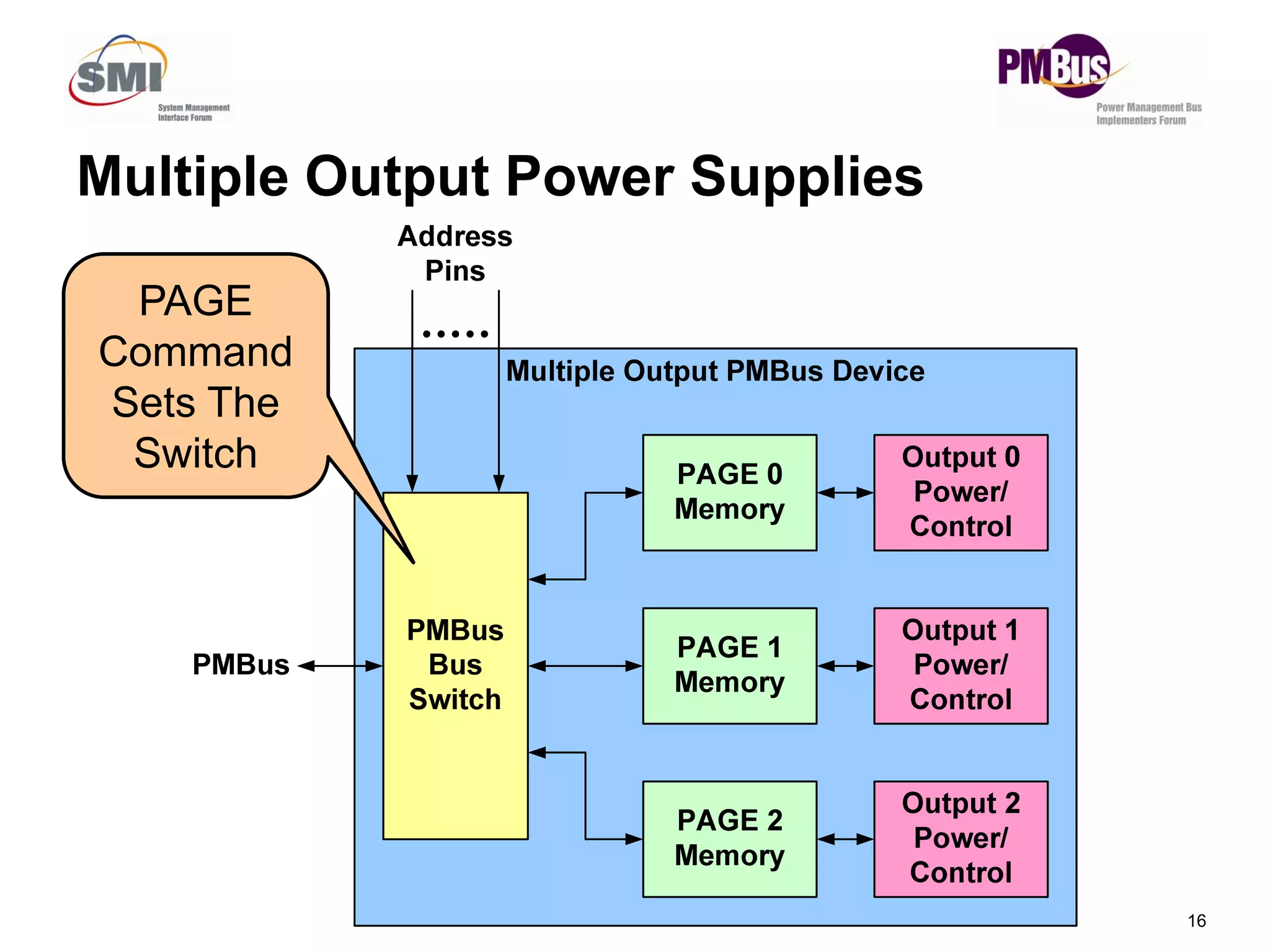
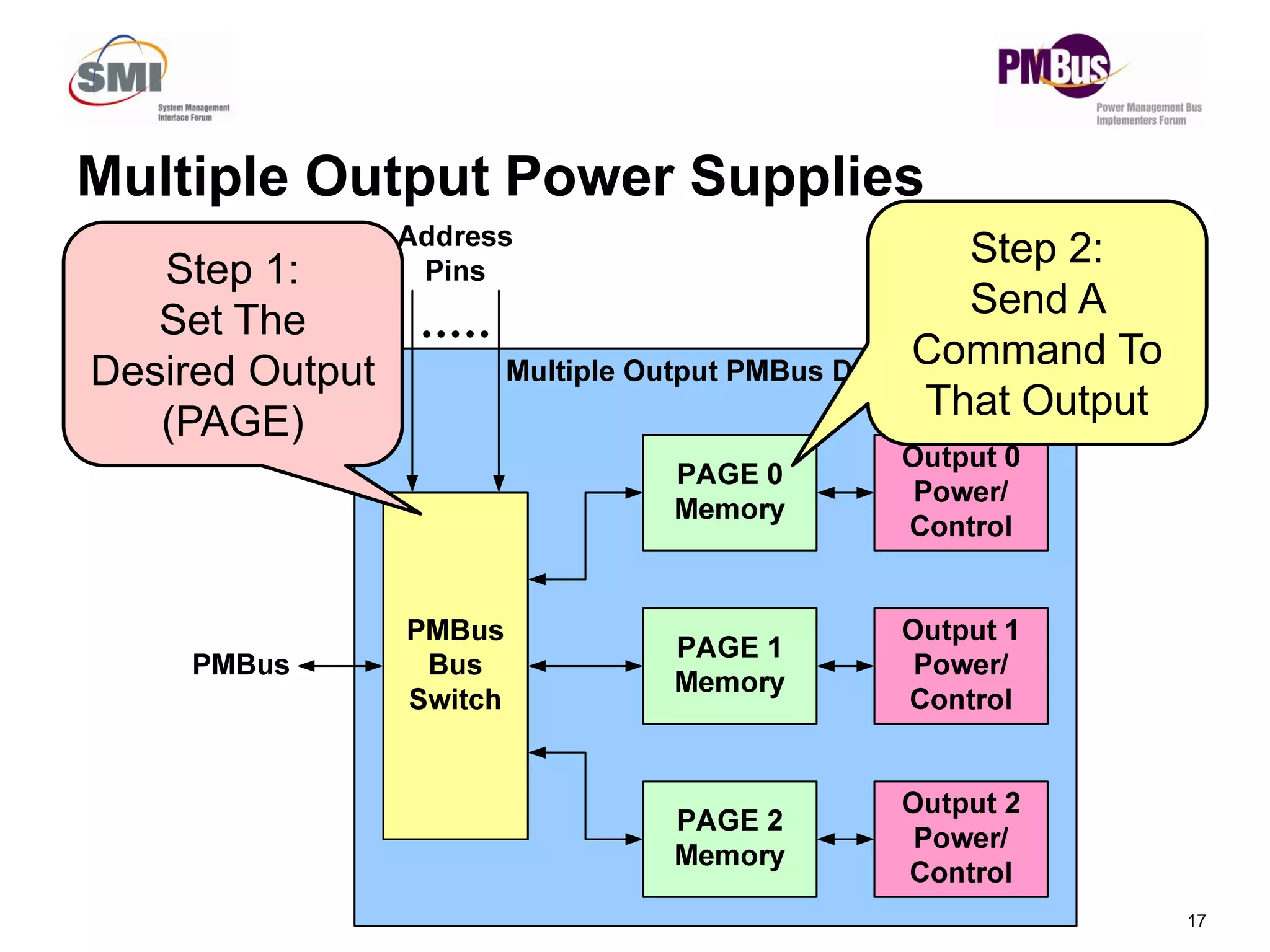
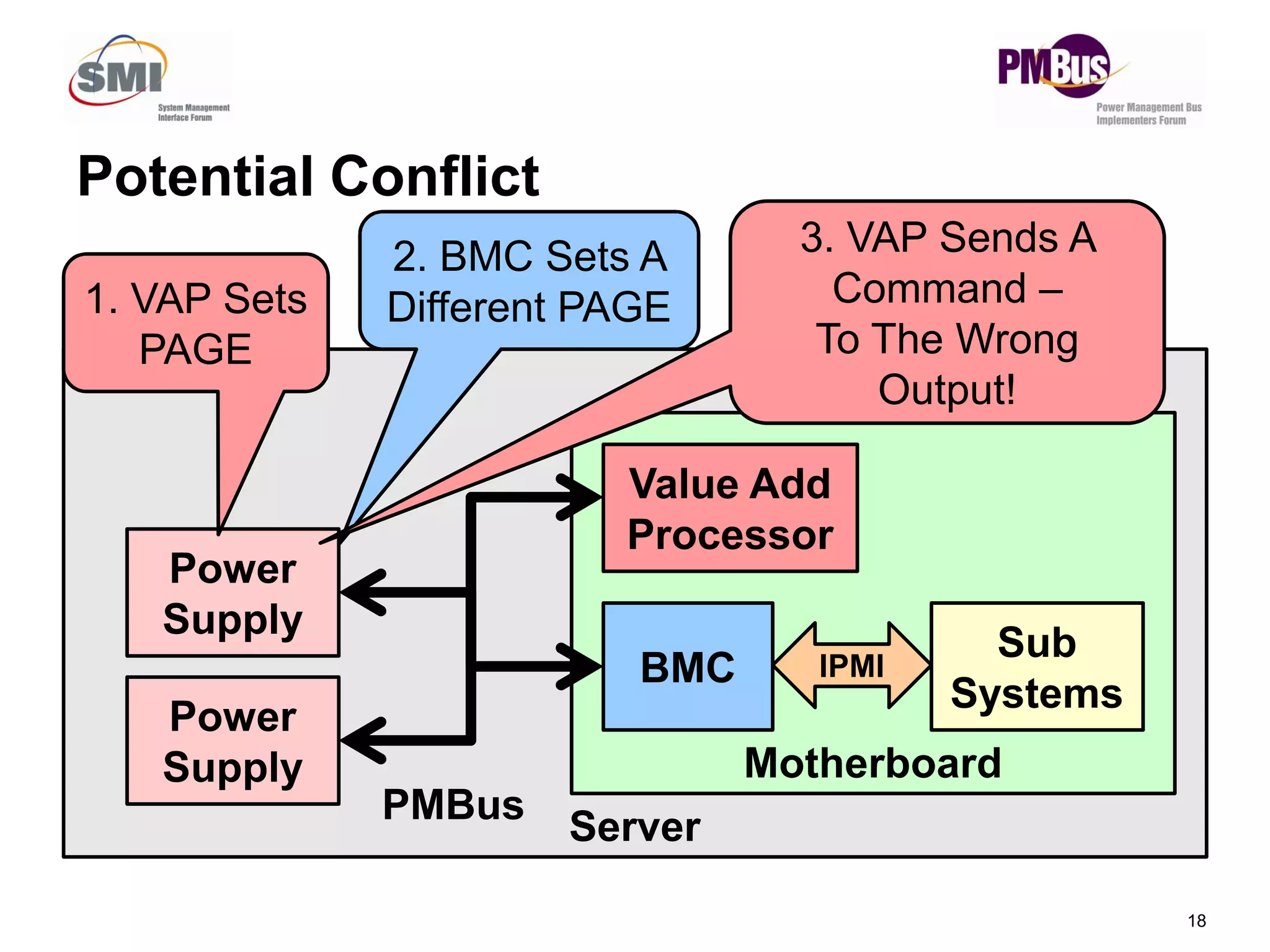

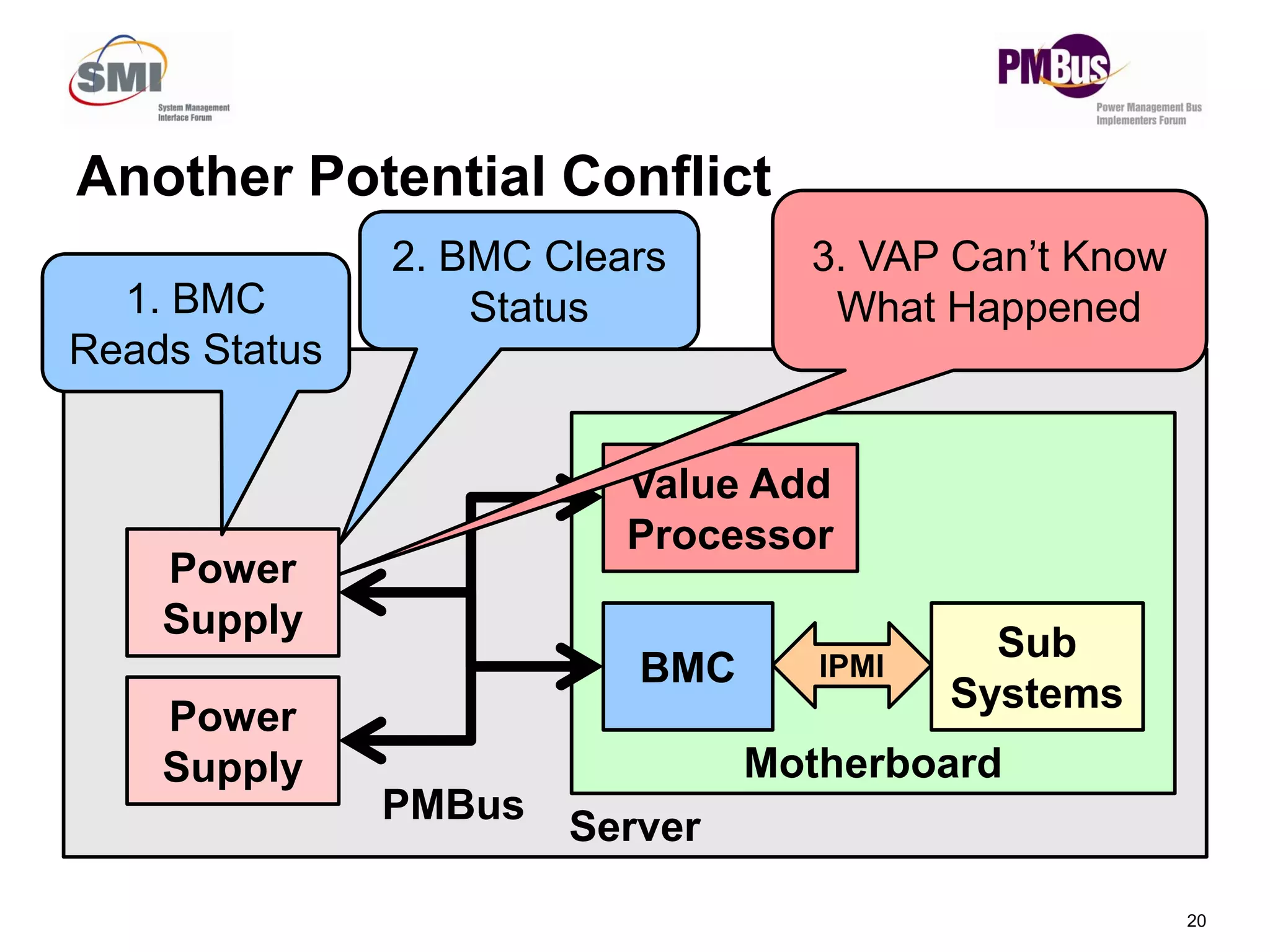


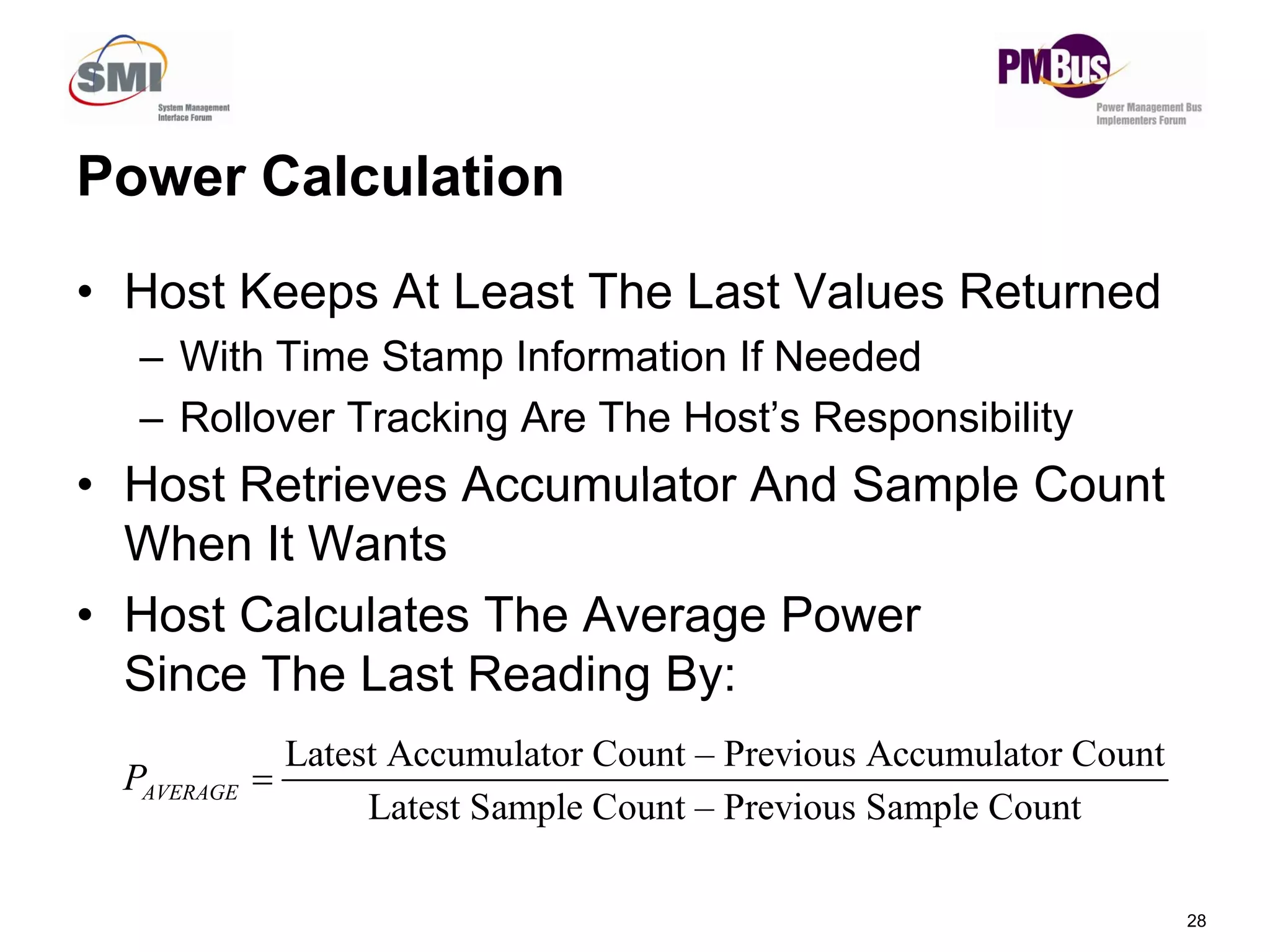
![• Commands Will Return Two Values
– An Accumulated Energy Reading (“Watt-Samples”)
– Current Number Of Power Samples
Discrete Time Power Calculation
Power Calculation
27
• Discrete Time Power Calculation
1 1
1 1
[ ] [ ] [ ]
N N
AVE
n n
P p n v n i n
N N
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmbusspecificationrev1-220724033851-247400f9/75/PMBus-Specification-Rev-1-2-Presentation-20100228-pdf-27-2048.jpg)