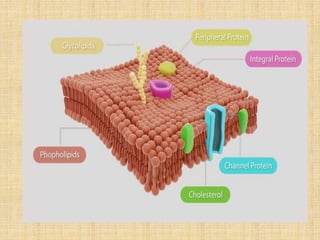
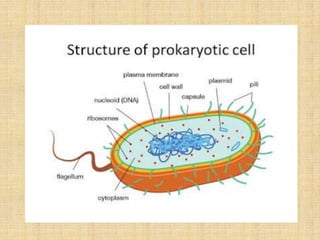
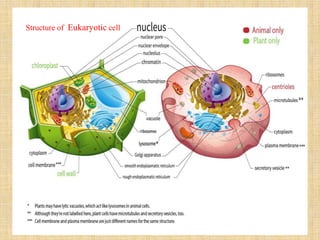
The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. It is composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates arranged in a phospholipid bilayer. In prokaryotic cells, the plasma membrane surrounds the cytoplasm, while in eukaryotic cells it surrounds the cytoplasm and encloses organelles. The plasma membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell and maintains the integrity and shape of the cell.