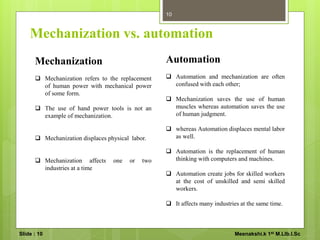
Library automation refers to the use of computers to automate typical library procedures like cataloging and circulation. It involves converting manual systems like card catalogs to digital systems like online public access catalogs (OPAC). Automating libraries provides benefits like reducing errors, improving access and control over collections, and allowing staff to focus on user services rather than clerical tasks. Key areas of library automation include acquisition, cataloging, circulation, serial publications control, and interlibrary loans.