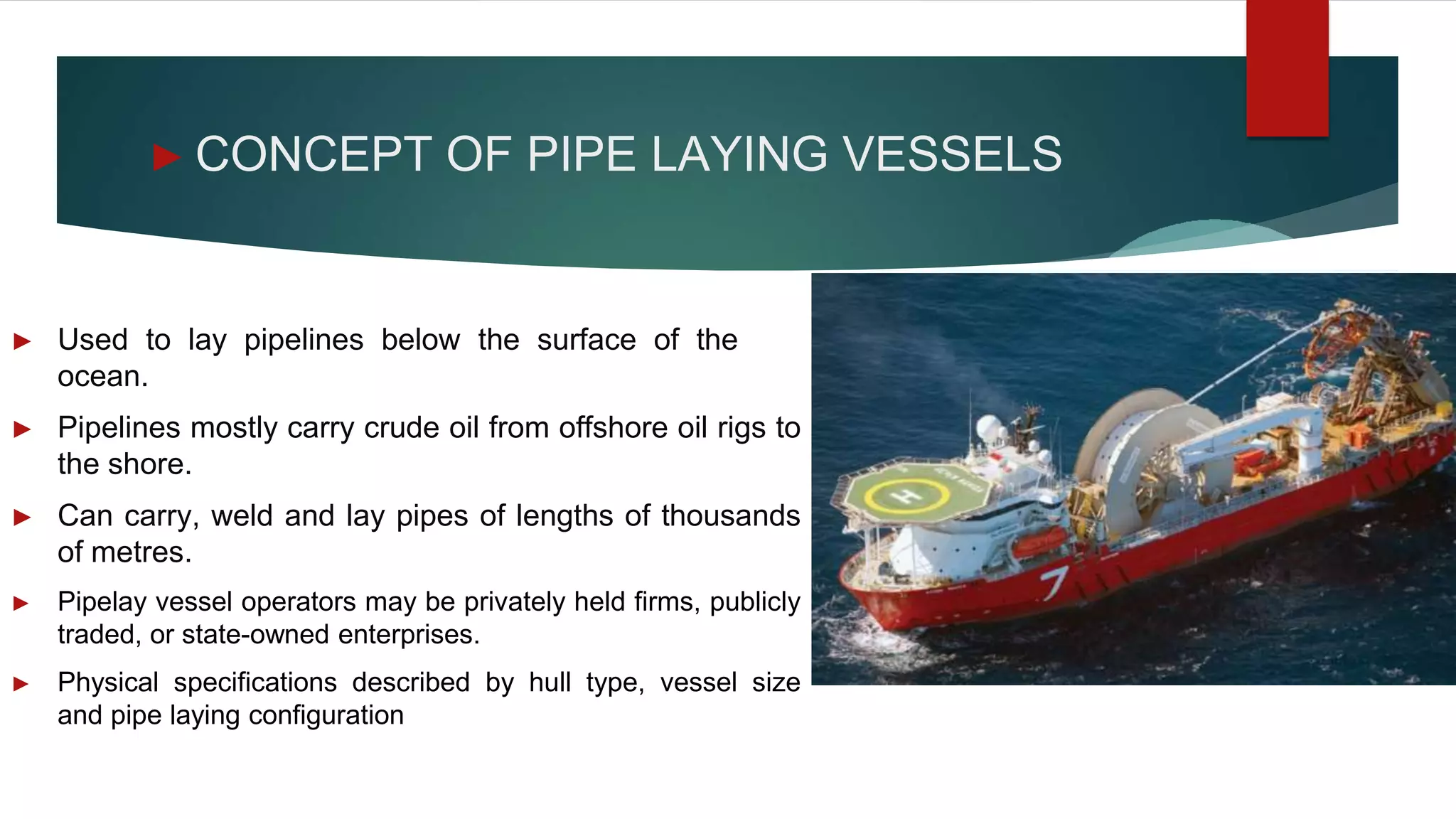
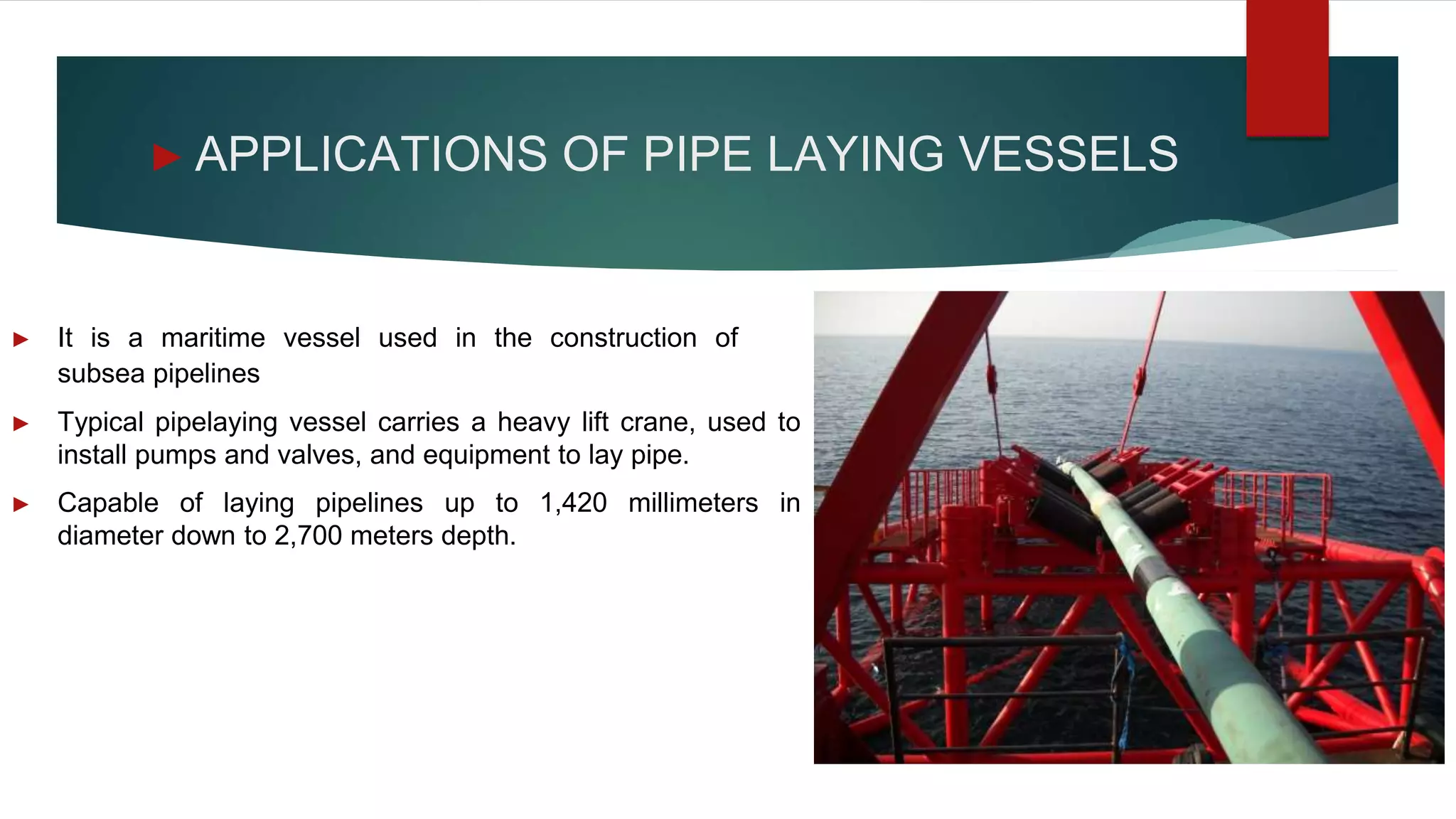
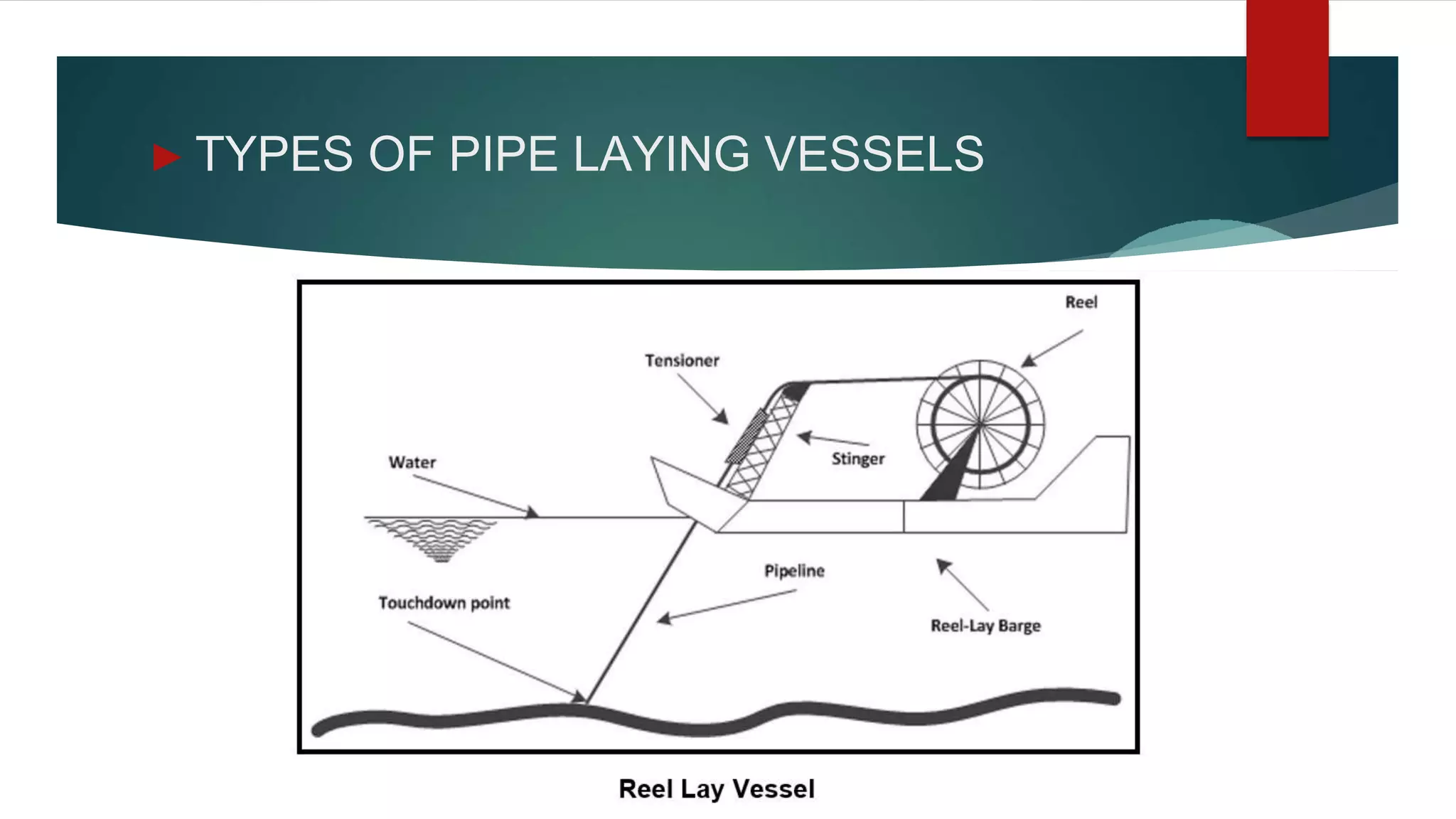
This document provides an introduction to pipe-laying vessels, including their concept and applications. Pipe-laying vessels are used to lay pipelines below the ocean surface to transport oil and gas from offshore rigs to shore. They can carry, weld, and lay pipes thousands of meters long. The document discusses dynamic positioning systems that maintain a vessel's position, pipeline route surveys, pipeline coatings for corrosion protection, and desired vessel characteristics such as storage capacity and speed.