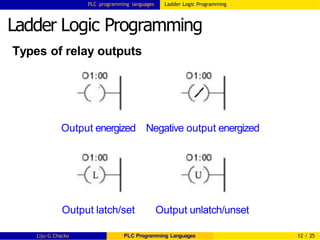
The document provides an overview of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) programming languages, including instruction list, structured text, functional block programming, ladder logic, and sequential function charts, based on the IEC 61131-3 standard. It explains each programming method's key concepts and structures, such as the use of graphical programming in ladder logic and concurrency in sequential function charts. Additionally, it highlights the process PLCs follow in automation and communication methods utilized for programming.






![PLC programming languages Structured Text Programming
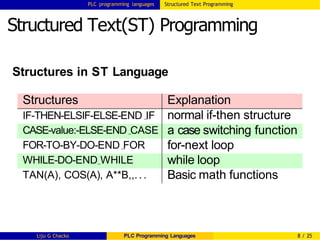
Structured Text Programming
Similar to high level language, such as Basic or C
Example-
Average of 5 numbers
F8:10 := 0;
WHILE (N7:0 < 5) DO
F8:10 := F8:10 + F8:[N7:0];
N7:0 := N7:0 + 1;
END_WHILE;
Liju G Chacko PLC Programming Languages 7 / 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plclanguages-131108224019-phpapp022-240503053703-353cb589/85/plclanguages-131108224019-phpapp02-2-pptx-7-320.jpg)

![PLC programming languages Sequential Function Chart
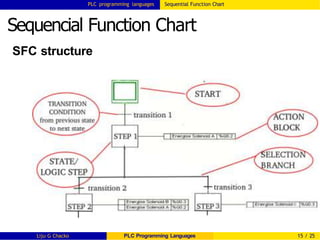
SEQUENTIAL FUNCTION CHART
Sequential Function Charts (SFCs) are a graphical
technique for writing concurrent control programs
SFC is based on GRAFCET (GRAphe Fonctionnel
de Commande Etapses/Transitions) [itself based on
binary petri nets]
Main components of SFC are:
Steps with associated actions
Transitions with associated logic conditions
Directed links between steps and transitions
Liju G Chacko PLC Programming Languages 14 / 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plclanguages-131108224019-phpapp022-240503053703-353cb589/85/plclanguages-131108224019-phpapp02-2-pptx-14-320.jpg)

![PLC programming languages Sequential Function Chart
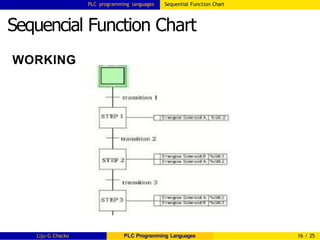
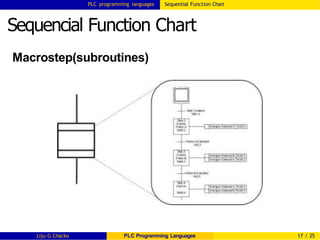
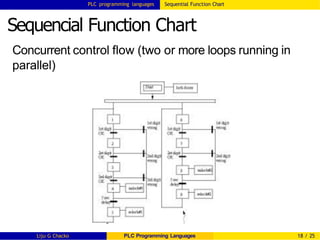
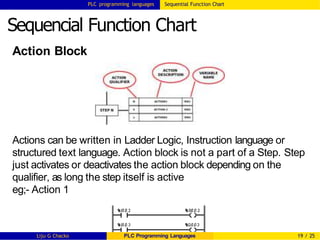
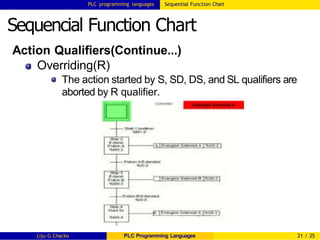
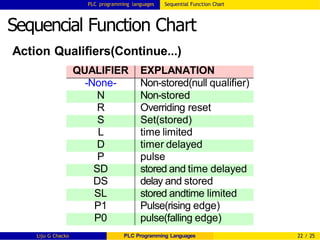
Sequencial Function Chart
Important rules for SFC evolution[IEC 61131-3]
1 Evolution of active states of steps shall take place
along the directed links.(i.e, transition from one step
to another should take place along the connected
lines only )
The clearing time of transitions(transition condition)
should be as short as possible. Clear the transition
condition as soon as the next step is activated.
2
Liju G Chacko PLC Programming Languages 23 / 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plclanguages-131108224019-phpapp022-240503053703-353cb589/85/plclanguages-131108224019-phpapp02-2-pptx-23-320.jpg)

