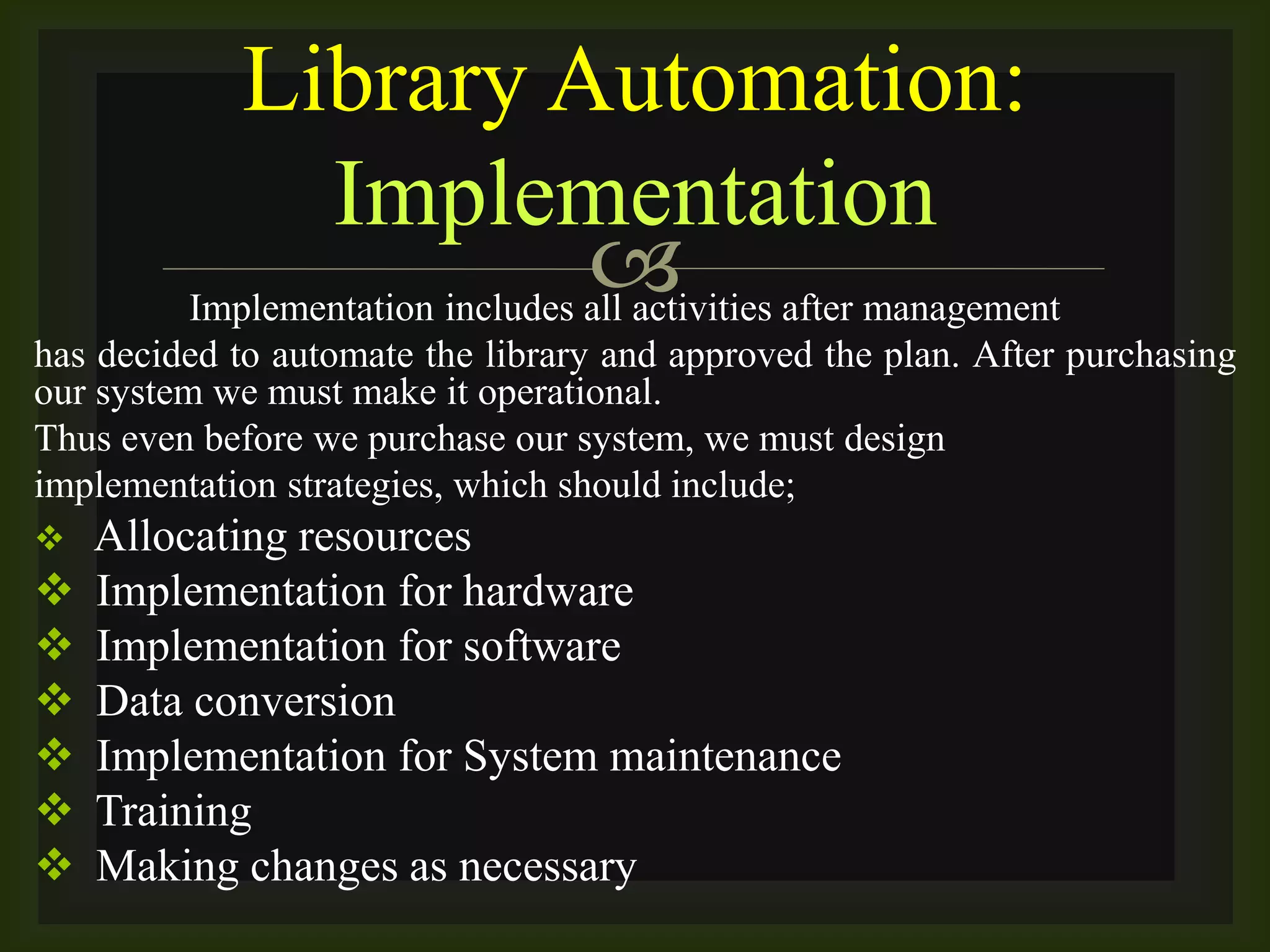
The document discusses library automation planning and implementation. It defines library automation as using computer and networking technologies in libraries. Planning is a systematic process for developing projects. The key steps of planning for library automation include establishing objectives and vision, assessing the present status, identifying gaps, conducting feasibility studies, developing technological plans, project proposals, and approval processes. Successful implementation requires factors like administrative support, staff competence, user requirements, infrastructure, data availability, and management skills.