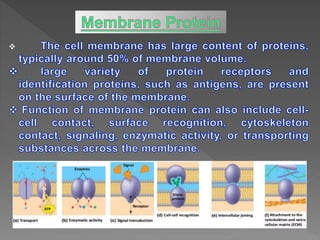
The document discusses the plasma membrane, which encloses the contents of the cell and separates it from the external environment. It describes the plasma membrane as being composed of 54% membrane lipids, 46% membrane proteins, and 5-10% membrane carbohydrates. The document also examines different types of animals based on their diets, including herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and scavengers.