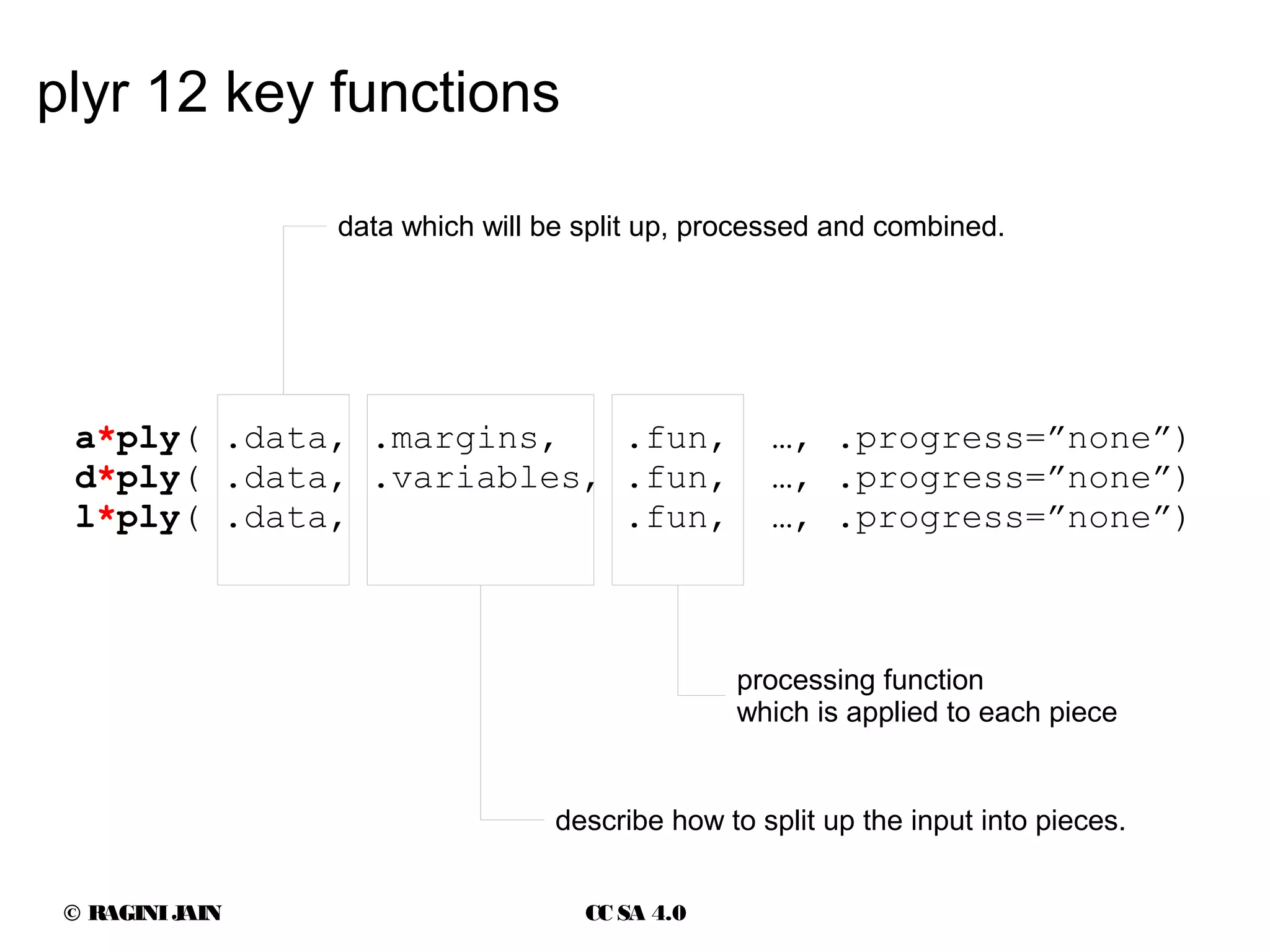
The document provides an overview of the 'plyr' package in R, which simplifies working with large datasets using a split-apply-combine strategy. It details how plyr can replace traditional loops and outlines its key functions and use cases, along with rules for splitting input data types. Additionally, it includes examples of data frame structures and references for further information.

![© RAGINIJAIN CC SA 4.0
'for-loop' is the traditional approach
large data set
counter
condition
[ ]
element access
useful for overlapping data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plyr-160206010918/75/Plyr-2-2048.jpg)