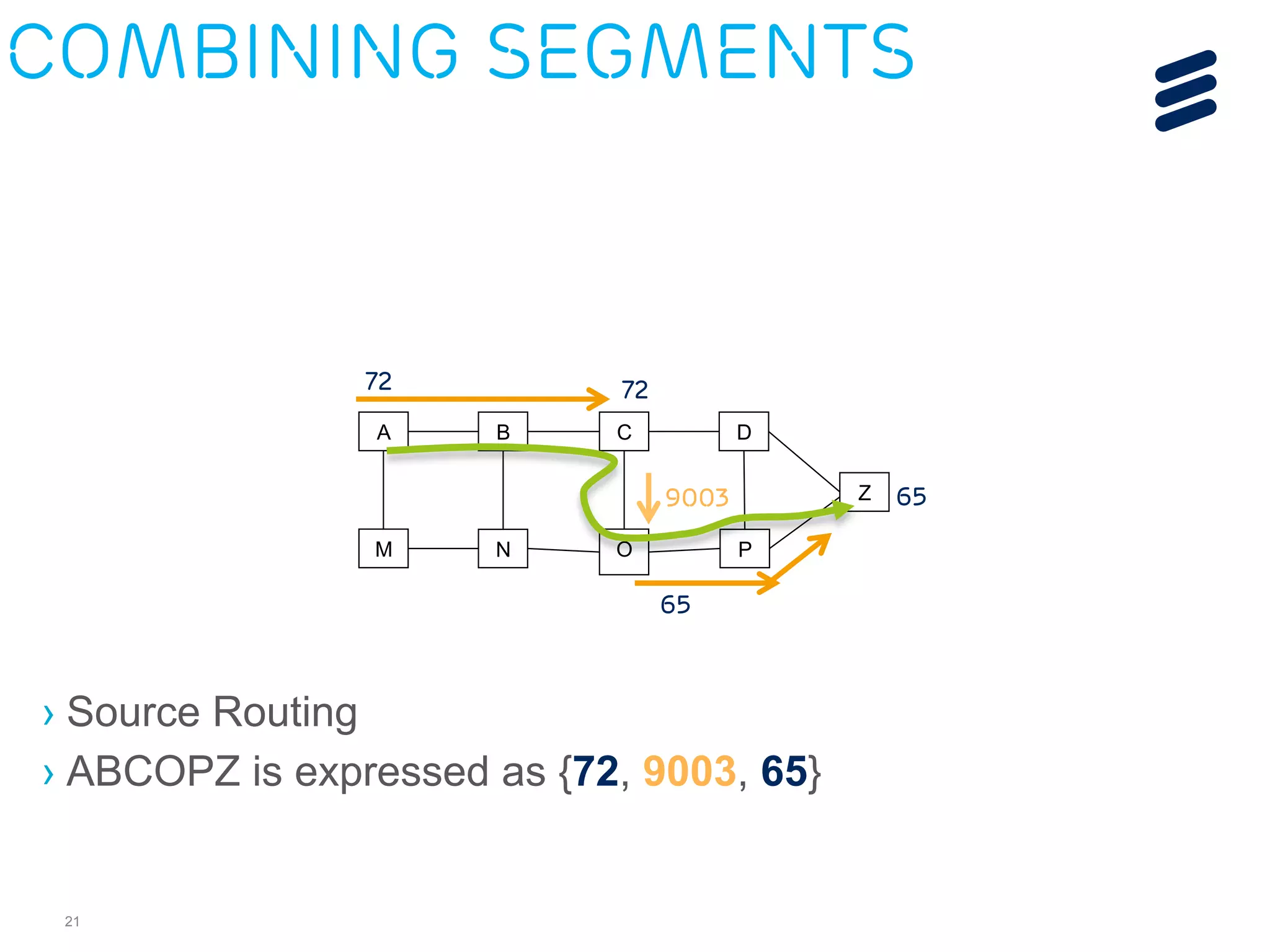
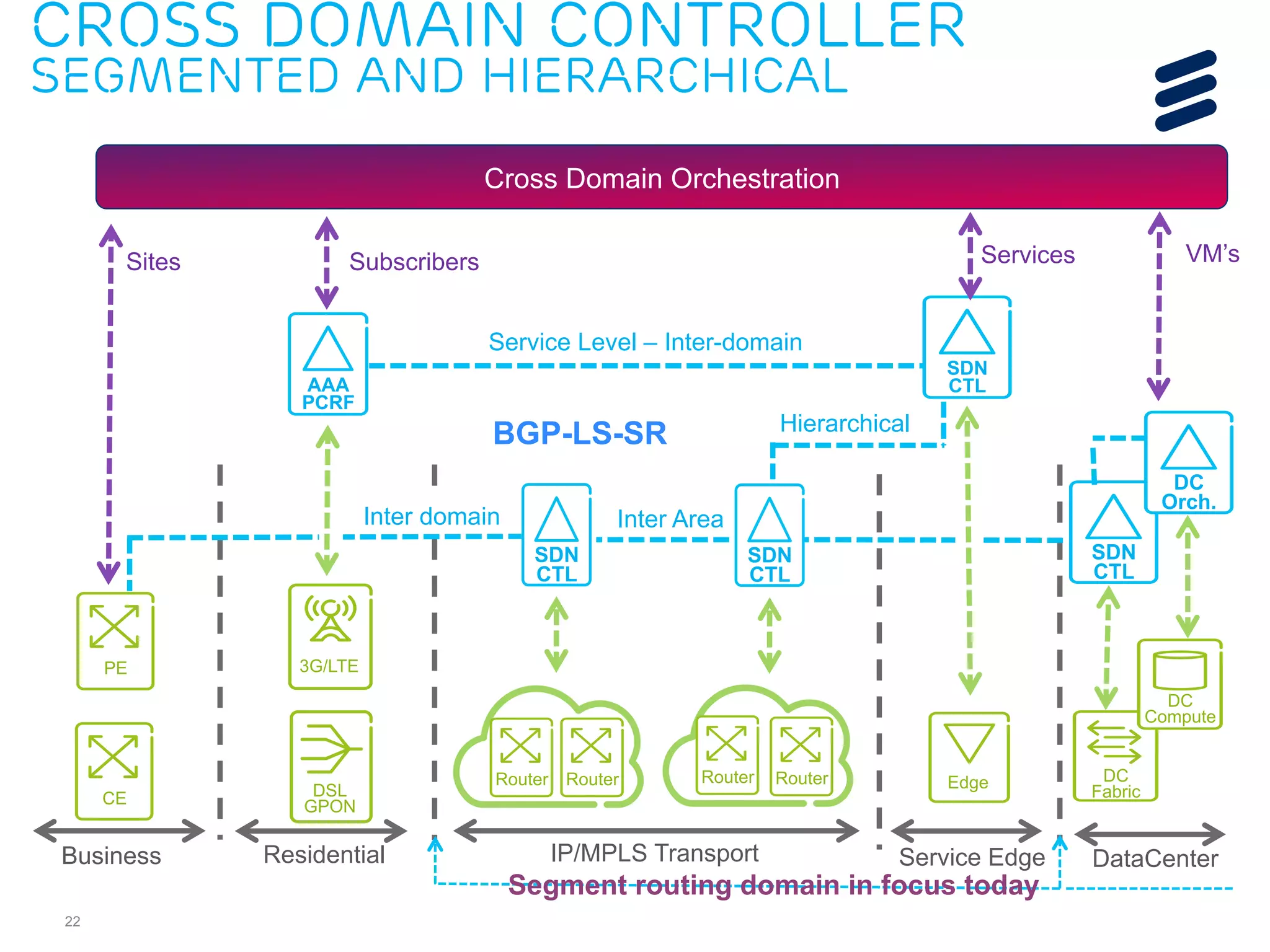
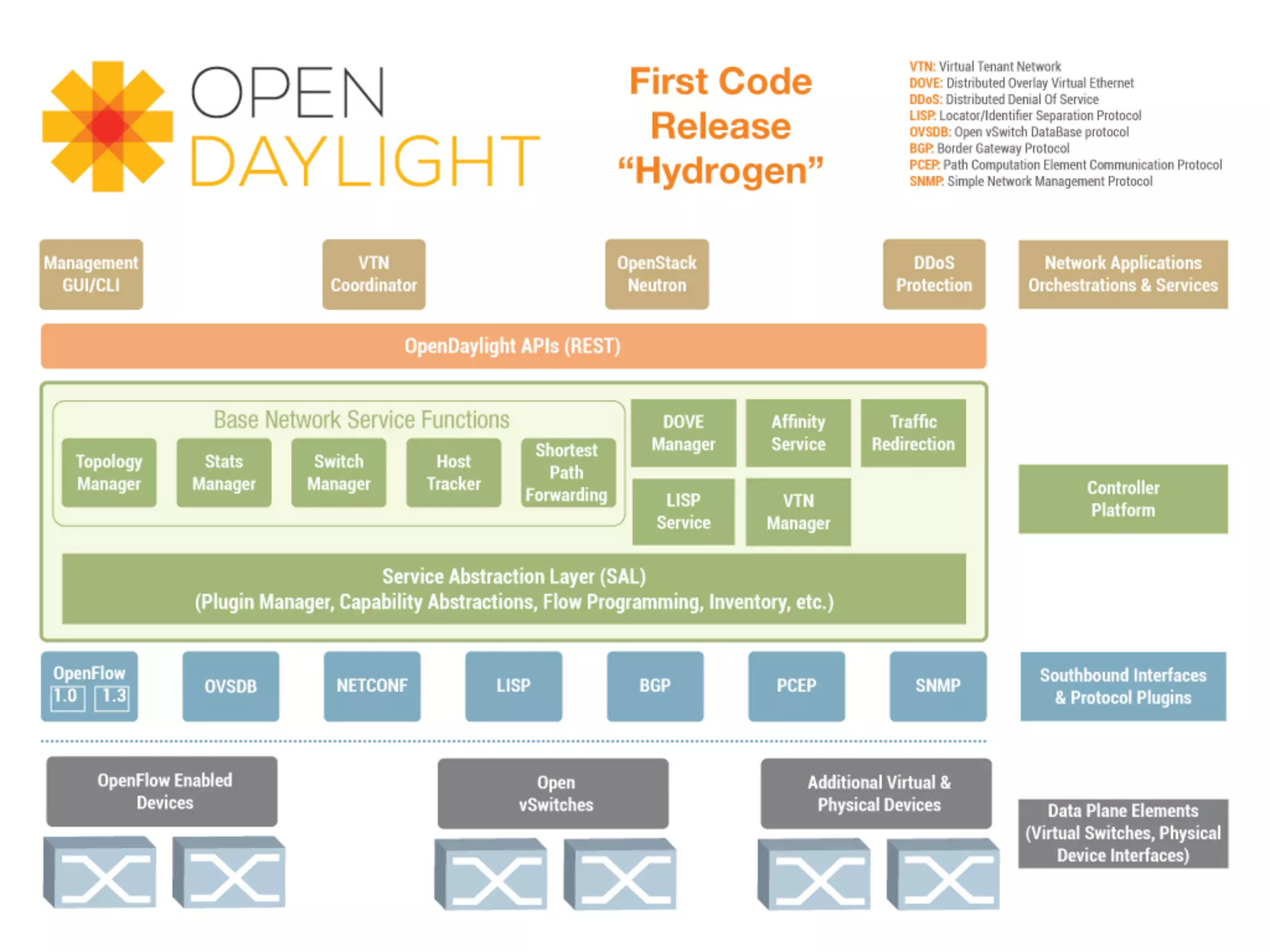
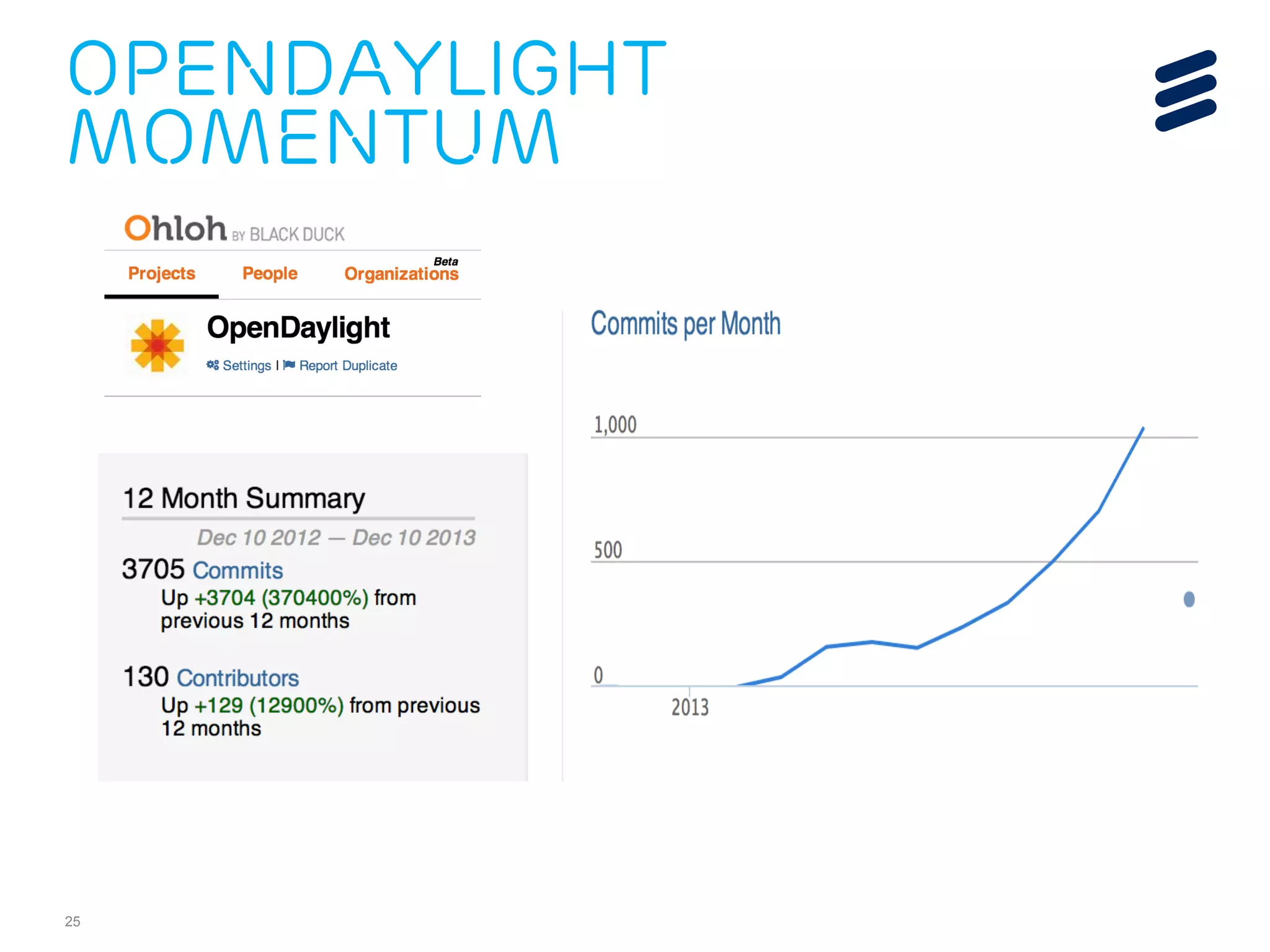
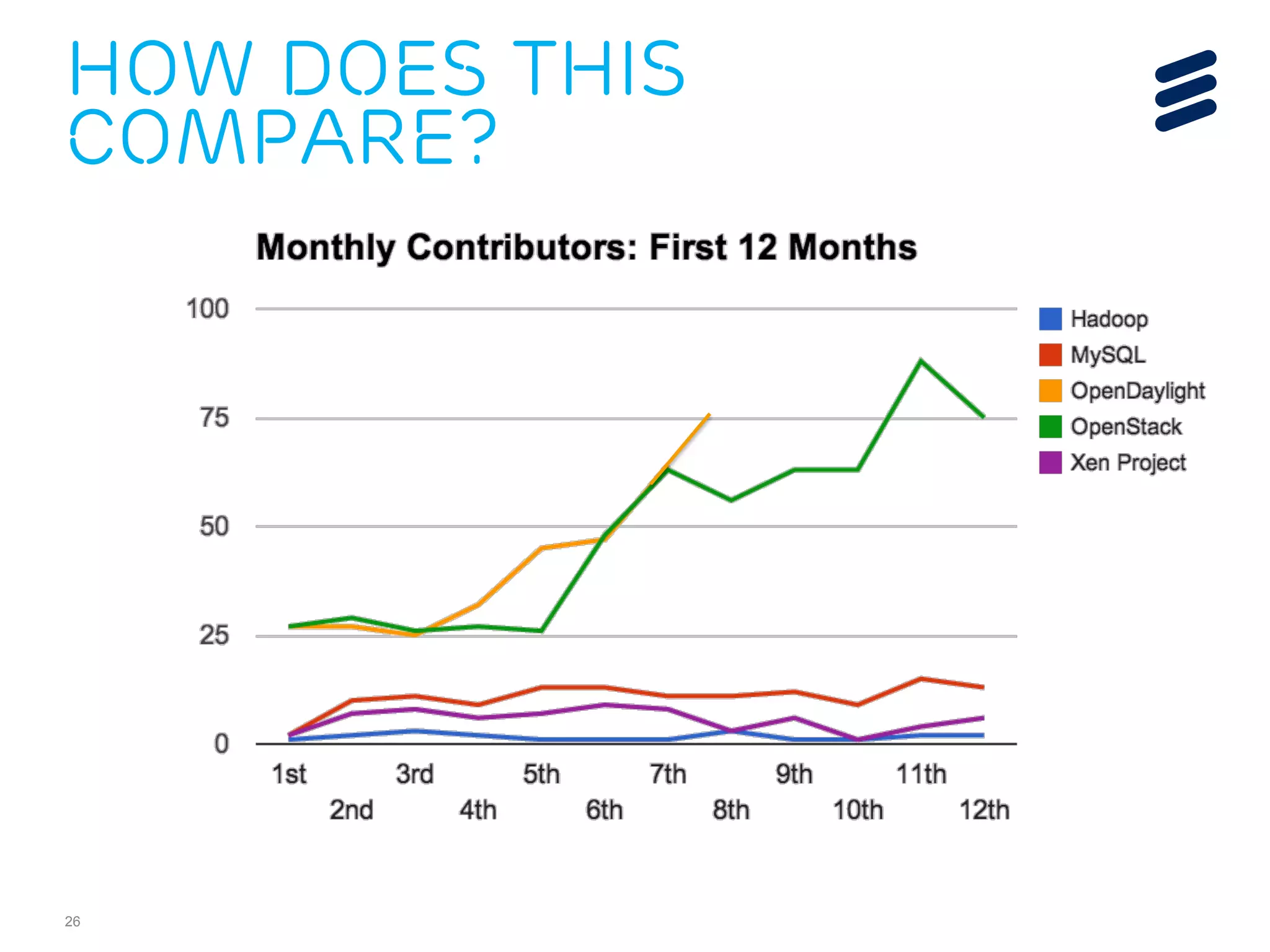
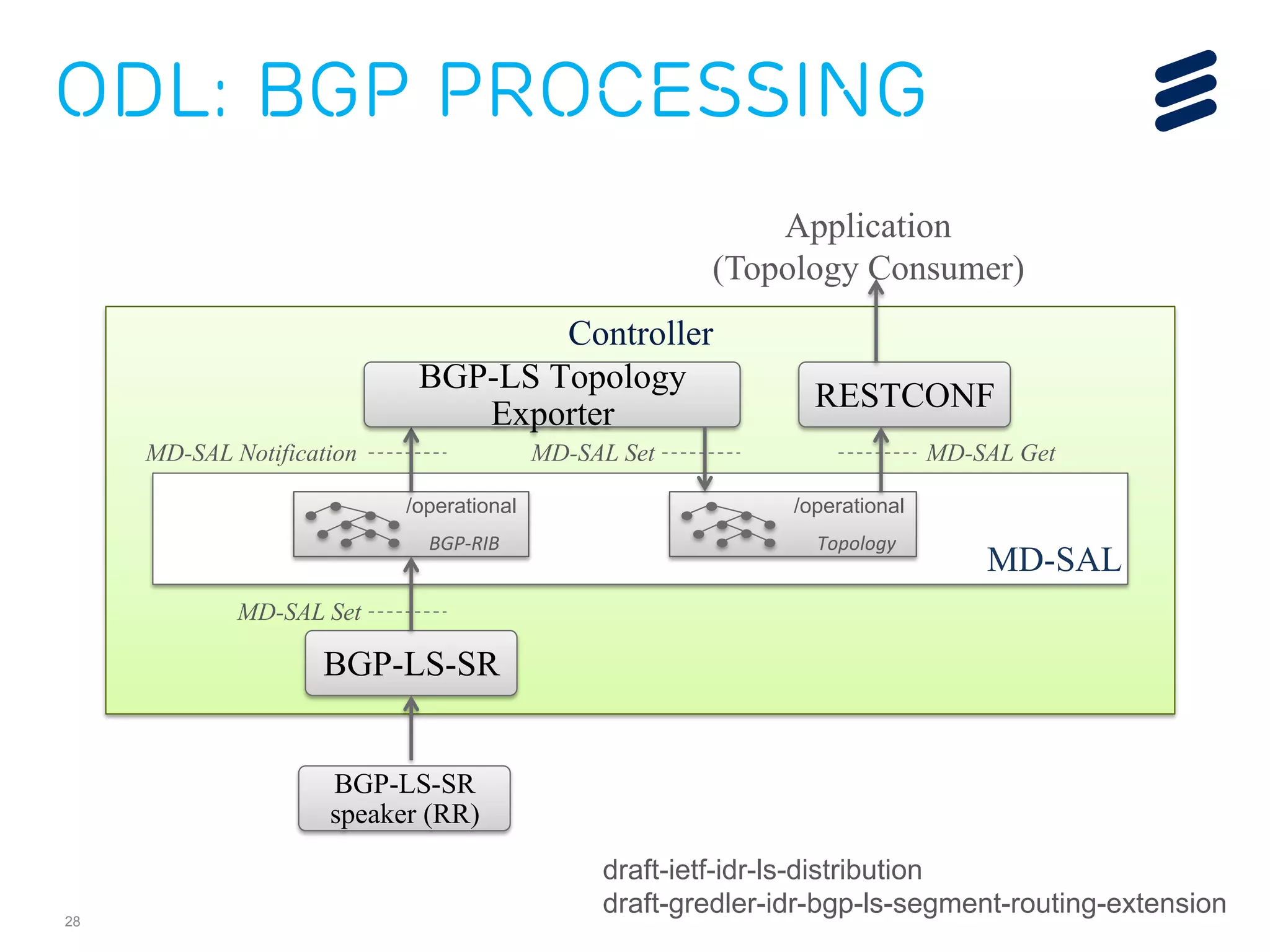
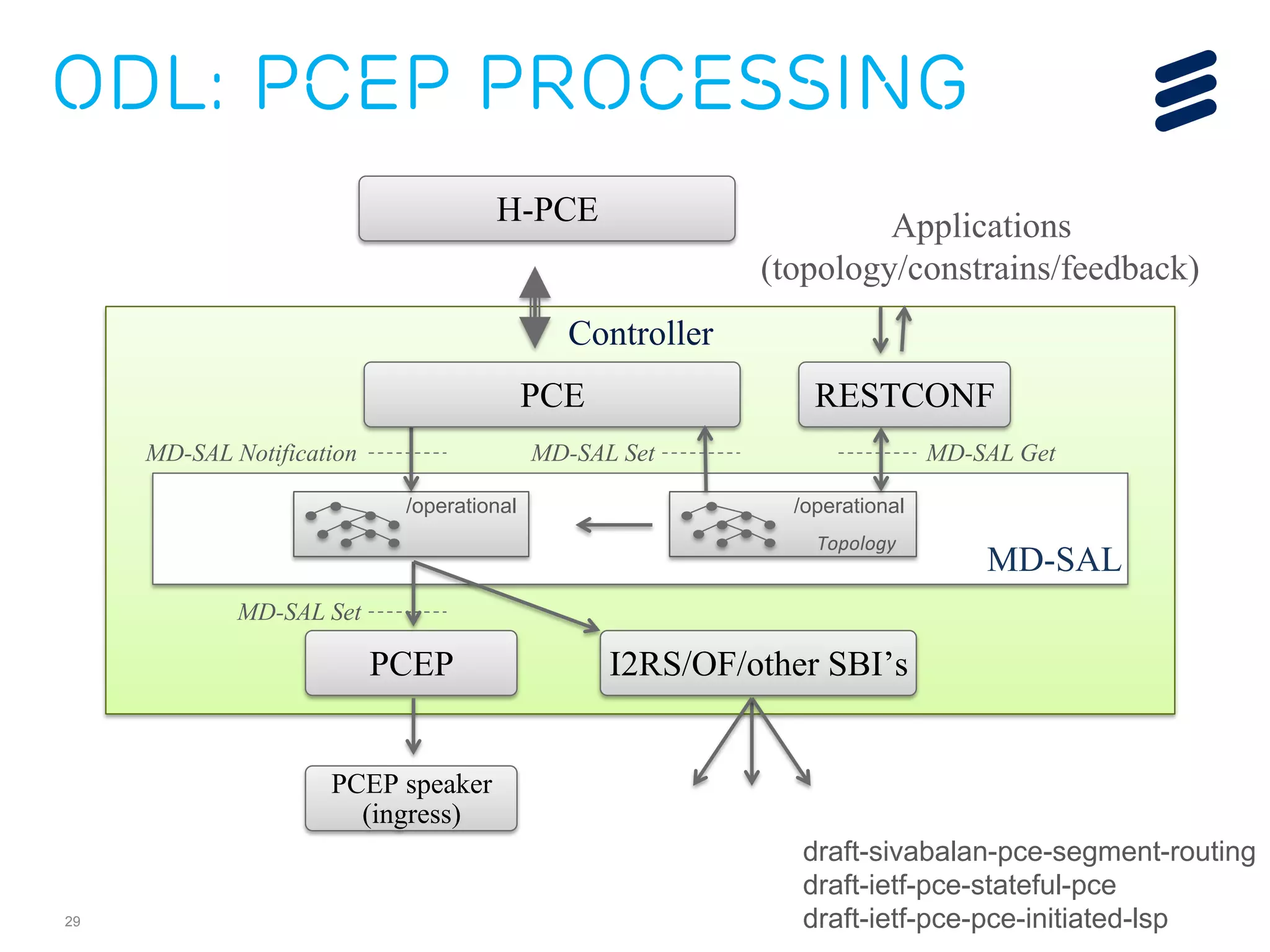
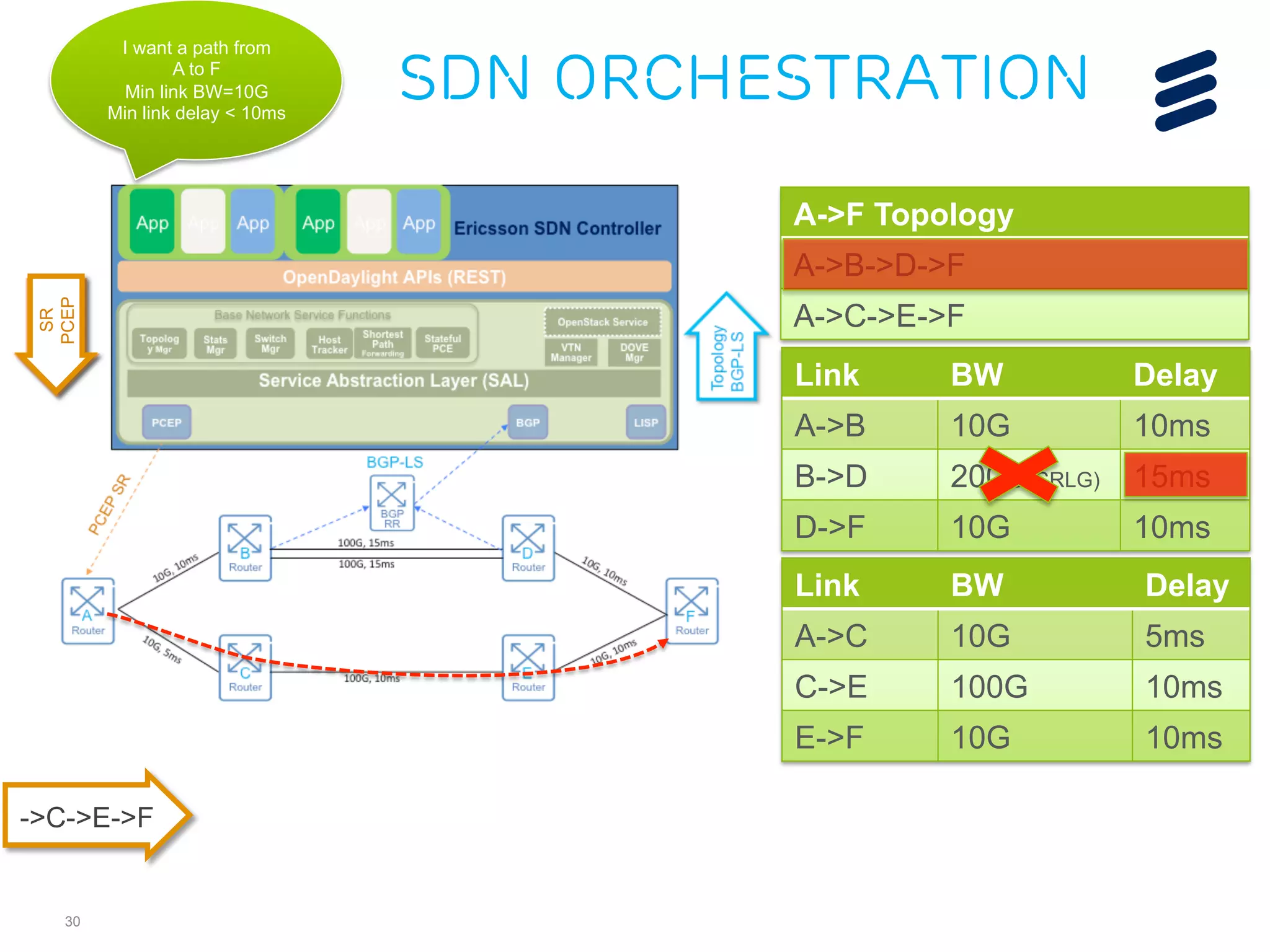
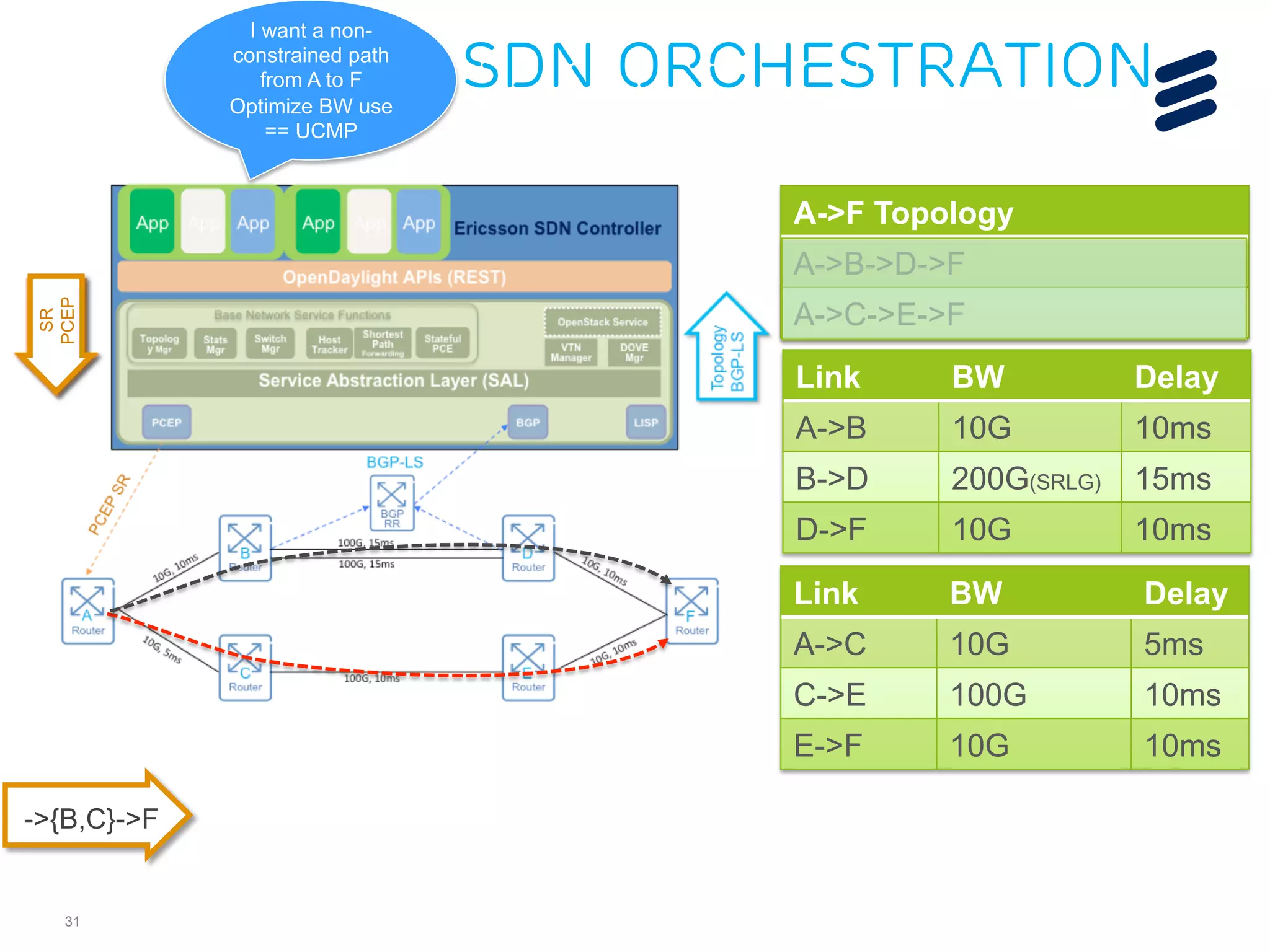
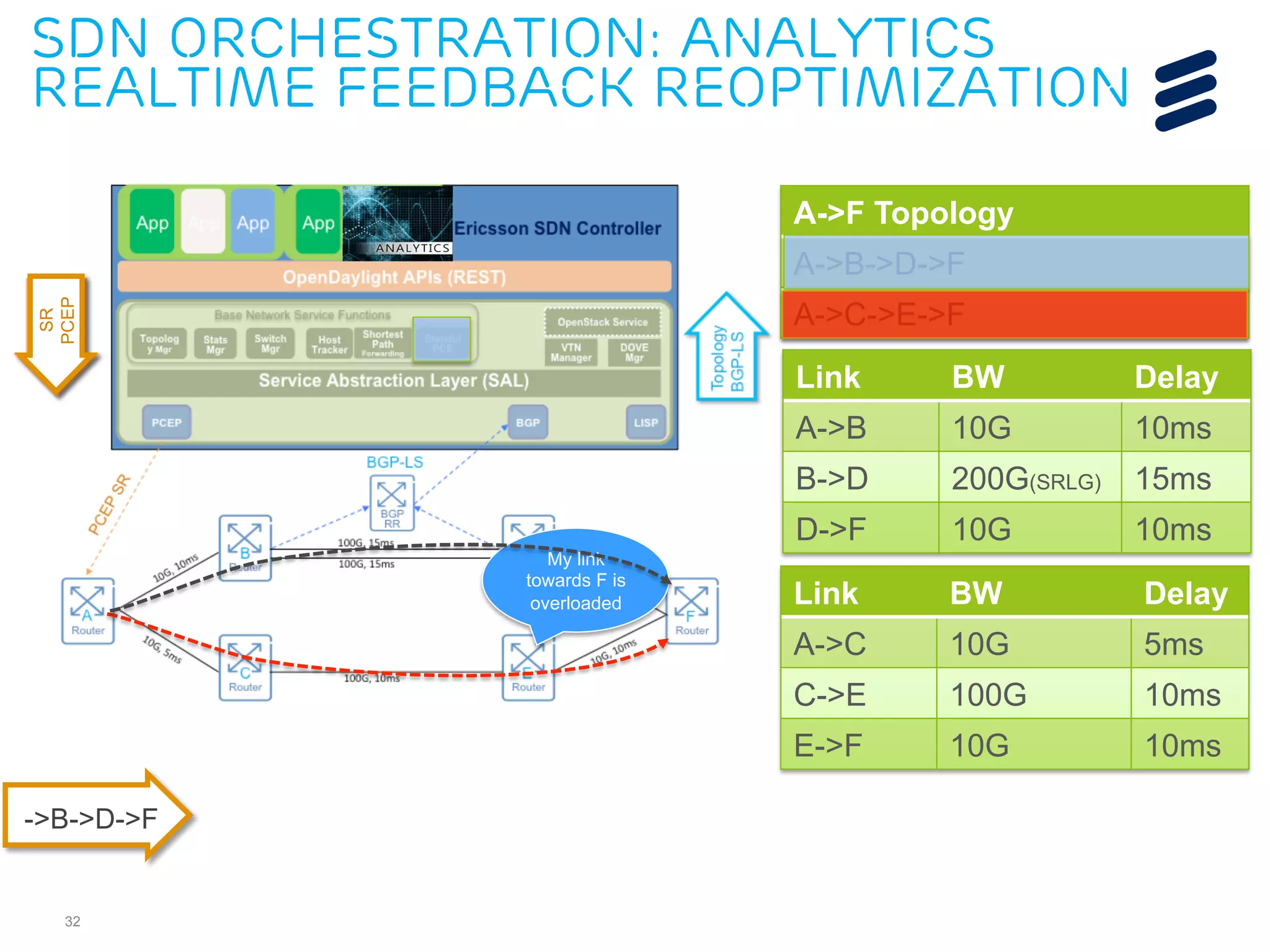
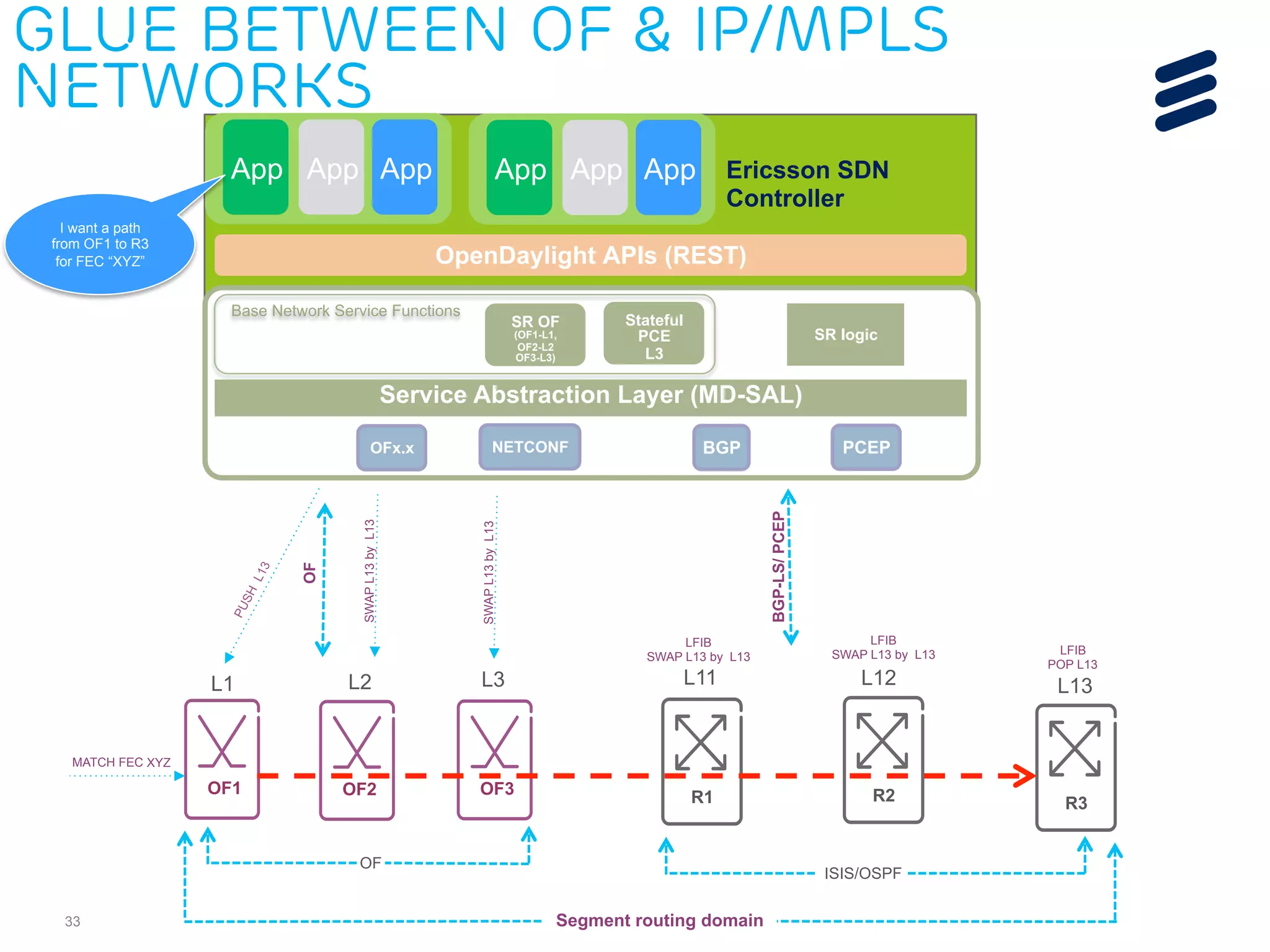
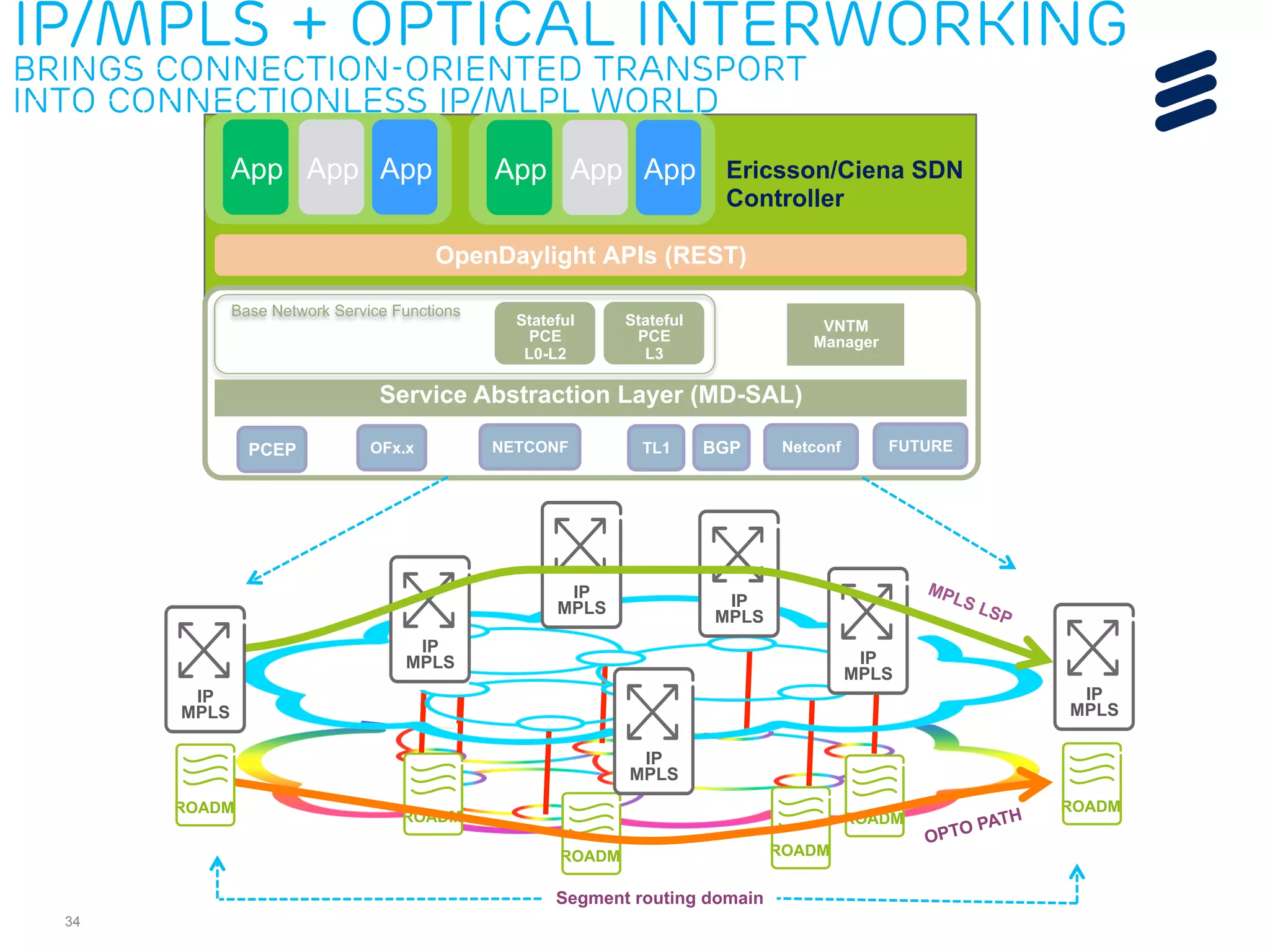
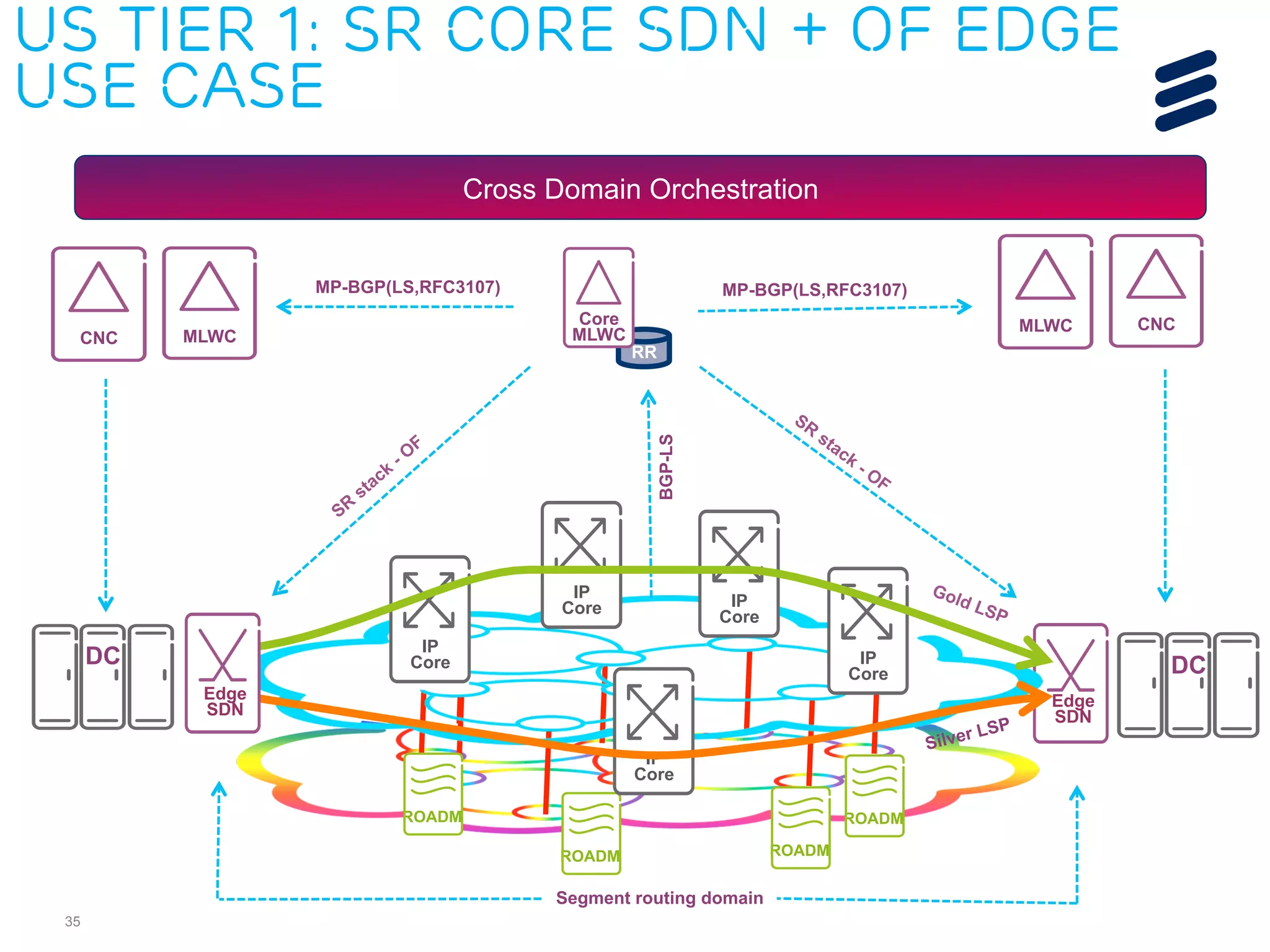
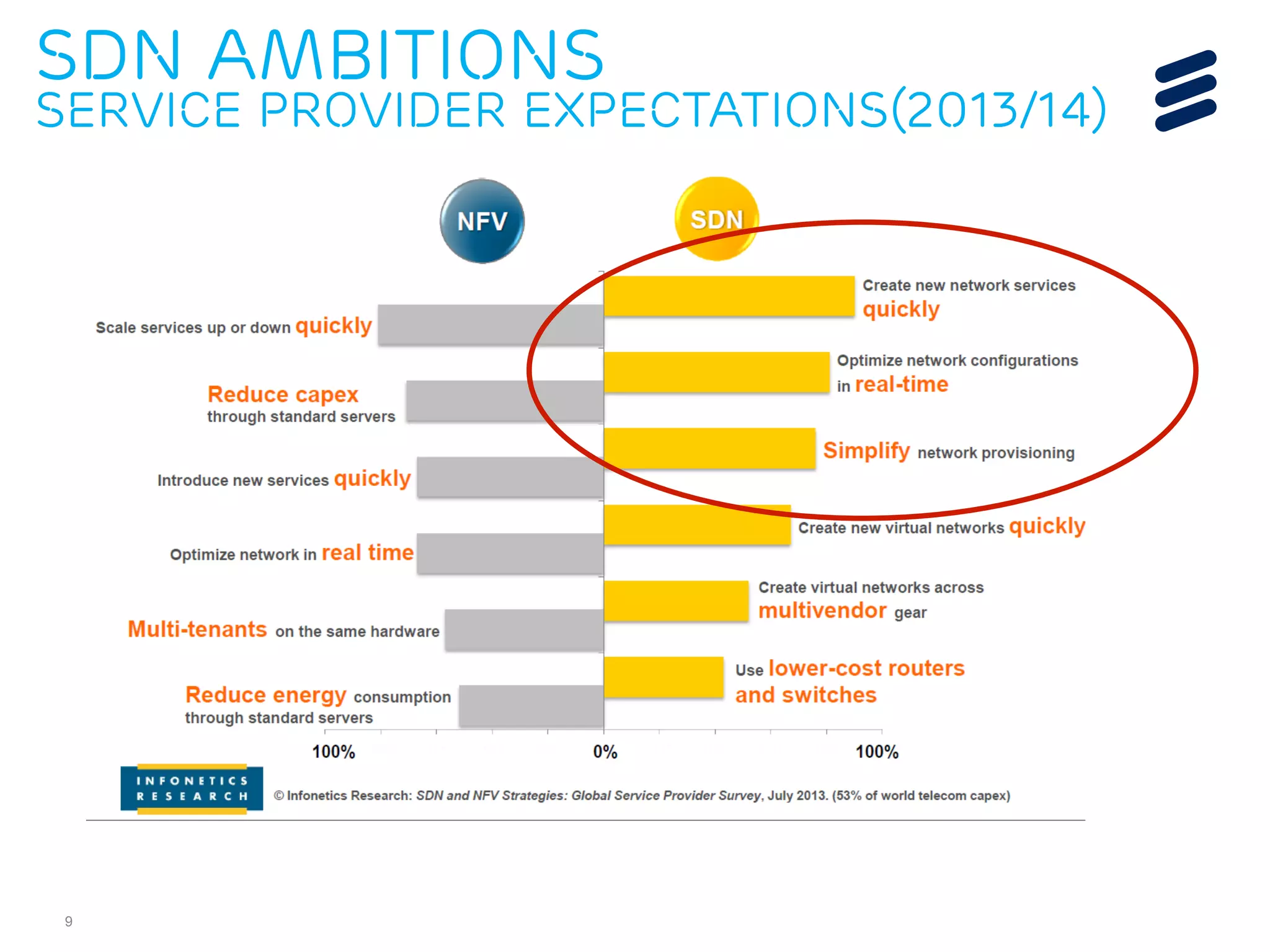
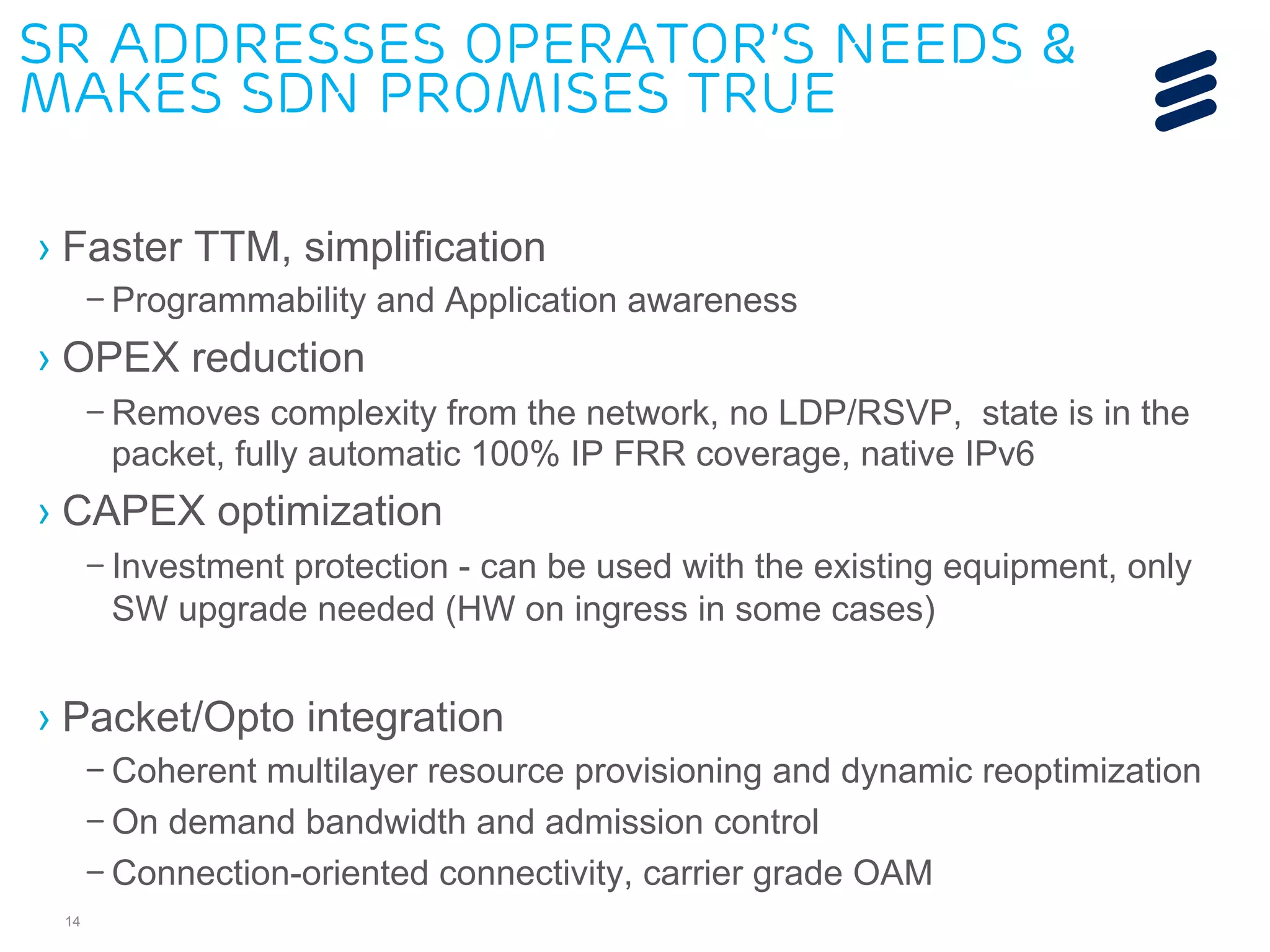
The document discusses the evolution of Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and the integration of Segment Routing (SR) for improved programmable and application-aware multilayer networking. Segment Routing addresses operator needs by simplifying network operations, optimizing costs, and providing flexible end-to-end path definitions through segments. It also highlights ongoing collaboration and draft submissions to IETF for implementing necessary extensions in routing protocols like IS-IS and OSPF.









![Sr Is Real and
happening!
› Excellent endorsement and leadership
from SP and Entreprise operators
› IETF: Multi-vendor consensus and collaboration:
IS-IS for IP Internets S. Previdi, Ed.
Internet-Draft C. Filsfils
Intended status: Standards Track A. Bashandy
Expires: December 20, 2014 Cisco Systems, Inc.
– Stefano Previdi - Cisco
– Jeff Tantsura - Ericsson
– Wim Hendericks - ALU
– Hannes Gredler - Juniper
› We have submitted detailed IETF drafts:
15
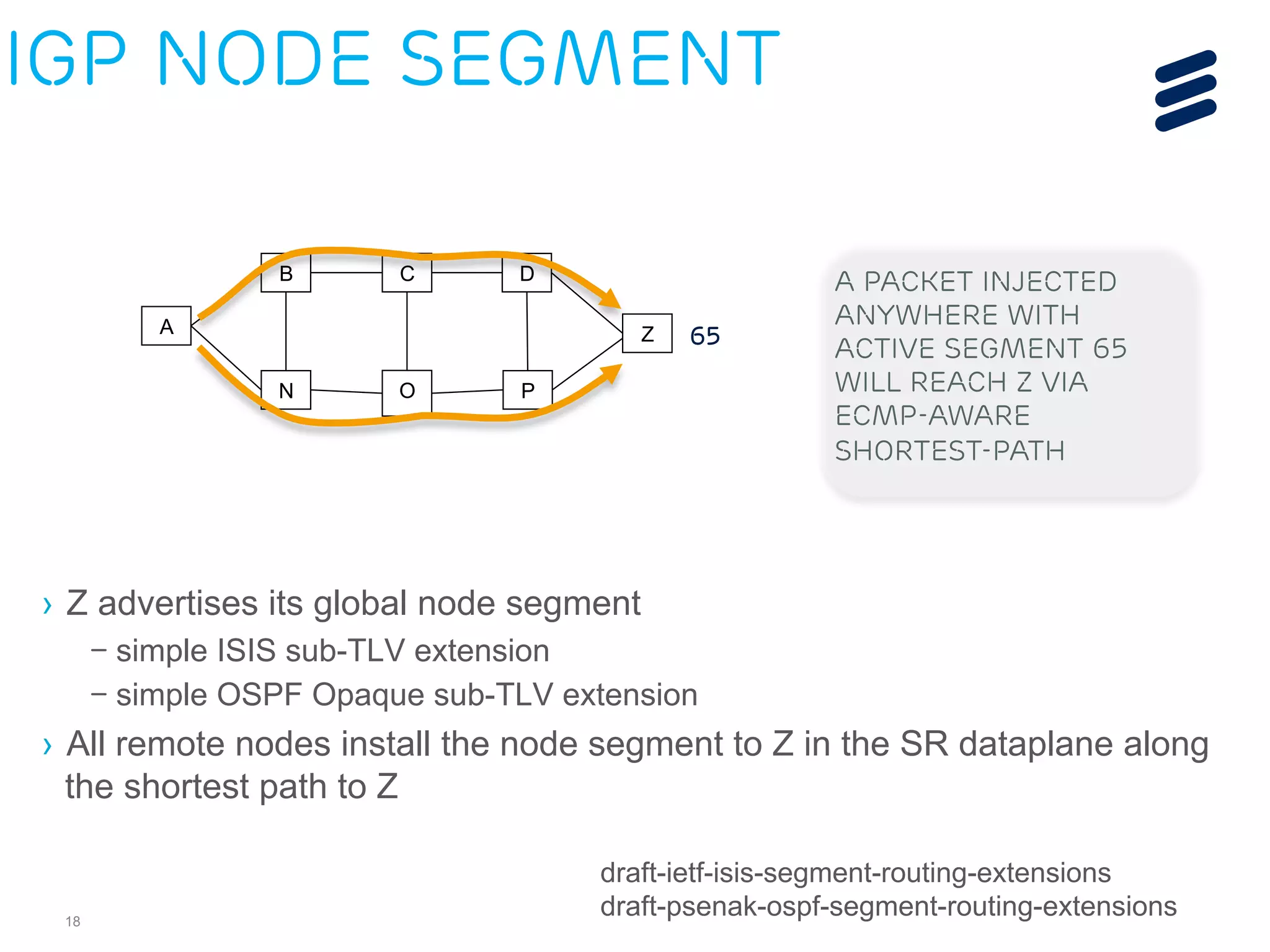
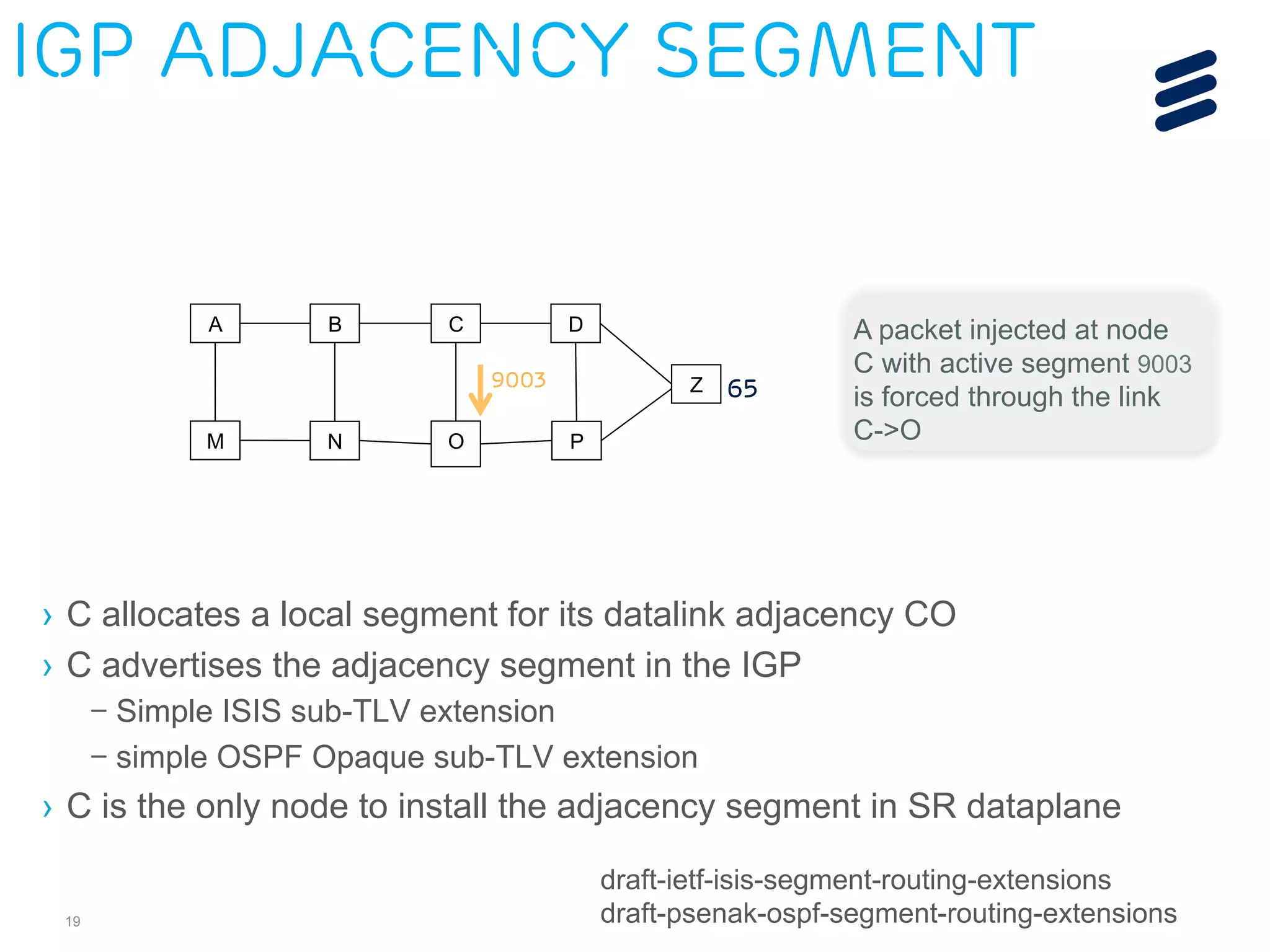
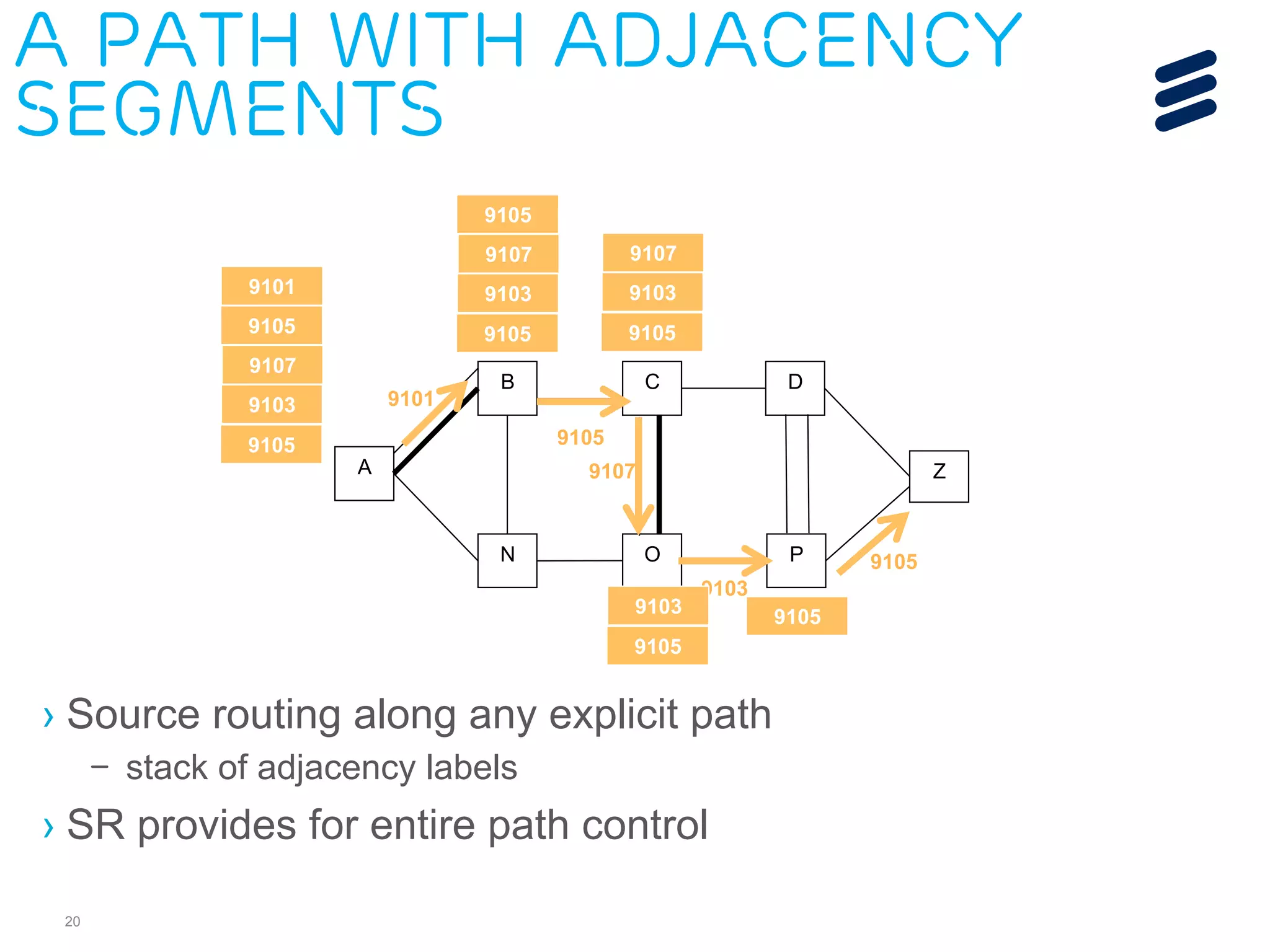
– Architecture
– Use-cases
– ISIS extensions
– OSPF extensions
– BGP extensions
– PCEP extensions
– FRR with 100% coverage
H. Gredler
Juniper Networks, Inc.
S. Litkowski
B. Decraene
Orange
J. Tantsura
Ericsson
June 18, 2014
IS-IS Extensions for Segment Routing
draft-ietf-isis-segment-routing-extensions-02
Abstract
Segment Routing (SR) allows for a flexible definition of end-to-end
paths within IGP topologies by encoding paths as sequences of
topological sub-paths, called "segments". These segments are
advertised by the link-state routing protocols (IS-IS and OSPF).
This draft describes the necessary IS-IS extensions that need to be
introduced for Segment Routing.
Requirements Language
The key words "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT",
"SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in this
document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119 [RFC2119].
Status of This Memo
This Internet-Draft is submitted in full conformance with the
provisions of BCP 78 and BCP 79.
Internet-Drafts are working documents of the Internet Engineering
Task Force (IETF). Note that other groups may also distribute
working documents as Internet-Drafts. The list of current Internet-
Drafts is at http://datatracker.ietf.org/drafts/current/.
Internet-Drafts are draft documents valid for a maximum of six months
and may be updated, replaced, or obsoleted by other documents at any](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jefftantsura-141003025953-phpapp02/75/PLNOG-13-Jeff-Tantsura-Programmable-and-Application-aware-IP-MPLS-networking-15-2048.jpg)